Latest YouTube Video
Saturday, June 4, 2016
Submit a tip
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/24pmiJX
via IFTTT
Ravens: The late legendary Muhammad Ali's 2012 preseason visit proved the inspiration behind Super Bowl run - Hensley (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Irongate — New Stuxnet-like Malware Targets Industrial Control Systems
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1Pby1ox
via IFTTT
Has Your TeamViewer Account Been Hacked? Here's What to Do Immediately
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/22EsgHt
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Lashunda Virgen
Reaching out & fulfilling purpose! Taking one day at a time with love. My hand in his, to a place he knows. I Love Jesus.
Fort Collins
Following: 16159 - Followers: 20557
June 04, 2016 at 01:58AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/Lashundaadu
NGC 4631: The Whale Galaxy

Vegetation greening trend in Canada and Alaska: 1984-2012
from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio: Most Recent Items http://ift.tt/1Zll9BX
via IFTTT
Friday, June 3, 2016
Orioles: All-Star RP Darren O'Day placed on the 15-day DL with a strained right hamstring; P Mike Wright called up (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Anonymous Leaks Database from South African Platinum Mining Corporation
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1U2saaE
via IFTTT
Have you ever suspected that Facebook secretly listening to you to target Ads?
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1X2vXa6
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 06/02/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/1WzdrWT
via IFTTT
Anonymous Crime Tip
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1Y6cepl
via IFTTT
Russia arrests 50 hackers who stole $25 million from Banks
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1sRTii0
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Matt Gourd
Digital content shinobi with a penchant for clear writing and rational thinking. Spare-time DJ, audiophile and competitive jogger.
London, England
https://t.co/ytniAarTur
Following: 3886 - Followers: 2911
June 03, 2016 at 06:48AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/matt_gourd
Hackers Selling Unpatched Microsoft Windows Zero-Day Exploit for $90,000
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/25B35r1
via IFTTT
Facebook Messenger App — Choose either End-to-End Encryption or Artificial Intelligence
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1Zixery
via IFTTT
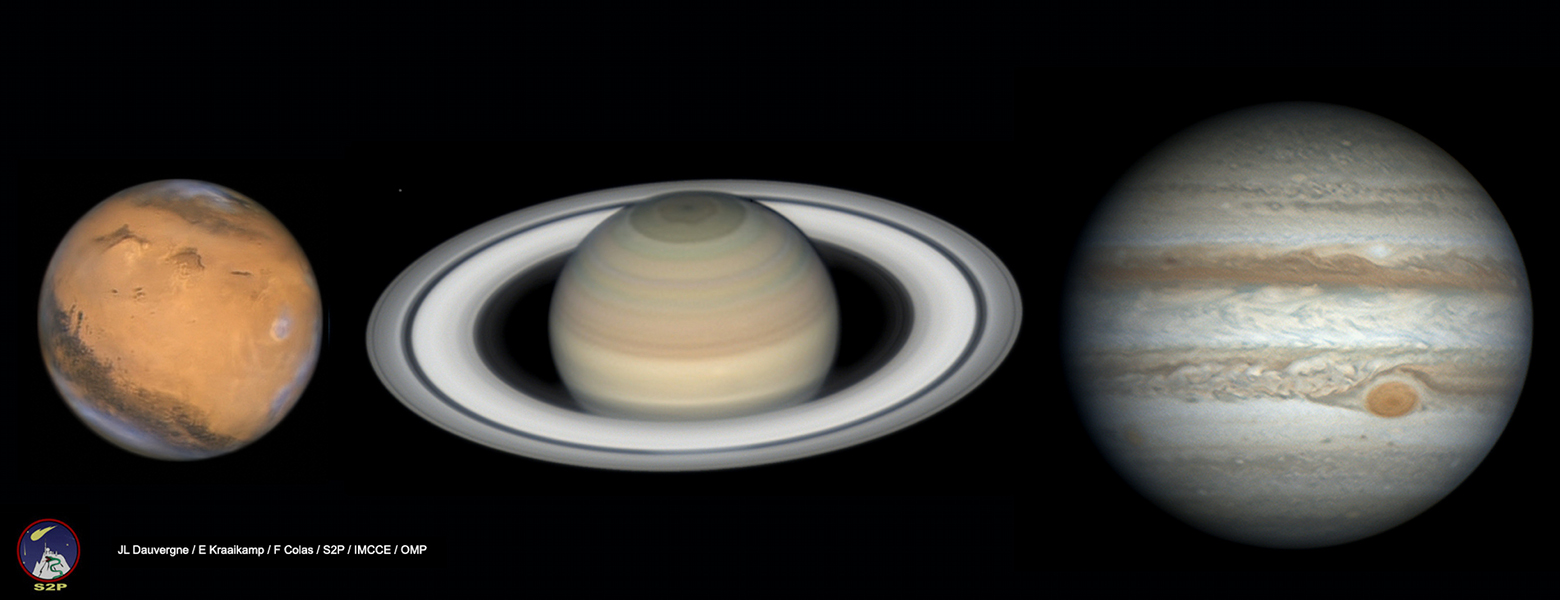
Three Planets from Pic du Midi
Mercury Transit 2016 from SDO/HMI
from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio: Most Recent Items http://ift.tt/1VAFrIC
via IFTTT
Mercury Transit 2016 from SDO/AIA at 171 Angstroms
from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio: Most Recent Items http://ift.tt/20WDrK5
via IFTTT
Mercury Transit 2016 from SDO/AIA at 304 Angstroms
from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio: Most Recent Items http://ift.tt/1VAFxjq
via IFTTT
Orioles Highlight: Mark Trumbo and Adam Jones each hit 2 homers, team goes deep 7 times in 12-7 win over Red Sox (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Thursday, June 2, 2016
I have a new follower on Twitter
Alayna Frankenberry
Content writing, Social media, online marketing and digital PR for @ContentFac (but mostly me talking about #TheXFiles and being way too proud of my cat).
