Latest YouTube Video
Saturday, March 12, 2016
Orioles: Buck Showalter says X-rays on C Matt Wieters' right elbow did not raise any concerns; no current plans for MRI (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Re: [FD] Security contact @ Gigabyte
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] Wordpress Configuration Error on XDA-Developers.com led to full Web-Server Access and shut down website
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Orioles: C Matt Wieters left Saturday's game vs. Twins in 1st inning with right elbow soreness; played in 6 spring games (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Orioles: C Matt Wieters left Saturday's game vs. Twins in 1st inning with right elbow soreness; played in 6 spring games (ESPN)
via IFTTT
[FD] Netgear ReadyNAS Surveillance: Unauthenticated Remote Command Execution
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] Kaltura Community Edition Multiple Vulnerabilities
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] Exim < 4.86.2 Local Root Privilege Escalation
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Anonymous Survey -- Please Reply
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/22bnzFe
via IFTTT
Anonymous tip leads to cocaine seizure
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1nEFEf9
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Helen Whiteside
Following: 963 - Followers: 719
March 12, 2016 at 05:38AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/Helenlookk
ISPs Sell Your Data to Advertisers, But FCC has a Plans to Protect Privacy
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1QTaZTO
via IFTTT
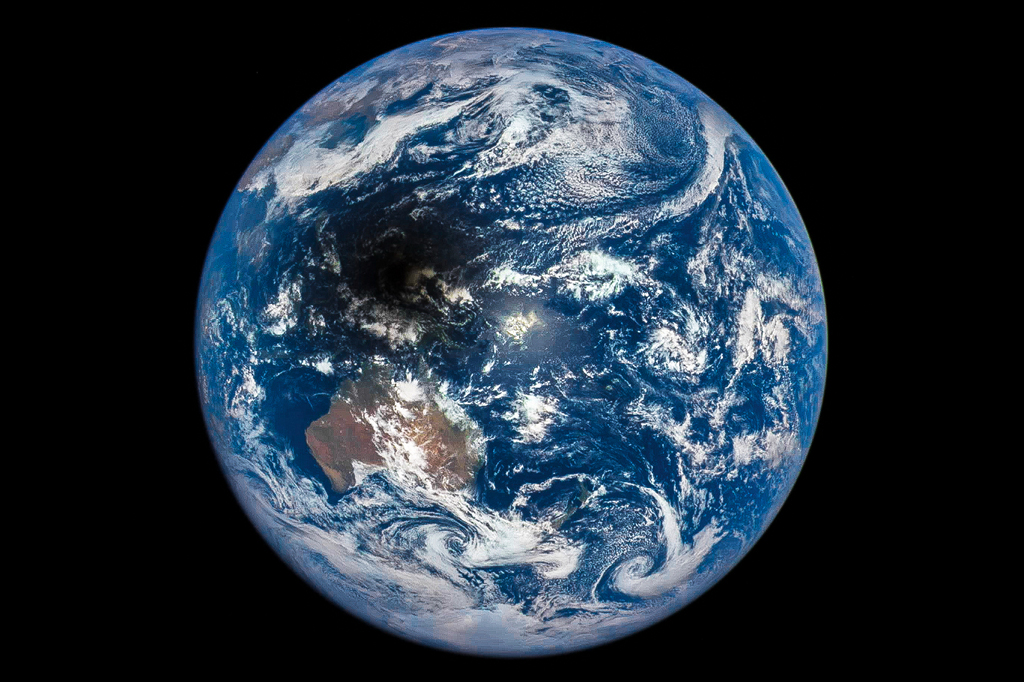
Annual Arctic Sea Ice Minimum 1979-2015 with Area Graph
from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio: Most Recent Items http://ift.tt/1YIG2a6
via IFTTT
Lunar Shadow Transit

How a Typo Stopped Hackers from Stealing $1 Billion from Bank
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1RdyhCZ
via IFTTT
Friday, March 11, 2016
Can I create an anonymous survey and if so how?
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1MdarWW
via IFTTT
Anonymous access
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1nCTWNi
via IFTTT
Ravens: As he leaves for the Raiders via free agency, G Kelechi Osemele says OL \"not really appreciated\" in Baltimore (ESPN)
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 03/10/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/1MbwywP
via IFTTT
eform displays regularly for anonymous users, but the eform embedded an entity block does not ...
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1UkcaQG
via IFTTT
Google Android N Preview — 6 Cool Features That You Should Know
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1UkbwCN
via IFTTT
Dark Sun over Ternate
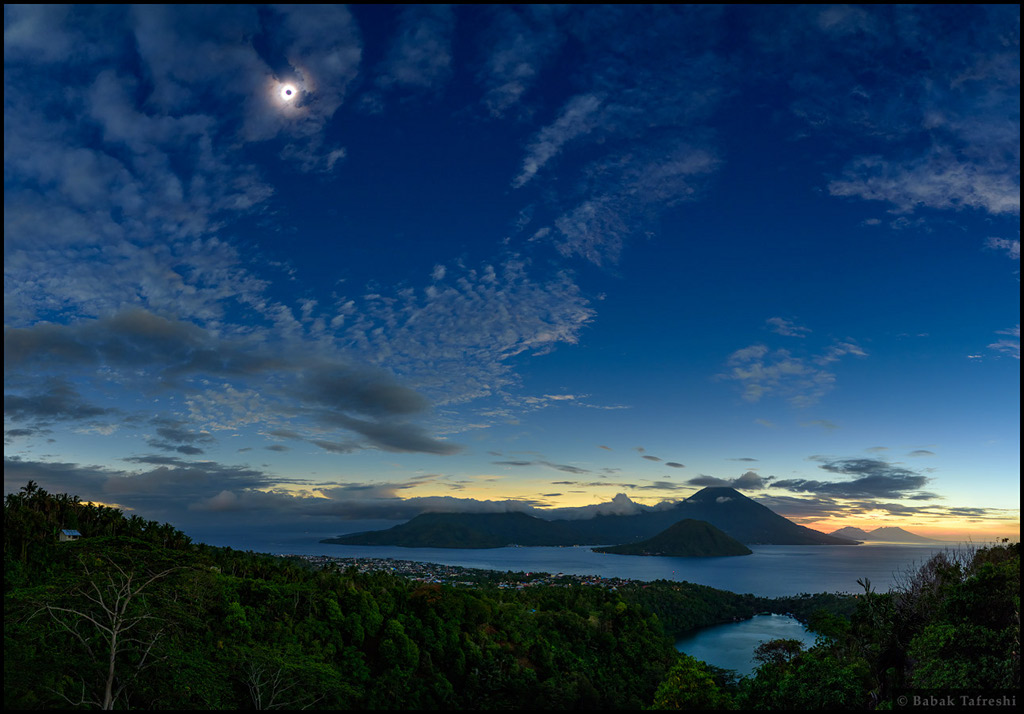

Thursday, March 10, 2016
I have a new follower on Twitter
Don Hornsby
Runner, #SocialMedia Strategist, #Leadership, Amateur Musician, Secret Poet, Craft Beer, .... and Coffee.