Pittsburgh
https://t.co/PxGaTGmrlu
Following: 2092 - Followers: 2659
June 02, 2016 at 11:25PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/AFrankenberry
Red Sox Correction: Xander Bogaerts extended hitting streak with 2-run single off left-center field wall (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Red Sox: SS Xander Bogaerts extends hitting streak to 26 games with 2-run double in 6th inning vs. Orioles (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Orioles: Yovani Gallardo threw 3 innings (59 pitches) in rehab start for Class-A Frederick; next rehab outing Tuesday (ESPN)
via IFTTT
On the equivalence between Kolmogorov-Smirnov and ROC curve metrics for binary classification. (arXiv:1606.00496v1 [cs.AI])
Binary decisions are very common in artificial intelligence. Applying a threshold on the continuous score gives the human decider the power to control the operating point to separate the two classes. The classifier,s discriminating power is measured along the continuous range of the score by the Area Under the ROC curve (AUC_ROC) in most application fields. Only finances uses the poor single point metric maximum Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) distance. This paper proposes the Area Under the KS curve (AUC_KS) for performance assessment and proves AUC_ROC = 0.5 + AUC_KS, as a simpler way to calculate the AUC_ROC. That is even more important for ROC averaging in ensembles of classifiers or n fold cross-validation. The proof is geometrically inspired on rotating all KS curve to make it lie on the top of the ROC chance diagonal. On the practical side, the independent variable on the abscissa on the KS curve simplifies the calculation of the AUC_ROC. On the theoretical side, this research gives insights on probabilistic interpretations of classifiers assessment and integrates the existing body of knowledge of the information theoretical ROC approach with the proposed statistical approach based on the thoroughly known KS distribution.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2878DMb
via IFTTT
Mining Software Components from Object-Oriented APIs. (arXiv:1606.00561v1 [cs.SE])
Object-oriented Application Programing Interfaces (APIs) support software reuse by providing pre-implemented functionalities. Due to the huge number of included classes, reusing and understanding large APIs is a complex task. Otherwise, software components are admitted to be more reusable and understandable entities than object-oriented ones. Thus, in this paper, we propose an approach for reengineering object-oriented APIs into component-based ones. We mine components as a group of classes based on the frequency they are used together and their ability to form a quality-centric component. To validate our approach, we experimented on 100 Java applications that used Android APIs.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/25A8fno
via IFTTT
The Challenge of Non-Technical Loss Detection using Artificial Intelligence: A Survey. (arXiv:1606.00626v1 [cs.AI])
Detection of non-technical losses (NTL) which include electricity theft, faulty meters or billing errors has attracted increasing attention from researchers in electrical engineering and computer science. NTLs cause significant harm to the economy, as in some countries they may range up to 40% of the total electricity distributed. The predominant research direction is employing artificial intelligence (AI) to solve this problem. Promising approaches have been reported falling into two categories: expert systems incorporating hand-crafted expert knowledge or machine learning, also called pattern recognition or data mining, which learns fraudulent consumption patterns from examples without being explicitly programmed. This paper first provides an overview about how NTLs are defined and their impact on economies. Next, it covers the fundamental pillars of AI relevant to this domain. It then surveys these research efforts in a comprehensive review of algorithms, features and data sets used. It finally identifies the key scientific and engineering challenges in NTL detection and suggests how they could be solved. We believe that those challenges have not sufficiently been addressed in past contributions and that covering those is necessary in order to advance NTL detection.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/24lBxne
via IFTTT
Death and Suicide in Universal Artificial Intelligence. (arXiv:1606.00652v1 [cs.AI])
Reinforcement learning (RL) is a general paradigm for studying intelligent behaviour, with applications ranging from artificial intelligence to psychology and economics. AIXI is a universal solution to the RL problem; it can learn any computable environment. A technical subtlety of AIXI is that it is defined using a mixture over semimeasures that need not sum to 1, rather than over proper probability measures. In this work we argue that the shortfall of a semimeasure can naturally be interpreted as the agent's estimate of the probability of its death. We formally define death for generally intelligent agents like AIXI, and prove a number of related theorems about their behaviour. Notable discoveries include that agent behaviour can change radically under positive linear transformations of the reward signal (from suicidal to dogmatically self-preserving), and that the agent's posterior belief that it will survive increases over time.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1VAlodl
via IFTTT
Multiresolution Recurrent Neural Networks: An Application to Dialogue Response Generation. (arXiv:1606.00776v1 [cs.CL])
We introduce the multiresolution recurrent neural network, which extends the sequence-to-sequence framework to model natural language generation as two parallel discrete stochastic processes: a sequence of high-level coarse tokens, and a sequence of natural language tokens. There are many ways to estimate or learn the high-level coarse tokens, but we argue that a simple extraction procedure is sufficient to capture a wealth of high-level discourse semantics. Such procedure allows training the multiresolution recurrent neural network by maximizing the exact joint log-likelihood over both sequences. In contrast to the standard log-likelihood objective w.r.t. natural language tokens (word perplexity), optimizing the joint log-likelihood biases the model towards modeling high-level abstractions. We apply the proposed model to the task of dialogue response generation in two challenging domains: the Ubuntu technical support domain, and Twitter conversations. On Ubuntu, the model outperforms competing approaches by a substantial margin, achieving state-of-the-art results according to both automatic evaluation metrics and a human evaluation study. On Twitter, the model appears to generate more relevant and on-topic responses according to automatic evaluation metrics. Finally, our experiments demonstrate that the proposed model is more adept at overcoming the sparsity of natural language and is better able to capture long-term structure.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1XUgfgj
via IFTTT
Prior Swapping for Data-Independent Inference. (arXiv:1606.00787v1 [stat.ML])
While Bayesian methods are praised for their ability to incorporate useful prior knowledge, in practice, priors that allow for computationally convenient or tractable inference are more commonly used. In this paper, we investigate the following question: for a given model, is it possible to use any convenient prior to infer a false posterior, and afterwards, given some true prior of interest, quickly transform this result into the true posterior?
We present a procedure to carry out this task: given an inferred false posterior and true prior, our algorithm generates samples from the true posterior. This transformation procedure, which we call "prior swapping" works for arbitrary priors. Notably, its cost is independent of data size. It therefore allows us, in some cases, to apply significantly less-costly inference procedures to more-sophisticated models than previously possible. It also lets us quickly perform any additional inferences, such as with updated priors or for many different hyperparameter settings, without touching the data. We prove that our method can generate asymptotically exact samples, and demonstrate it empirically on a number of models and priors.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1XUgiZm
via IFTTT
Multi-View Treelet Transform. (arXiv:1606.00800v1 [stat.ML])
Current multi-view factorization methods make assumptions that are not acceptable for many kinds of data, and in particular, for graphical data with hierarchical structure. At the same time, current hierarchical methods work only in the single-view setting. We generalize the Treelet Transform to the Multi-View Treelet Transform (MVTT) to allow for the capture of hierarchical structure when multiple views are avilable. Further, we show how this generalization is consistent with the existing theory and how it might be used in denoising empirical networks and in computing the shared response of functional brain data.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1sQy6J9
via IFTTT
On the satisfiability problem for SPARQL patterns. (arXiv:1406.1404v2 [cs.DB] UPDATED)
The satisfiability problem for SPARQL patterns is undecidable in general, since the expressive power of SPARQL 1.0 is comparable with that of the relational algebra. The goal of this paper is to delineate the boundary of decidability of satisfiability in terms of the constraints allowed in filter conditions. The classes of constraints considered are bound-constraints, negated bound-constraints, equalities, nonequalities, constant-equalities, and constant-nonequalities. The main result of the paper can be summarized by saying that, as soon as inconsistent filter conditions can be formed, satisfiability is undecidable. The key insight in each case is to find a way to emulate the set difference operation. Undecidability can then be obtained from a known undecidability result for the algebra of binary relations with union, composition, and set difference. When no inconsistent filter conditions can be formed, satisfiability is efficiently decidable by simple checks on bound variables and on the use of literals. The paper also points out that satisfiability for the so-called `well-designed' patterns can be decided by a check on bound variables and a check for inconsistent filter conditions.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1pVVLkE
via IFTTT
Uncertain programming model for multi-item solid transportation problem. (arXiv:1606.00002v1 [math.OC] CROSS LISTED)
In this paper, an uncertain Multi-objective Multi-item Solid Transportation Problem (MMSTP) based on uncertainty theory is presented. In the model, transportation costs, supplies, demands and conveyances parameters are taken to be uncertain parameters. There are restrictions on some items and conveyances of the model. Therefore, some particular items cannot be transported by some exceptional conveyances. Using the advantage of uncertainty theory, the MMSTP is first converted into an equivalent deterministic MMSTP. By applying convex combination method and minimizing distance function method, the deterministic MMSTP is reduced into single objective programming problems. Thus, both single objective programming problems are solved using Maple 18.02 optimization toolbox. Finally, a numerical example is given to illustrate the performance of the models.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1sNv88v
via IFTTT
[FD] Nagios XI Multiple Vulnerabilities
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Ravens: Pittsburgh's Markus Wheaton and Stephon Tuitt say Baltimore, not Cincinnati, remains the team's biggest rival (ESPN)
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Virtual Training Inc
Here at Virtual Training Innovation, we believe in creating less hassle for employers when it comes to training their new employees.
Santa Clara, CA
http://t.co/6jGm0JeKNd
Following: 3634 - Followers: 3275
June 02, 2016 at 03:56PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/VTrainingInc
SportsCenter Video: Ravens' Eugene Monroe says players have been \"very supportive\" of his backing of medical marijuana (ESPN)
via IFTTT
File uploads fail as anonymous user with caching on with multiple file fields
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1TLN7D6
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Consciousness Sci
OM! CONSCIOUSNESS SCIENCE | #AI #consciousness #intelligence #idealism #realism #nonduality #panpsychism #universalconsciousness #IoT || https://t.co/UQQKblJzA6
https://t.co/YOQBXKjDbn
Following: 1673 - Followers: 325
June 02, 2016 at 12:01PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/consciousci_sv
Jay Z Responds To Pundit Tomi Lahren On 'Drug Dealers Anonymous'
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/25CSAad
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 06/01/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/1X0wBog
via IFTTT
[FD] SEC Consult SA-20160602-0 :: Multiple critical vulnerabilities in Ubee EVW3226 Advanced wireless voice gateway
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
New Music: Pusha T Drops Drug Dealers Anonymous, featuring Jay Z
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1WxKLxt
via IFTTT
Pusha T & Jay Z Are “Drug Dealers Anonymous&rdquo
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1TYZP4X
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Baseball Polls
Posting and creating interesting baseball related polls and questions. (I do not own any of the material posted).