Columbus, OH
http://t.co/ynj2DqQ6YG
Following: 14112 - Followers: 18647
March 10, 2016 at 09:39PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/donhornsby
Building a Fine-Grained Entity Typing System Overnight for a New X (X = Language, Domain, Genre). (arXiv:1603.03112v1 [cs.CL])
Recent research has shown great progress on fine-grained entity typing. Most existing methods require pre-defining a set of types and training a multi-class classifier from a large labeled data set based on multi-level linguistic features. They are thus limited to certain domains, genres and languages. In this paper, we propose a novel unsupervised entity typing framework by combining symbolic and distributional semantics. We start from learning general embeddings for each entity mention, compose the embeddings of specific contexts using linguistic structures, link the mention to knowledge bases and learn its related knowledge representations. Then we develop a novel joint hierarchical clustering and linking algorithm to type all mentions using these representations. This framework doesn't rely on any annotated data, predefined typing schema, or hand-crafted features, therefore it can be quickly adapted to a new domain, genre and language. Furthermore, it has great flexibility at incorporating linguistic structures (e.g., Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR), dependency relations) to improve specific context representation. Experiments on genres (news and discussion forum) show comparable performance with state-of-the-art supervised typing systems trained from a large amount of labeled data. Results on various languages (English, Chinese, Japanese, Hausa, and Yoruba) and domains (general and biomedical) demonstrate the portability of our framework.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1LfxqWh
via IFTTT
Inferring Fine-grained Details on User Activities and Home Location from Social Media: Detecting Drinking-While-Tweeting Patterns in Communities. (arXiv:1603.03181v1 [cs.AI])
Nearly all previous work on geo-locating latent states and activities from social media confounds general discussions about activities, self-reports of users participating in those activities at times in the past or future, and self-reports made at the immediate time and place the activity occurs. Activities, such as alcohol consumption, may occur at different places and types of places, and it is important not only to detect the local regions where these activities occur, but also to analyze the degree of participation in them by local residents. In this paper, we develop new machine learning based methods for fine-grained localization of activities and home locations from Twitter data. We apply these methods to discover and compare alcohol consumption patterns in a large urban area, New York City, and a more suburban and rural area, Monroe County. We find positive correlations between the rate of alcohol consumption reported among a community's Twitter users and the density of alcohol outlets, demonstrating that the degree of correlation varies significantly between urban and suburban areas. While our experiments are focused on alcohol use, our methods for locating homes and distinguishing temporally-specific self-reports are applicable to a broad range of behaviors and latent states.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1QIoSX7
via IFTTT
A Markovian-based Approach for Daily Living Activities Recognition. (arXiv:1603.03251v1 [cs.HC])
Recognizing the activities of daily living plays an important role in healthcare. It is necessary to use an adapted model to simulate the human behavior in a domestic space to monitor the patient harmonically and to intervene in the necessary time. In this paper, we tackle this problem using the hierarchical hidden Markov model for representing and recognizing complex indoor activities. We propose a new grammar, called "Home By Room Activities Language", to facilitate the complexity of human scenarios and consider the abnormal activities.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Lfxp4P
via IFTTT
Hierarchical Linearly-Solvable Markov Decision Problems. (arXiv:1603.03267v1 [cs.AI])
We present a hierarchical reinforcement learning framework that formulates each task in the hierarchy as a special type of Markov decision process for which the Bellman equation is linear and has analytical solution. Problems of this type, called linearly-solvable MDPs (LMDPs) have interesting properties that can be exploited in a hierarchical setting, such as efficient learning of the optimal value function or task compositionality. The proposed hierarchical approach can also be seen as a novel alternative to solving LMDPs with large state spaces. We derive a hierarchical version of the so-called Z-learning algorithm that learns different tasks simultaneously and show empirically that it significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art learning methods in two classical hierarchical reinforcement learning domains: the taxi domain and an autonomous guided vehicle task.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1LfxqFR
via IFTTT
Spectral Ranking using Seriation. (arXiv:1406.5370v4 [cs.LG] UPDATED)
We describe a seriation algorithm for ranking a set of items given pairwise comparisons between these items. Intuitively, the algorithm assigns similar rankings to items that compare similarly with all others. It does so by constructing a similarity matrix from pairwise comparisons, using seriation methods to reorder this matrix and construct a ranking. We first show that this spectral seriation algorithm recovers the true ranking when all pairwise comparisons are observed and consistent with a total order. We then show that ranking reconstruction is still exact when some pairwise comparisons are corrupted or missing, and that seriation based spectral ranking is more robust to noise than classical scoring methods. Finally, we bound the ranking error when only a random subset of the comparions are observed. An additional benefit of the seriation formulation is that it allows us to solve semi-supervised ranking problems. Experiments on both synthetic and real datasets demonstrate that seriation based spectral ranking achieves competitive and in some cases superior performance compared to classical ranking methods.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1p7LaGZ
via IFTTT
Recent advances on inconsistency indices for pairwise comparisons - a commentary. (arXiv:1503.08289v3 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
This paper recalls the definition of consistency for pairwise comparison matrices and briefly presents the concept of inconsistency index in connection to other aspects of the theory of pairwise comparisons. By commenting on a recent contribution by Koczkodaj and Szwarc, it will be shown that the discussion on inconsistency indices is far from being over, and the ground is still fertile for debates.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/19sZ9kg
via IFTTT
Novel Feature Extraction, Selection and Fusion for Effective Malware Family Classification. (arXiv:1511.04317v2 [cs.CR] UPDATED)
Modern malware is designed with mutation characteristics, namely polymorphism and metamorphism, which causes an enormous growth in the number of variants of malware samples. Categorization of malware samples on the basis of their behaviors is essential for the computer security community, because they receive huge number of malware everyday, and the signature extraction process is usually based on malicious parts characterizing malware families. Microsoft released a malware classification challenge in 2015 with a huge dataset of near 0.5 terabytes of data, containing more than 20K malware samples. The analysis of this dataset inspired the development of a novel paradigm that is effective in categorizing malware variants into their actual family groups. This paradigm is presented and discussed in the present paper, where emphasis has been given to the phases related to the extraction, and selection of a set of novel features for the effective representation of malware samples. Features can be grouped according to different characteristics of malware behavior, and their fusion is performed according to a per-class weighting paradigm. The proposed method achieved a very high accuracy ($\approx$ 0.998) on the Microsoft Malware Challenge dataset.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1NyCIXw
via IFTTT
Thursday Eve: Debtors Anonymous Provides Hope and Recovery for Debtors
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1WdjDQP
via IFTTT
Anonymous tip claims raw milk caused illnesses at West Virginia Capitol
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1U5Qp8k
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Karl
Professional chef and aspiring trader.
New York
Following: 5261 - Followers: 10179
March 10, 2016 at 06:19PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/Karl554Ash
An anonymous source claims that Kanye West supports Trump, probably because they both like ...
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1pAb3RK
via IFTTT
Je vous congnois
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/24T7lCT
via IFTTT
Anonymous - Hampton Inn & Suites Tampa - North
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/222HucJ
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Top Ten Blogger
This is the official twitter feed for my blog The Top 10 of Anything and Everything my mission in life is to make people smile. Nothing more, nothing less.
Wales, UK
http://t.co/4SmWtJ1rZi
Following: 31771 - Followers: 40756
March 10, 2016 at 08:35AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/Worlds_Top_10
ISS Daily Summary Report – 03/9/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/1U4VoWN
via IFTTT
Gov't handed 28000 signatures after anonymous blog inspires mothers
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/222lheU
via IFTTT
[FD] [SE-2012-01] Broken security fix in Oracle Java SE 7/8/9
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Edge On Galaxy NGC 5866
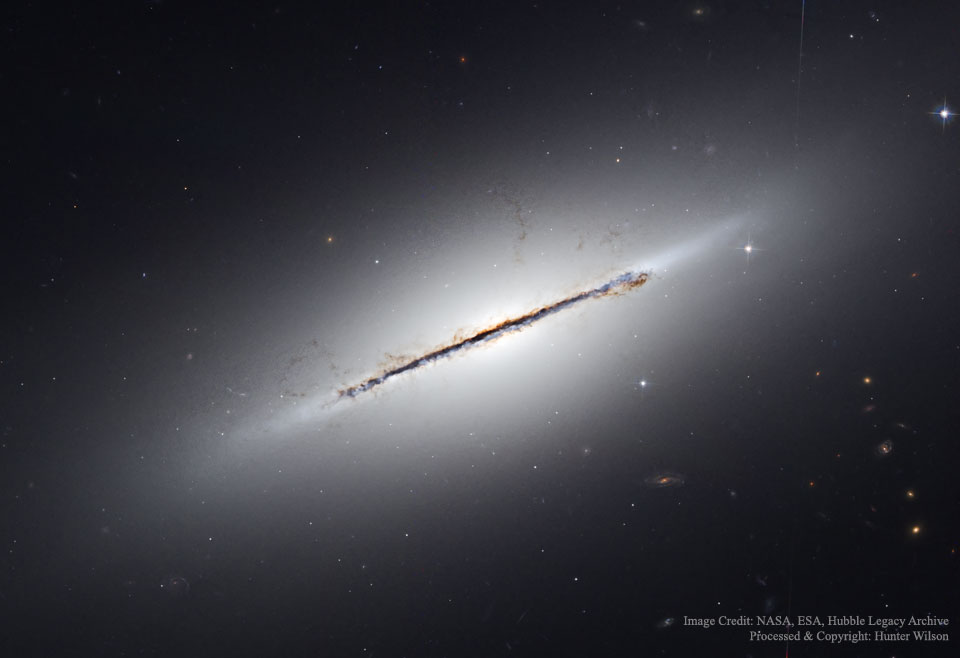

Wednesday, March 9, 2016
Re: [FD] Windows Mail Find People DLL side loading vulnerability
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] Open Vulnerablity ID tracker instead of CVE. Maybe
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] Security contact @ Gigabyte
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Learning to Blend Computer Game Levels. (arXiv:1603.02738v1 [cs.AI])
We present an approach to generate novel computer game levels that blend different game concepts in an unsupervised fashion. Our primary contribution is an analogical reasoning process to construct blends between level design models learned from gameplay videos. The models represent probabilistic relationships between elements in the game. An analogical reasoning process maps features between two models to produce blended models that can then generate new level chunks. As a proof-of-concept we train our system on the classic platformer game Super Mario Bros. due to its highly-regarded and well understood level design. We evaluate the extent to which the models represent stylistic level design knowledge and demonstrate the ability of our system to explain levels that were blended by human expert designers.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1RS3yi1
via IFTTT
Pairwise Choice Markov Chains. (arXiv:1603.02740v1 [stat.ML])
As datasets capturing human choices grow in richness and scale, particularly in online domains, there is an increasing need for choice models that explain and predict complex empirical choices that violate traditional choice-theoretic assumptions such as regularity, stochastic transitivity, or Luce's choice axiom. In this work we introduce a Pairwise Choice Markov Chain (PCMC) model of discrete choice that is free of all those assumptions while still satisfying the attractive foundational axiom of uniform expansion. Uniform expansion is known to imply Luce's choice axiom in the context of independent random utility models (RUMs), but the PCMC model is not a RUM (let alone an independent RUM). Inference for the PCMC model is straight-forward, and we thus introduce it as the first inferentially tractable model of discrete choice known to satisfy uniform expansion without the choice axiom, regularity, or strict stochastic transitivity. It is thus more flexible than even Tversky's Elimination By Aspects model, which assumes regularity and is also known to be inferentially intractable. We show that our model learns and predicts synthetic non-transitive data well. Our analysis also synthesizes several recent observations connecting the Multinomial Logit (MNL) model and Markov chains; the PCMC model retains the Multinomial Logit model as a special case.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1UTUprX
via IFTTT
Implicit Discourse Relation Classification via Multi-Task Neural Networks. (arXiv:1603.02776v1 [cs.CL])