Following: 120 - Followers: 3
June 02, 2016 at 12:12AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/Baseballpolls4
Wednesday, June 1, 2016
Hear Jay Z and Pusha T Confess on 'Drug Dealers Anonymous'
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1XR7raQ
via IFTTT
Red Sox: SS Xander Bogaerts extends hitting streak to 25 games with a single in the 6th inning vs. the Orioles (ESPN)
via IFTTT
How to avoid ethically relevant Machine Consciousness. (arXiv:1606.00058v1 [cs.AI])
This paper discusses the root cause of systems perceiving the self experience and how to exploit adaptive and learning features without introducing ethically problematic system properties.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Ui4smg
via IFTTT
Quantifying the probable approximation error of probabilistic inference programs. (arXiv:1606.00068v1 [cs.AI])
This paper introduces a new technique for quantifying the approximation error of a broad class of probabilistic inference programs, including ones based on both variational and Monte Carlo approaches. The key idea is to derive a subjective bound on the symmetrized KL divergence between the distribution achieved by an approximate inference program and its true target distribution. The bound's validity (and subjectivity) rests on the accuracy of two auxiliary probabilistic programs: (i) a "reference" inference program that defines a gold standard of accuracy and (ii) a "meta-inference" program that answers the question "what internal random choices did the original approximate inference program probably make given that it produced a particular result?" The paper includes empirical results on inference problems drawn from linear regression, Dirichlet process mixture modeling, HMMs, and Bayesian networks. The experiments show that the technique is robust to the quality of the reference inference program and that it can detect implementation bugs that are not apparent from predictive performance.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1UfY7YT
via IFTTT
Applications of Probabilistic Programming (Master's thesis, 2015). (arXiv:1606.00075v1 [cs.AI])
This thesis describes work on two applications of probabilistic programming: the learning of probabilistic program code given specifications, in particular program code of one-dimensional samplers; and the facilitation of sequential Monte Carlo inference with help of data-driven proposals. The latter is presented with experimental results on a linear Gaussian model and a non-parametric dependent Dirichlet process mixture of objects model for object recognition and tracking.
In Chapter 1 we provide a brief introduction to probabilistic programming.
In Chapter 3 we present an approach to automatic discovery of samplers in the form of probabilistic programs. We formulate a Bayesian approach to this problem by specifying a grammar-based prior over probabilistic program code. We use an approximate Bayesian computation method to learn the programs, whose executions generate samples that statistically match observed data or analytical characteristics of distributions of interest. In our experiments we leverage different probabilistic programming systems to perform Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling over the space of programs. Experimental results have demonstrated that, using the proposed methodology, we can learn approximate and even some exact samplers. Finally, we show that our results are competitive with regard to genetic programming methods.
In Chapter 3, we describe a way to facilitate sequential Monte Carlo inference in probabilistic programming using data-driven proposals. In particular, we develop a distance-based proposal for the non-parametric dependent Dirichlet process mixture of objects model. We implement this approach in the probabilistic programming system Anglican, and show that for that model data-driven proposals provide significant performance improvements. We also explore the possibility of using neural networks to improve data-driven proposals.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/25BIN4f
via IFTTT
Hardness of the Pricing Problem for Chains in Barter Exchanges. (arXiv:1606.00117v1 [cs.DS])
Kidney exchange is a barter market where patients trade willing but medically incompatible donors. These trades occur via cycles, where each patient-donor pair both gives and receives a kidney, and via chains, which begin with an altruistic donor who does not require a kidney in return. For logistical reasons, the maximum length of a cycle is typically limited to a small constant, while chains can be much longer. Given a compatibility graph of patient-donor pairs, altruists, and feasible potential transplants between them, finding even a maximum-cardinality set of vertex-disjoint cycles and chains is NP-hard. There has been much work on developing provably optimal solvers that are efficient in practice. One of the leading techniques has been branch and price, where column generation is used to incrementally bring cycles and chains into the optimization model on an as-needed basis. In particular, only positive-price columns need to be brought into the model. We prove that finding a positive-price chain is NP-complete. This shows incorrectness of two leading branch-and-price solvers that suggested polynomial-time chain pricing algorithms.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/25BHP8c
via IFTTT
A Survey of Qualitative Spatial and Temporal Calculi -- Algebraic and Computational Properties. (arXiv:1606.00133v1 [cs.AI])
Qualitative Spatial and Temporal Reasoning (QSTR) is concerned with symbolic knowledge representation, typically over infinite domains. The motivations for employing QSTR techniques range from exploiting computational properties that allow efficient reasoning to capture human cognitive concepts in a computational framework. The notion of a qualitative calculus is one of the most prominent QSTR formalisms. This article presents the first overview of all qualitative calculi developed to date and their computational properties, together with generalized definitions of the fundamental concepts and methods, which now encompass all existing calculi. Moreover, we provide a classification of calculi according to their algebraic properties.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Ui4udW
via IFTTT
A structured argumentation framework for detaching conditional obligations. (arXiv:1606.00339v1 [cs.AI])
We present a general formal argumentation system for dealing with the detachment of conditional obligations. Given a set of facts, constraints, and conditional obligations, we answer the question whether an unconditional obligation is detachable by considering reasons for and against its detachment. For the evaluation of arguments in favor of detaching obligations we use a Dung-style argumentation-theoretical semantics. We illustrate the modularity of the general framework by considering some extensions, and we compare the framework to some related approaches from the literature.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/25BI6rD
via IFTTT
How to move beyond general game playing artificial intelligence by player modelling. (arXiv:1606.00401v1 [cs.HC])
General game playing artificial intelligence has recently seen important advances due to the various techniques known as 'deep learning'. However the advances conceal equally important limitations in their reliance on: massive data sets; fortuitously constructed problems; and absence of any human-level complexity, including other human opponents. On the other hand, deep learning systems which do beat human champions, such as in Go, do not generalise well. The power of deep learning simultaneously exposes its weakness. Given that deep learning is mostly clever reconfigurations of well-established methods, moving beyond the state of art calls for forward-thinking visionary solutions, not just more of the same. I present the argument that general game playing artificial intelligence will require a generalised player model. This is because games are inherently human artefacts which therefore, as a class of problems, contain cases which require a human-style problem solving approach. I relate this argument to the performance of state of art general game playing agents. I then describe a concept for a formal category theoretic basis to a generalised player model. This formal model approach integrates my existing 'Behavlets' method for psychologically-derived player modelling:
Cowley, B., Charles, D. (2016). Behavlets: a Method for Practical Player Modelling using Psychology-Based Player Traits and Domain Specific Features. User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction, 26(2), 257-306.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Ui3BCm
via IFTTT
MLB: Red Sox OF Mookie Betts hits 2nd home run of game in 2nd inning; ties league record with 5 HRs in a two-game span (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Orioles recall P T.J. McFarland (1.69 ERA) from Triple-A Norfolk; P Ashur Tolliver optioned to minors (ESPN)
via IFTTT
427 Million Myspace Passwords leaked in major Security Breach
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1VwsejQ
via IFTTT
[FD] Joomla SecurityCheck extension - Multiple vulnerabilities
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] CVE-2016-3670 Stored Cross Site Scripting in Liferay CE
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] Keystone Assembler Engine is out!
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] XSS in CMSimple <= v4.6.2
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] Faraday v1.0.20 is here! New conflict resolution, hosts and services views & bug fixes!
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
ISS Daily Summary Report – 05/31/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/1UtVUvC
via IFTTT
Allow comments in anonymous peer reviews
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1P3BS6N
via IFTTT
Stars and Gas of the Running Chicken Nebula

Tuesday, May 31, 2016
Orioles Video: Adam Jones goes 2-for-4 with an RBI but can't overcome Red Sox OF Mookie Betts' 3 HRs in 6-2 loss (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Pusha T enlists Jay Z for 'Drug Dealers Anonymous'
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1P30VH7
via IFTTT
MLB: Mookie Betts launches 3 home runs, Xander Bogaerts extends hit streak to 24 games as Red Sox defeat Orioles 6-2 (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Red Sox: SS Xander Bogaerts extends hitting streak to 24 games with a single in the 7th inning vs. the Orioles (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Manuscript, D-Mbs Mus.ms. 1503 h (Anonymous)
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1XdTMfC
via IFTTT
Interdependent Scheduling Games. (arXiv:1605.09497v1 [cs.GT])
We propose a model of interdependent scheduling games in which each player controls a set of services that they schedule independently. A player is free to schedule his own services at any time; however, each of these services only begins to accrue reward for the player when all predecessor services, which may or may not be controlled by the same player, have been activated. This model, where players have interdependent services, is motivated by the problems faced in planning and coordinating large-scale infrastructures, e.g., restoring electricity and gas to residents after a natural disaster or providing medical care in a crisis when different agencies are responsible for the delivery of staff, equipment, and medicine. We undertake a game-theoretic analysis of this setting and in particular consider the issues of welfare maximization, computing best responses, Nash dynamics, and existence and computation of Nash equilibria.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1WXDE14
via IFTTT
Psychologically based Virtual-Suspect for Interrogative Interview Training. (arXiv:1605.09505v1 [cs.AI])
In this paper, we present a Virtual-Suspect system which can be used to train inexperienced law enforcement personnel in interrogation strategies. The system supports different scenario configurations based on historical data. The responses presented by the Virtual-Suspect are selected based on the psychological state of the suspect, which can be configured as well. Furthermore, each interrogator's statement affects the Virtual-Suspect's current psychological state, which may lead the interrogation in different directions. In addition, the model takes into account the context in which the statements are made. Experiments with 24 subjects demonstrate that the Virtual-Suspect's behavior is similar to that of a human who plays the role of the suspect.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1r1ZCCl
via IFTTT
Determining the Characteristic Vocabulary for a Specialized Dictionary using Word2vec and a Directed Crawler. (arXiv:1605.09564v1 [cs.CL])
Specialized dictionaries are used to understand concepts in specific domains, especially where those concepts are not part of the general vocabulary, or having meanings that differ from ordinary languages. The first step in creating a specialized dictionary involves detecting the characteristic vocabulary of the domain in question. Classical methods for detecting this vocabulary involve gathering a domain corpus, calculating statistics on the terms found there, and then comparing these statistics to a background or general language corpus. Terms which are found significantly more often in the specialized corpus than in the background corpus are candidates for the characteristic vocabulary of the domain. Here we present two tools, a directed crawler, and a distributional semantics package, that can be used together, circumventing the need of a background corpus. Both tools are available on the web.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1TVOIZ7
via IFTTT
Controlling Exploration Improves Training for Deep Neural Networks. (arXiv:1605.09593v1 [cs.LG])
Stochastic optimization methods are widely used for training of deep neural networks. However, it is still a challenging research problem to achieve effective training by using stochastic optimization methods. This is due to the difficulties in finding good parameters on a loss function that have many saddle points. In this paper, we propose a stochastic optimization method called STDProp for effective training of deep neural networks. Its key idea is to effectively explore parameters on a complex surface of a loss function. We additionally develop momentum version of STDProp. While our approaches are easy to implement with high memory efficiency, it is more effective than other practical stochastic optimization methods for deep neural networks.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1XdJSLb
via IFTTT
Curiosity-driven Exploration in Deep Reinforcement Learning via Bayesian Neural Networks. (arXiv:1605.09674v1 [cs.LG])
Scalable and effective exploration remains a key challenge in reinforcement learning (RL). While there are methods with optimality guarantees in the setting of discrete state and action spaces, these methods cannot be applied in high-dimensional deep RL scenarios. As such, most contemporary RL relies on simple heuristics such as epsilon-greedy exploration or adding Gaussian noise to the controls. This paper introduces Variational Information Maximizing Exploration (VIME), an exploration strategy based on maximization of information gain about the agent's belief of environment dynamics. We propose a practical implementation, using variational inference in Bayesian neural networks which efficiently handles continuous state and action spaces. VIME modifies the MDP reward function, and can be applied with several different underlying RL algorithms. We demonstrate that VIME achieves significantly better performance compared to heuristic exploration methods across a variety of continuous control tasks and algorithms, including tasks with very sparse rewards.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1RKQdoC
via IFTTT
Information Theoretically Aided Reinforcement Learning for Embodied Agents. (arXiv:1605.09735v1 [cs.AI])
Reinforcement learning for embodied agents is a challenging problem. The accumulated reward to be optimized is often a very rugged function, and gradient methods are impaired by many local optimizers. We demonstrate, in an experimental setting, that incorporating an intrinsic reward can smoothen the optimization landscape while preserving the global optimizers of interest. We show that policy gradient optimization for locomotion in a complex morphology is significantly improved when supplementing the extrinsic reward by an intrinsic reward defined in terms of the mutual information of time consecutive sensor readings.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Wvymdf