Without discourse connectives, classifying implicit discourse relations is a challenging task and a bottleneck for building a practical discourse parser. Previous research usually makes use of one kind of discourse framework such as PDTB or RST to improve the classification performance on discourse relations. Actually, under different discourse annotation frameworks, there exist multiple corpora which have internal connections. To exploit the combination of different discourse corpora, we design related discourse classification tasks specific to a corpus, and propose a novel Convolutional Neural Network embedded multi-task learning system to synthesize these tasks by learning both unique and shared representations for each task. The experimental results on the PDTB implicit discourse relation classification task demonstrate that our model achieves significant gains over baseline systems.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1UgeIPI
via IFTTT
Robot Dream. (arXiv:1603.03007v1 [cs.RO])
In this position paper we present a novel approach to neurobiologically plausible implementation of emotional reactions and behaviors for real-time autonomous robotic systems. The working metaphor we use is the "day" and "night" phases of mammalian life. During the "day" phase a robotic system stores the inbound information and is controlled by a light-weight rule-based system in real time. In contrast to that, during the "night" phase the stored information is been transferred to the supercomputing system to update the realistic neural network: emotional and behavioral strategies.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1RS3wXr
via IFTTT
Summarization of Films and Documentaries Based on Subtitles and Scripts. (arXiv:1506.01273v3 [cs.CL] UPDATED)
We assess the performance of generic text summarization algorithms applied to films and documentaries, using the well-known behavior of summarization of news articles as reference. We use three datasets: (i) news articles, (ii) film scripts and subtitles, and (iii) documentary subtitles. Standard ROUGE metrics are used for comparing generated summaries against news abstracts, plot summaries, and synopses. We show that the best performing algorithms are LSA, for news articles and documentaries, and LexRank and Support Sets, for films. Despite the different nature of films and documentaries, their relative behavior is in accordance with that obtained for news articles.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1BL5nnn
via IFTTT
Nonparametric Bayesian Double Articulation Analyzer for Direct Language Acquisition from Continuous Speech Signals. (arXiv:1506.06646v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
Human infants can discover words directly from unsegmented speech signals without any explicitly labeled data. In this paper, we develop a novel machine learning method called nonparametric Bayesian double articulation analyzer (NPB-DAA) that can directly acquire language and acoustic models from observed continuous speech signals. For this purpose, we propose an integrative generative model that combines a language model and an acoustic model into a single generative model called the "hierarchical Dirichlet process hidden language model" (HDP-HLM). The HDP-HLM is obtained by extending the hierarchical Dirichlet process hidden semi-Markov model (HDP-HSMM) proposed by Johnson et al. An inference procedure for the HDP-HLM is derived using the blocked Gibbs sampler originally proposed for the HDP-HSMM. This procedure enables the simultaneous and direct inference of language and acoustic models from continuous speech signals. Based on the HDP-HLM and its inference procedure, we developed a novel double articulation analyzer. By assuming HDP-HLM as a generative model of observed time series data, and by inferring latent variables of the model, the method can analyze latent double articulation structure, i.e., hierarchically organized latent words and phonemes, of the data in an unsupervised manner. The novel unsupervised double articulation analyzer is called NPB-DAA.
The NPB-DAA can automatically estimate double articulation structure embedded in speech signals. We also carried out two evaluation experiments using synthetic data and actual human continuous speech signals representing Japanese vowel sequences. In the word acquisition and phoneme categorization tasks, the NPB-DAA outperformed a conventional double articulation analyzer (DAA) and baseline automatic speech recognition system whose acoustic model was trained in a supervised manner.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1N2s0JW
via IFTTT
Deep Tracking: Seeing Beyond Seeing Using Recurrent Neural Networks. (arXiv:1602.00991v2 [cs.LG] UPDATED)
This paper presents to the best of our knowledge the first end-to-end object tracking approach which directly maps from raw sensor input to object tracks in sensor space without requiring any feature engineering or system identification in the form of plant or sensor models. Specifically, our system accepts a stream of raw sensor data at one end and, in real-time, produces an estimate of the entire environment state at the output including even occluded objects. We achieve this by framing the problem as a deep learning task and exploit sequence models in the form of recurrent neural networks to learn a mapping from sensor measurements to object tracks. In particular, we propose a learning method based on a form of input dropout which allows learning in an unsupervised manner, only based on raw, occluded sensor data without access to ground-truth annotations. We demonstrate our approach using a synthetic dataset designed to mimic the task of tracking objects in 2D laser data -- as commonly encountered in robotics applications -- and show that it learns to track many dynamic objects despite occlusions and the presence of sensor noise.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1RZdrNo
via IFTTT
Banner does not respond to anonymous users
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1nxs9xW
via IFTTT
Re: [FD] Netgear GS105Ev2 - Multiple Vulnerabilities
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] New Security Tool: MrLooquer - IPv6 Intelligence
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] Advisory X41-2016-001: Memory Corruption Vulnerability in "libotr"
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Loyset denisot (Anonymous)
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1UTjRhi
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 03/8/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/1YxKMPL
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
D Torres
Following: 95 - Followers: 172
March 09, 2016 at 02:57PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/ChristmanSilas
I have a new follower on Twitter
Champsfa
Be a Champion! We are a collective of highly motivated Academy coaches. Coming soon. Watch this space. #TALENTISAMYTH
Following: 9363 - Followers: 27137
March 09, 2016 at 02:36PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/champsfa
Anonymous users receive the wrong course blocker error.