via IFTTT
Towards ontology driven learning of visual concept detectors. (arXiv:1605.09757v1 [cs.IR])
The maturity of deep learning techniques has led in recent years to a breakthrough in object recognition in visual media. While for some specific benchmarks, neural techniques seem to match if not outperform human judgement, challenges are still open for detecting arbitrary concepts in arbitrary videos. In this paper, we propose a system that combines neural techniques, a large scale visual concepts ontology, and an active learning loop, to provide on the fly model learning of arbitrary concepts. We give an overview of the system as a whole, and focus on the central role of the ontology for guiding and bootstrapping the learning of new concepts, improving the recall of concept detection, and, on the user end, providing semantic search on a library of annotated videos.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1ZbBCZk
via IFTTT
Technical Report: Directed Controller Synthesis of Discrete Event Systems. (arXiv:1605.09772v1 [cs.SY])
This paper presents a Directed Controller Synthesis (DCS) technique for discrete event systems. The DCS method explores the solution space for reactive controllers guided by a domain-independent heuristic. The heuristic is derived from an efficient abstraction of the environment based on the componentized way in which complex environments are described. Then by building the composition of the components on-the-fly DCS obtains a solution by exploring a reduced portion of the state space. This work focuses on untimed discrete event systems with safety and co-safety (i.e. reachability) goals. An evaluation for the technique is presented comparing it to other well-known approaches to controller synthesis (based on symbolic representation and compositional analyses).
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Vu4lJK
via IFTTT
Adversarial Feature Learning. (arXiv:1605.09782v1 [cs.LG])
The ability of the Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) framework to learn generative models mapping from simple latent distributions to arbitrarily complex data distributions has been demonstrated empirically, with compelling results showing generators learn to "linearize semantics" in the latent space of such models. Intuitively, such latent spaces may serve as useful feature representations for auxiliary problems where semantics are relevant. However, in their existing form, GANs have no means of learning the inverse mapping -- projecting data back into the latent space. We propose Bidirectional Generative Adversarial Networks (BiGANs) as a means of learning this inverse mapping, and demonstrate that the resulting learned feature representation is useful for auxiliary supervised discrimination tasks, competitive with contemporary approaches to unsupervised and self-supervised feature learning.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1XdJZGt
via IFTTT
Collaborative Filtering Bandits. (arXiv:1502.03473v7 [cs.LG] UPDATED)
Classical collaborative filtering, and content-based filtering methods try to learn a static recommendation model given training data. These approaches are far from ideal in highly dynamic recommendation domains such as news recommendation and computational advertisement, where the set of items and users is very fluid. In this work, we investigate an adaptive clustering technique for content recommendation based on exploration-exploitation strategies in contextual multi-armed bandit settings. Our algorithm takes into account the collaborative effects that arise due to the interaction of the users with the items, by dynamically grouping users based on the items under consideration and, at the same time, grouping items based on the similarity of the clusterings induced over the users. The resulting algorithm thus takes advantage of preference patterns in the data in a way akin to collaborative filtering methods. We provide an empirical analysis on medium-size real-world datasets, showing scalability and increased prediction performance (as measured by click-through rate) over state-of-the-art methods for clustering bandits. We also provide a regret analysis within a standard linear stochastic noise setting.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Dn3PTW
via IFTTT
Hierarchical Deep Reinforcement Learning: Integrating Temporal Abstraction and Intrinsic Motivation. (arXiv:1604.06057v2 [cs.LG] UPDATED)
Learning goal-directed behavior in environments with sparse feedback is a major challenge for reinforcement learning algorithms. The primary difficulty arises due to insufficient exploration, resulting in an agent being unable to learn robust value functions. Intrinsically motivated agents can explore new behavior for its own sake rather than to directly solve problems. Such intrinsic behaviors could eventually help the agent solve tasks posed by the environment. We present hierarchical-DQN (h-DQN), a framework to integrate hierarchical value functions, operating at different temporal scales, with intrinsically motivated deep reinforcement learning. A top-level value function learns a policy over intrinsic goals, and a lower-level function learns a policy over atomic actions to satisfy the given goals. h-DQN allows for flexible goal specifications, such as functions over entities and relations. This provides an efficient space for exploration in complicated environments. We demonstrate the strength of our approach on two problems with very sparse, delayed feedback: (1) a complex discrete stochastic decision process, and (2) the classic ATARI game `Montezuma's Revenge'.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Qoq3Yd
via IFTTT
Drug Dealers Anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/20S1SbI
via IFTTT
Theme cache issue for anonymous users
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1P1UJ2i
via IFTTT
Drupal 8 Caching Problem for anonymous users
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1Ufs62Z
via IFTTT
100 NFL Predictions: Ravens will trade Eugene Monroe to first team that loses a starting left tackle to injury this year (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Orioles: C Caleb Joseph to be placed on the 15-day DL after he took a foul ball off his groin area in Monday's game (ESPN)
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 05/30/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/1TTWIKl
via IFTTT
[FD] [RT-SA-2016-005] Unauthenticated File Upload in Relay Ajax Directory Manager may Lead to Remote Command Execution
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] [RT-SA-2016-004] Websockify: Remote Code Execution via Buffer Overflow
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
I have a new follower on Twitter
InEight Inc.