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1nwKElZ
via IFTTT
Rumor Central: Ravens are \"looking seriously\" at ex-Vikings WR Mike Wallace - report; team also in market for another TE (ESPN)
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Bob Carver
Twitter Top 10 #CyberSecurity, opinions are my own #privacy #disruptive #startups #bitcoin #bigdata #Cloud #mobile #IoT #NewNormal #speaker RT != agree
the world
https://t.co/hjqtTBqFyV
Following: 8061 - Followers: 9481
March 09, 2016 at 08:44AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/cybersecboardrm
SimpleCrop preview not working for anonymous users
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1LQPHJK
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Applied Innovations
The Windows Cloud Hosting Experts - Always Available, Always Easy
United States
http://t.co/wtyGmEIIQm
Following: 3847 - Followers: 4605
March 09, 2016 at 03:56AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/appliedi
[FD] LSE Leading Security Experts GmbH - LSE-2016-01-01 - Wordpress ProjectTheme - Multiple Vulnerabilities
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Solar Eclipse Shoes in the Classroom

More than 1 Million Websites Install Free SSL Certificate (and Counting...)
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1QCpq0x
via IFTTT
JPSS Multi Mission Concept of Operations
from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio: Most Popular
via IFTTT
Tuesday, March 8, 2016
I have a new follower on Twitter
Sheila Dixon
Proud mother of 2 living in West Baltimore running for Mayor. Let's reclaim, revive and rebuild. Authority: Friends for Sheila Dixon, Geneva Smith, Treasurer
Baltimore, MD
https://t.co/phs4NygQzG
Following: 3618 - Followers: 4474
March 08, 2016 at 09:09PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/SheilaforMayor
UTA-poly and UTA-splines: additive value functions with polynomial marginals. (arXiv:1603.02626v1 [math.OC])
Additive utility function models are widely used in multiple criteria decision analysis. In such models, a numerical value is associated to each alternative involved in the decision problem. It is computed by aggregating the scores of the alternative on the different criteria of the decision problem. The score of an alternative is determined by a marginal value function that evolves monotonically as a function of the performance of the alternative on this criterion. Determining the shape of the marginals is not easy for a decision maker. It is easier for him/her to make statements such as "alternative $a$ is preferred to $b$". In order to help the decision maker, UTA disaggregation procedures use linear programming to approximate the marginals by piecewise linear functions based only on such statements. In this paper, we propose to infer polynomials and splines instead of piecewise linear functions for the marginals. In this aim, we use semidefinite programming instead of linear programming. We illustrate this new elicitation method and present some experimental results.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1URcTtb
via IFTTT
Formal Ontology Learning on Factual IS-A Corpus in English using Description Logics. (arXiv:1312.6947v2 [cs.CL] UPDATED)
Ontology Learning (OL) is the computational task of generating a knowledge base in the form of an ontology given an unstructured corpus whose content is in natural language (NL). Several works can be found in this area most of which are limited to statistical and lexico-syntactic pattern matching based techniques Light-Weight OL. These techniques do not lead to very accurate learning mostly because of several linguistic nuances in NL. Formal OL is an alternative (less explored) methodology were deep linguistics analysis is made using theory and tools found in computational linguistics to generate formal axioms and definitions instead simply inducing a taxonomy. In this paper we propose "Description Logic (DL)" based formal OL framework for learning factual IS-A type sentences in English. We claim that semantic construction of IS-A sentences is non trivial. Hence, we also claim that such sentences requires special studies in the context of OL before any truly formal OL can be proposed. We introduce a learner tool, called DLOL_IS-A, that generated such ontologies in the owl format. We have adopted "Gold Standard" based OL evaluation on IS-A rich WCL v.1.1 dataset and our own Community representative IS-A dataset. We observed significant improvement of DLOL_IS-A when compared to the light-weight OL tool Text2Onto and formal OL tool FRED.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/Jo9nFN
via IFTTT
Multigrid with rough coefficients and Multiresolution operator decomposition from Hierarchical Information Games. (arXiv:1503.03467v4 [math.NA] UPDATED)
We introduce a near-linear complexity (geometric and meshless/algebraic) multigrid/multiresolution method for PDEs with rough ($L^\infty$) coefficients with rigorous a-priori accuracy and performance estimates. The method is discovered through a decision/game theory formulation of the problems of (1) identifying restriction and interpolation operators (2) recovering a signal from incomplete measurements based on norm constraints on its image under a linear operator (3) gambling on the value of the solution of the PDE based on a hierarchy of nested measurements of its solution or source term. The resulting elementary gambles form a hierarchy of (deterministic) basis functions of $H^1_0(\Omega)$ (gamblets) that (1) are orthogonal across subscales/subbands with respect to the scalar product induced by the energy norm of the PDE (2) enable sparse compression of the solution space in $H^1_0(\Omega)$ (3) induce an orthogonal multiresolution operator decomposition. The operating diagram of the multigrid method is that of an inverted pyramid in which gamblets are computed locally (by virtue of their exponential decay), hierarchically (from fine to coarse scales) and the PDE is decomposed into a hierarchy of independent linear systems with uniformly bounded condition numbers. The resulting algorithm is parallelizable both in space (via localization) and in bandwith/subscale (subscales can be computed independently from each other). Although the method is deterministic it has a natural Bayesian interpretation under the measure of probability emerging (as a mixed strategy) from the information game formulation and multiresolution approximations form a martingale with respect to the filtration induced by the hierarchy of nested measurements.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1MuzVAz
via IFTTT
Negatively Correlated Search. (arXiv:1504.04914v2 [cs.NE] UPDATED)
Evolutionary Algorithms (EAs) have been shown to be powerful tools for complex optimization problems, which are ubiquitous in both communication and big data analytics. This paper presents a new EA, namely Negatively Correlated Search (NCS), which maintains multiple individual search processes in parallel and models the search behaviors of individual search processes as probability distributions. NCS explicitly promotes negatively correlated search behaviors by encouraging differences among the probability distributions (search behaviors). By this means, individual search processes share information and cooperate with each other to search diverse regions of a search space, which makes NCS a promising method for non-convex optimization. The cooperation scheme of NCS could also be regarded as a novel diversity preservation scheme that, different from other existing schemes, directly promotes diversity at the level of search behaviors rather than merely trying to maintain diversity among candidate solutions. Empirical studies showed that NCS is competitive to well-established search methods in the sense that NCS achieved the best overall performance on 20 multimodal (non-convex) continuous optimization problems. The advantages of NCS over state-of-the-art approaches are also demonstrated with a case study on the synthesis of unequally spaced linear antenna arrays.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1yMutq5
via IFTTT
BIRDNEST: Bayesian Inference for Ratings-Fraud Detection. (arXiv:1511.06030v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
Review fraud is a pervasive problem in online commerce, in which fraudulent sellers write or purchase fake reviews to manipulate perception of their products and services. Fake reviews are often detected based on several signs, including 1) they occur in short bursts of time; 2) fraudulent user accounts have skewed rating distributions. However, these may both be true in any given dataset. Hence, in this paper, we propose an approach for detecting fraudulent reviews which combines these 2 approaches in a principled manner, allowing successful detection even when one of these signs is not present. To combine these 2 approaches, we formulate our Bayesian Inference for Rating Data (BIRD) model, a flexible Bayesian model of user rating behavior. Based on our model we formulate a likelihood-based suspiciousness metric, Normalized Expected Surprise Total (NEST). We propose a linear-time algorithm for performing Bayesian inference using our model and computing the metric. Experiments on real data show that BIRDNEST successfully spots review fraud in large, real-world graphs: the 50 most suspicious users of the Flipkart platform flagged by our algorithm were investigated and all identified as fraudulent by domain experts at Flipkart.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1X1JcZz
via IFTTT
LSTM Neural Reordering Feature for Statistical Machine Translation. (arXiv:1512.00177v2 [cs.CL] UPDATED)
Artificial neural networks are powerful models, which have been widely applied into many aspects of machine translation, such as language modeling and translation modeling. Though notable improvements have been made in these areas, the reordering problem still remains a challenge in statistical machine translations. In this paper, we present a novel neural reordering model that directly models word pairs and alignment. By utilizing LSTM recurrent neural networks, much longer context could be learned for reordering prediction. Experimental results on NIST OpenMT12 Arabic-English and Chinese-English 1000-best rescoring task show that our LSTM neural reordering feature is robust and achieves significant improvements over various baseline systems.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Tt5y0j
via IFTTT
Censoring Representations with an Adversary. (arXiv:1511.05897v3 [cs.LG] CROSS LISTED)
In practice, there are often explicit constraints on what representations or decisions are acceptable in an application of machine learning. For example it may be a legal requirement that a decision must not favour a particular group. Alternatively it can be that that representation of data must not have identifying information. We address these two related issues by learning flexible representations that minimize the capability of an adversarial critic. This adversary is trying to predict the relevant sensitive variable from the representation, and so minimizing the performance of the adversary ensures there is little or no information in the representation about the sensitive variable. We demonstrate this adversarial approach on two problems: making decisions free from discrimination and removing private information from images. We formulate the adversarial model as a minimax problem, and optimize that minimax objective using a stochastic gradient alternate min-max optimizer. We demonstrate the ability to provide discriminant free representations for standard test problems, and compare with previous state of the art methods for fairness, showing statistically significant improvement across most cases. The flexibility of this method is shown via a novel problem: removing annotations from images, from unaligned training examples of annotated and unannotated images, and with no a priori knowledge of the form of annotation provided to the model.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1QOg8Q3
via IFTTT
[FD] Windows Mail Find People DLL side loading vulnerability
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Orioles: Addition of Pedro Alvarez \"further complicates\" outfield situation in Baltimore, writes Eddie Matz (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Ravens: Former Saints TE Benjamin Watson agrees to deal - Jamison Hensley, multiple reports; 74 catches, 6 TD in 2015 (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Food Addicts in Recovery Anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1QJA5Ve
via IFTTT
Ravens: Ohio State DE Joey Bosa goes No. 6 in Mel Kiper's Mock Draft 3.0; \"hard to pass on a talent as complete\" (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Mail anonymous user always in site default language
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/21jDD5A
via IFTTT
Ravens: OL Kelechi Osemele to leave Baltimore, sign with Raiders - NFL Network; switched to LT for 2015's final 4 games (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Maloney and Vance call on Congress to stop anonymous terrorist and criminal shell corporation ...