Creator of project cost management software for EC&O, mining, oil & gas, utilities, and industrial machinery & components industries.
Scottsdale, AZ
http://t.co/MJEylUMfOV
Following: 4473 - Followers: 4454
May 31, 2016 at 07:39AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/ineightsoftware
Anonymous Tip Leads to Underage Party Bust near Hazleton
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1UeWg6k
via IFTTT
Add `crossorigin="anonymous"`
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1Z9uNav
via IFTTT
Monday, May 30, 2016
Hacker Selling 65 Million Passwords From Tumblr Data Breach
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/25xgKmy
via IFTTT
Iran orders all Messaging Apps to store its citizens' data within Country
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/25vdLHS
via IFTTT
Anonymous Icon, Anonymous Icon Eps10, Anonymous Icon Vector, Anonymous Icon Eps ...
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1RH9Eid
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Bobby Morris
Following: 3672 - Followers: 1314
May 30, 2016 at 09:17PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/Morris07C
Computational Estimate Visualisation and Evaluation of Agent Classified Rules Learning System. (arXiv:1605.08878v1 [cs.CY])
Student modelling and agent classified rules learning as applied in the development of the intelligent Preassessment System has been presented in [10],[11]. In this paper, we now demystify the theory behind the development of the pre-assessment system followed by some computational experimentation and graph visualisation of the agent classified rules learning algorithm in the estimation and prediction of classified rules. In addition, we present some preliminary results of the pre-assessment system evaluation. From the results, it is gathered that the system has performed according to its design specification.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1PdQTbP
via IFTTT
MCMC assisted by Belief Propagaion. (arXiv:1605.09042v1 [stat.ML])
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) and Belief Propagation (BP) are the most popular algorithms for computational inference in Graphical Models (GM). In principle, MCMC is an exact probabilistic method which, however, often suffers from exponentially slow mixing. In contrast, BP is a deterministic method, which is typically fast, empirically very successful, however in general lacking control of accuracy over loopy graphs. In this paper, we introduce MCMC algorithms correcting the approximation error of BP, i.e., we provide a way to compensate for BP errors via a consecutive BP-aware MCMC. Our framework is based on the Loop Calculus (LC) approach which allows to express the BP error as a sum of weighted generalized loops. Although the full series is computationally intractable, it is known that a truncated series, summing up all 2-regular loops, is computable in polynomial-time for planar pair-wise binary GMs and it also provides a highly accurate approximation empirically. Motivated by this, we first propose a polynomial-time approximation MCMC scheme for the truncated series of general (non-planar) pair-wise binary models. Our main idea here is to use the Worm algorithm, known to provide fast mixing in other (related) problems, and then design an appropriate rejection scheme to sample 2-regular loops. Furthermore, we also design an efficient rejection-free MCMC scheme for approximating the full series. The main novelty underlying our design is in utilizing the concept of cycle basis, which provides an efficient decomposition of the generalized loops. In essence, the proposed MCMC schemes run on transformed GM built upon the non-trivial BP solution, and our experiments show that this synthesis of BP and MCMC outperforms both direct MCMC and bare BP schemes.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/27ZAKgo
via IFTTT
Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks. (arXiv:1605.09081v1 [stat.ML])
Convoulutional Neural Networks (CNNs) exhibit extraordinary performance on a variety of machine learning tasks. However, their mathematical properties and behavior are quite poorly understood. There is some work, in the form of a framework, for analyzing the operations that they perform. The goal of this project is to present key results from this theory, and provide intuition for why CNNs work.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1qYArAG
via IFTTT
Control of Memory, Active Perception, and Action in Minecraft. (arXiv:1605.09128v1 [cs.AI])
In this paper, we introduce a new set of reinforcement learning (RL) tasks in Minecraft (a flexible 3D world). We then use these tasks to systematically compare and contrast existing deep reinforcement learning (DRL) architectures with our new memory-based DRL architectures. These tasks are designed to emphasize, in a controllable manner, issues that pose challenges for RL methods including partial observability (due to first-person visual observations), delayed rewards, high-dimensional visual observations, and the need to use active perception in a correct manner so as to perform well in the tasks. While these tasks are conceptually simple to describe, by virtue of having all of these challenges simultaneously they are difficult for current DRL architectures. Additionally, we evaluate the generalization performance of the architectures on environments not used during training. The experimental results show that our new architectures generalize to unseen environments better than existing DRL architectures.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1U8VOXB
via IFTTT
Internal Guidance for Satallax. (arXiv:1605.09293v1 [cs.LO])
We propose a new internal guidance method for automated theorem provers based on the given-clause algorithm. Our method influences the choice of unprocessed clauses using positive and negative examples from previous proofs. To this end, we present an efficient scheme for Naive Bayesian classification by generalising label occurrences to types with monoid structure. This makes it possible to extend existing fast classifiers, which consider only positive examples, with negative ones. We implement the method in the higher-order logic prover Satallax, where we modify the delay with which propositions are processed. We evaluated our method on a simply-typed higher-order logic version of the Flyspeck project, where it solves 26% more problems than Satallax without internal guidance.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1PdQIx9
via IFTTT
Synthesizing the preferred inputs for neurons in neural networks via deep generator networks. (arXiv:1605.09304v1 [cs.NE])
Deep neural networks (DNNs) have demonstrated state-of-the-art results on many pattern recognition tasks, especially vision classification problems. Understanding the inner workings of such computational brains is both fascinating basic science that is interesting in its own right - similar to why we study the human brain - and will enable researchers to further improve DNNs. One path to understanding how a neural network functions internally is to study what each of its neurons has learned to detect. One such method is called activation maximization (AM), which synthesizes an input (e.g. an image) that highly activates a neuron. Here we dramatically improve the qualitative state of the art of activation maximization by harnessing a powerful, learned prior: a deep generator network (DGN). The algorithm (1) generates qualitatively state-of-the-art synthetic images that look almost real, (2) reveals the features learned by each neuron in an interpretable way, (3) generalizes well to new datasets and somewhat well to different network architectures without requiring the prior to be relearned, and (4) can be considered as a high-quality generative method (in this case, by generating novel, creative, interesting, recognizable images).