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1X9EfcH
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 03/7/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/1p4INpH
via IFTTT
'Guccifer,' who Hacked former President, to be extradited to the US
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1LOlZ7W
via IFTTT
Hacker arrested for ATM Skimming escaped from Prison
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1UakAdx
via IFTTT
Hackers and Cyber Experts to Come Together at NullCon 2016
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1X9kG4e
via IFTTT
Hacker Reveals How to Hack Any Facebook Account
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1ToAhiq
via IFTTT
Your iPhone will Alert You if You are Being Monitored At Work
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1pcywZb
via IFTTT
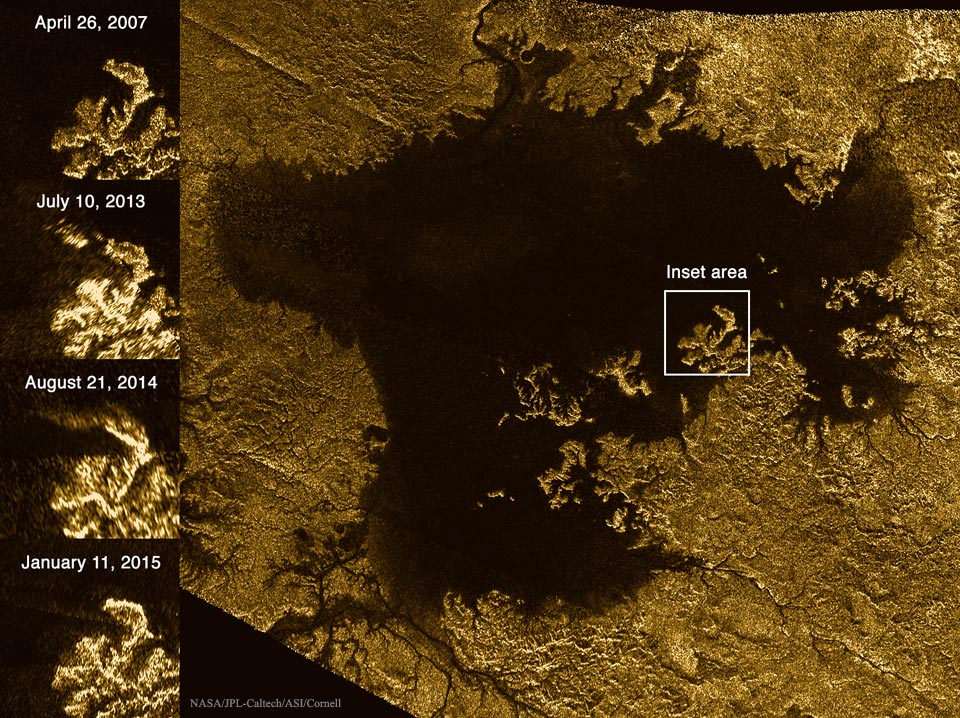
Mystery Feature Now Disappears in Titan Lake
Orioles: Pedro Alvarez agrees to 1-year, $5.75 million deal - Jim Bowden, media reports; had 27 HR, 77 RBI last season (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Monday, March 7, 2016
I have a new follower on Twitter
Songtive
Songtive is a songwriting tool, band and social network which allows you experiment with arrangements and chord progressions with the help from other users.
http://t.co/IeNSSj0AHR
Following: 4592 - Followers: 3733
March 07, 2016 at 11:40PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/songtiveapp
A Linked Data Scalability Challenge: Concept Reuse Leads to Semantic Decay. (arXiv:1603.01722v1 [cs.AI])
The increasing amount of available Linked Data resources is laying the foundations for more advanced Semantic Web applications. One of their main limitations, however, remains the general low level of data quality. In this paper we focus on a measure of quality which is negatively affected by the increase of the available resources. We propose a measure of semantic richness of Linked Data concepts and we demonstrate our hypothesis that the more a concept is reused, the less semantically rich it becomes. This is a significant scalability issue, as one of the core aspects of Linked Data is the propagation of semantic information on the Web by reusing common terms. We prove our hypothesis with respect to our measure of semantic richness and we validate our model empirically. Finally, we suggest possible future directions to address this scalability problem.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1U0xMTc
via IFTTT
An Argument-based Creative Assistant for Harmonic Blending. (arXiv:1603.01770v1 [cs.SD])
Conceptual blending is a powerful tool for computational creativity where, for example, the properties of two harmonic spaces may be combined in a consistent manner to produce a novel harmonic space. However, deciding about the importance of property features in the input spaces and evaluating the results of conceptual blending is a nontrivial task. In the specific case of musical harmony, defining the salient features of chord transitions and evaluating invented harmonic spaces requires deep musicological background knowledge. In this paper, we propose a creative tool that helps musicologists to evaluate and to enhance harmonic innovation. This tool allows a music expert to specify arguments over given transition properties. These arguments are then considered by the system when defining combinations of features in an idiom-blending process. A music expert can assess whether the new harmonic idiom makes musicological sense and re-adjust the arguments (selection of features) to explore alternative blends that can potentially produce better harmonic spaces. We conclude with a discussion of future work that would further automate the harmonisation process.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Rxyemf
via IFTTT
Hierarchical Decision Making In Electricity Grid Management. (arXiv:1603.01840v1 [cs.AI])
The power grid is a complex and vital system that necessitates careful reliability management. Managing the grid is a difficult problem with multiple time scales of decision making and stochastic behavior due to renewable energy generations, variable demand and unplanned outages. Solving this problem in the face of uncertainty requires a new methodology with tractable algorithms. In this work, we introduce a new model for hierarchical decision making in complex systems. We apply reinforcement learning (RL) methods to learn a proxy, i.e., a level of abstraction, for real-time power grid reliability. We devise an algorithm that alternates between slow time-scale policy improvement, and fast time-scale value function approximation. We compare our results to prevailing heuristics, and show the strength of our method.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1M3HJYn
via IFTTT
Composing inference algorithms as program transformations. (arXiv:1603.01882v1 [stat.ML])
Probabilistic inference procedures are usually coded painstakingly from scratch, for each target model and each inference algorithm. We reduce this coding effort by generating inference procedures from models automatically. We make this code generation modular by decomposing inference algorithms into reusable program transformations. These source-to-source transformations perform exact inference as well as generate probabilistic programs that compute expectations, densities, and MCMC samples. The resulting inference procedures run in time comparable to that of handwritten procedures.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1M3HJrw
via IFTTT
Adaptive Visualisation System for Construction Building Information Models Using Saliency. (arXiv:1603.02028v1 [cs.CV])
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a recent construction process based on a 3D model, containing every component related to the building achievement. Architects, structure engineers, method engineers, and others participant to the building process work on this model through the design-to-construction cycle. The high complexity and the large amount of information included in these models raise several issues, delaying its wide adoption in the industrial world. One of the most important is the visualization: professionals have difficulties to find out the relevant information for their job. Actual solutions suffer from two limitations: the BIM models information are processed manually and insignificant information are simply hidden, leading to inconsistencies in the building model. This paper describes a system relying on an ontological representation of the building information to label automatically the building elements. Depending on the user's department, the visualization is modified according to these labels by automatically adjusting the colors and image properties based on a saliency model. The proposed saliency model incorporates several adaptations to fit the specificities of architectural images.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1U0xMCJ
via IFTTT
Unscented Bayesian Optimization for Safe Robot Grasping. (arXiv:1603.02038v1 [cs.RO])
We address the robot grasp optimization problem of unknown objects considering uncertainty in the input space. Grasping unknown objects can be achieved by using a trial and error exploration strategy. Bayesian optimization is a sample efficient optimization algorithm that is especially suitable for this setups as it actively reduces the number of trials for learning about the function to optimize. In fact, this active object exploration is the same strategy that infants do to learn optimal grasps. One problem that arises while learning grasping policies is that some configurations of grasp parameters may be very sensitive to error in the relative pose between the object and robot end-effector. We call these configurations unsafe because small errors during grasp execution may turn good grasps into bad grasps. Therefore, to reduce the risk of grasp failure, grasps should be planned in safe areas. We propose a new algorithm, Unscented Bayesian optimization that is able to perform sample efficient optimization while taking into consideration input noise to find safe optima. The contribution of Unscented Bayesian optimization is twofold as if provides a new decision process that drives exploration to safe regions and a new selection procedure that chooses the optimal in terms of its safety without extra analysis or computational cost. Both contributions are rooted on the strong theory behind the unscented transformation, a popular nonlinear approximation method. We show its advantages with respect to the classical Bayesian optimization both in synthetic problems and in realistic robot grasp simulations. The results highlights that our method achieves optimal and robust grasping policies after few trials while the selected grasps remain in safe regions.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1QHsqXh
via IFTTT
Learning Shared Representations in Multi-task Reinforcement Learning. (arXiv:1603.02041v1 [cs.AI])
We investigate a paradigm in multi-task reinforcement learning (MT-RL) in which an agent is placed in an environment and needs to learn to perform a series of tasks, within this space. Since the environment does not change, there is potentially a lot of common ground amongst tasks and learning to solve them individually seems extremely wasteful. In this paper, we explicitly model and learn this shared structure as it arises in the state-action value space. We will show how one can jointly learn optimal value-functions by modifying the popular Value-Iteration and Policy-Iteration procedures to accommodate this shared representation assumption and leverage the power of multi-task supervised learning. Finally, we demonstrate that the proposed model and training procedures, are able to infer good value functions, even under low samples regimes. In addition to data efficiency, we will show in our analysis, that learning abstractions of the state space jointly across tasks leads to more robust, transferable representations with the potential for better generalization. this shared representation assumption and leverage the power of multi-task supervised learning. Finally, we demonstrate that the proposed model and training procedures, are able to infer good value functions, even under low samples regimes. In addition to data efficiency, we will show in our analysis, that learning abstractions of the state space jointly across tasks leads to more robust, transferable representations with the potential for better generalization.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1puOSfM
via IFTTT
Learning Hand-Eye Coordination for Robotic Grasping with Deep Learning and Large-Scale Data Collection. (arXiv:1603.02199v1 [cs.LG])
We describe a learning-based approach to hand-eye coordination for robotic grasping from monocular images. To learn hand-eye coordination for grasping, we trained a large convolutional neural network to predict the probability that task-space motion of the gripper will result in successful grasps, using only monocular camera images and independently of camera calibration or the current robot pose. This requires the network to observe the spatial relationship between the gripper and objects in the scene, thus learning hand-eye coordination. We then use this network to servo the gripper in real time to achieve successful grasps. To train our network, we collected over 800,000 grasp attempts over the course of two months, using between 6 and 14 robotic manipulators at any given time, with differences in camera placement and hardware. Our experimental evaluation demonstrates that our method achieves effective real-time control, can successfully grasp novel objects, and corrects mistakes by continuous servoing.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1puOSfG
via IFTTT
An Online Mechanism for Ridesharing in Autonomous Mobility-on-Demand Systems. (arXiv:1603.02208v1 [cs.AI])
With proper management, Autonomous Mobility-on-Demand (AMoD) systems have great potential to satisfy urban population's mobility demand by providing safe, convenient, and affordable ridesharing services. Meanwhile, such systems can substantially decrease private car ownership and use, and thus significantly reduce traffic congestion, energy consumption and carbon emissions. In order to schedule the assignments optimally, an AMoD system requires detailed information about the demand from passengers. However, chances are that passengers do not cooperate with the service providers because of self-interestedness. Therefore, an online mechanism is desirable if it incentivizes passengers to truthfully report their actual demand. For the purpose of promoting ridesharing, we hereby introduce an integrated online ridesharing mechanism (IORS). Numerical results show that the IORS mechanism outperforms the offline, auction-based mechanism substantially. It has a very close performance compared to the optimal solution, with less computation time required and no future knowledge about the demand needed.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1RxybXB
via IFTTT