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1U8Wg8k
via IFTTT
Unsupervised Discovery of El Nino Using Causal Feature Learning on Microlevel Climate Data. (arXiv:1605.09370v1 [stat.ML])
We show that the climate phenomena of El Nino and La Nina arise naturally as states of macro-variables when our recent causal feature learning framework (Chalupka 2015, Chalupka 2016) is applied to micro-level measures of zonal wind (ZW) and sea surface temperatures (SST) taken over the equatorial band of the Pacific Ocean. The method identifies these unusual climate states on the basis of the relation between ZW and SST patterns without any input about past occurrences of El Nino or La Nina. The simpler alternatives of (i) clustering the SST fields while disregarding their relationship with ZW patterns, or (ii) clustering the joint ZW-SST patterns, do not discover El Nino. We discuss the degree to which our method supports a causal interpretation and use a low-dimensional toy example to explain its success over other clustering approaches. Finally, we propose a new robust and scalable alternative to our original algorithm (Chalupka 2016), which circumvents the need for high-dimensional density learning.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1PdQupM
via IFTTT
Computing rational decisions in extensive games with limited foresight. (arXiv:1502.03683v6 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
We introduce a class of extensive form games where players might not be able to foresee the possible consequences of their decisions and form a model of their opponents which they exploit to achieve a more profitable outcome. We improve upon existing models of games with limited foresight, endowing players with the ability of higher-order reasoning and proposing a novel solution concept to address intuitions coming from real game play. We analyse the resulting equilibria, devising an effective procedure to compute them.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1D1Dwnu
via IFTTT
Generalized Support and Formal Development of Constraint Propagators. (arXiv:1504.05846v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
Constraint programming is a family of techniques for solving combinatorial problems, where the problem is modelled as a set of decision variables (typically with finite domains) and a set of constraints that express relations among the decision variables. One key concept in constraint programming is propagation: reasoning on a constraint or set of constraints to derive new facts, typically to remove values from the domains of decision variables. Specialised propagation algorithms (propagators) exist for many classes of constraints.
The concept of support is pervasive in the design of propagators. Traditionally, when a domain value ceases to have support, it may be removed because it takes part in no solutions. Arc-consistency algorithms such as AC2001 make use of support in the form of a single domain value. GAC algorithms such as GAC-Schema use a tuple of values to support each literal. We generalize these notions of support in two ways. First, we allow a set of tuples to act as support. Second, the supported object is generalized from a set of literals (GAC-Schema) to an entire constraint or any part of it.
We design a methodology for developing correct propagators using generalized support. A constraint is expressed as a family of support properties, which may be proven correct against the formal semantics of the constraint. Using Curry-Howard isomorphism to interpret constructive proofs as programs, we show how to derive correct propagators from the constructive proofs of the support properties. The framework is carefully designed to allow efficient algorithms to be produced. Derived algorithms may make use of dynamic literal triggers or watched literals for efficiency. Finally, two case studies of deriving efficient algorithms are given.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Hnu0NX
via IFTTT
Value Iteration Networks. (arXiv:1602.02867v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
We introduce the value iteration network (VIN): a fully differentiable neural network with a `planning module' embedded within. VINs can learn to plan, and are suitable for predicting outcomes that involve planning-based reasoning, such as policies for reinforcement learning. Key to our approach is a novel differentiable approximation of the value-iteration algorithm, which can be represented as a convolutional neural network, and trained end-to-end using standard backpropagation. We evaluate VIN based policies on discrete and continuous path-planning domains, and on a natural-language based search task. We show that by learning an explicit planning computation, VIN policies generalize better to new, unseen domains.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1XhcmQD
via IFTTT
Fundamental Differences between Dropout and Weight Decay in Deep Networks. (arXiv:1602.04484v3 [cs.LG] UPDATED)
We analyze dropout in deep networks with rectified linear units and the quadratic loss. Our results expose surprising differences between the behavior of dropout and more traditional regularizers like weight decay. For example, on some simple data sets dropout training produces negative weights even though the output is the sum of the inputs. This provides a counterpoint to the suggestion that dropout discourages co-adaptation of weights. We also show that the dropout penalty can grow exponentially in the depth of the network while the weight-decay penalty remains essentially linear, and that dropout is insensitive to various re-scalings of the input features, outputs, and network weights. This last insensitivity implies that there are no isolated local minima of the dropout training criterion. Our work uncovers new properties of dropout, extends our understanding of why dropout succeeds, and lays the foundation for further progress.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1KSFax2
via IFTTT
Reinforcement Learning of POMDPs using Spectral Methods. (arXiv:1602.07764v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
We propose a new reinforcement learning algorithm for partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDP) based on spectral decomposition methods. While spectral methods have been previously employed for consistent learning of (passive) latent variable models such as hidden Markov models, POMDPs are more challenging since the learner interacts with the environment and possibly changes the future observations in the process. We devise a learning algorithm running through episodes, in each episode we employ spectral techniques to learn the POMDP parameters from a trajectory generated by a fixed policy. At the end of the episode, an optimization oracle returns the optimal memoryless planning policy which maximizes the expected reward based on the estimated POMDP model. We prove an order-optimal regret bound with respect to the optimal memoryless policy and efficient scaling with respect to the dimensionality of observation and action spaces.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1THDTM1
via IFTTT