Latest YouTube Video
Saturday, May 21, 2016
Allow anonymous user to access pipelines
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1TzJmDX
via IFTTT
Anonymous Texter Has Hilarious Conversation as Ross Geller From
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1WJnRn4
via IFTTT
Top Websites Using Audio Fingerprinting to Secretly Track Web Users
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1Tyma99
via IFTTT
Bug Hunter Found Ways to Hack Any Instagram Accounts
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/241jDWz
via IFTTT
Ecuador Bank Hacked — $12 Million Stolen in 3rd Attack on SWIFT System
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1XGL8VG
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
COURSEKEN
Discover the best courses on web.
https://t.co/y6bUu2X1d5
Following: 69556 - Followers: 86872
May 21, 2016 at 03:03AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/courseken
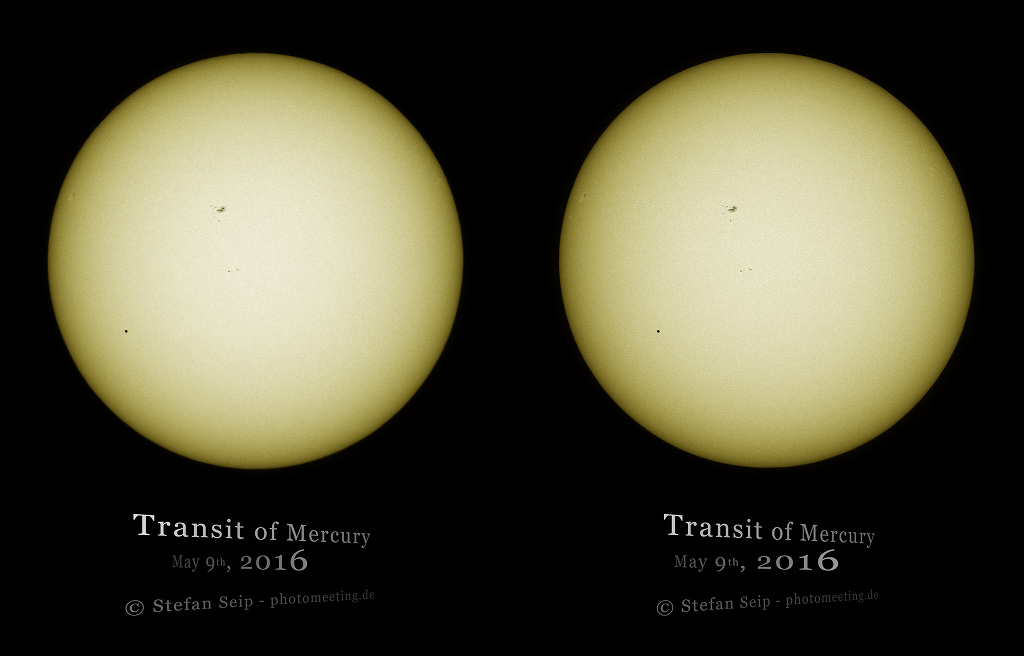
3D Mercury Transit
2016 Mars Opposition
from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio: Most Recent Items http://ift.tt/1Tt3576
via IFTTT
Friday, May 20, 2016
'Anonymous' protesters, newspaper reporter arrested
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1TpONSx
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Daily Fantasy Promos
Best place for Daily Fantasy Football and Basketball - FanDuel ! Use promo code STACKS for 100% deposit match up to $200. To join, click below
https://t.co/mS0qhsLPxH
Following: 7135 - Followers: 15603
May 20, 2016 at 06:22PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/DFFPromos
Orioles: Recent history says Baltimore won't fade anytime soon, writes Eddie Matz; \"maybe these Birds are built to last\" (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Can evaluation forms be anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/256texH
via IFTTT
How do you engage anonymous leads?
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1XFcaN8
via IFTTT
De La Soul Share
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1TsaJ1J
via IFTTT
Vectorization of anonymous functions
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1U5dH9v
via IFTTT
Anonymous Fl. new threat against State Attorney Aronberg
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1TuFWT6
via IFTTT
http://ift.tt/1qyGlIranonymous/xynhypskcc-5gog3_5ad6scrooge0-3da72terminator-7480 ...
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1VdXHHs
via IFTTT
Facebook Sued for illegally Scanning Users' Private Messages
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/27HlHaO
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 05/19/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/1W62uMe
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Plasma Air Int'l
Plasma Air manufactures air purification products using bipolar ionization technology utilizing ASHRAE's Standard 62.1 IAQ Procedure reducing outside air intake
Stamford, CT
http://t.co/MhiAj1Xwbj
Following: 2129 - Followers: 2454
May 20, 2016 at 03:42AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/PlasmaAir
The Surface of Europa
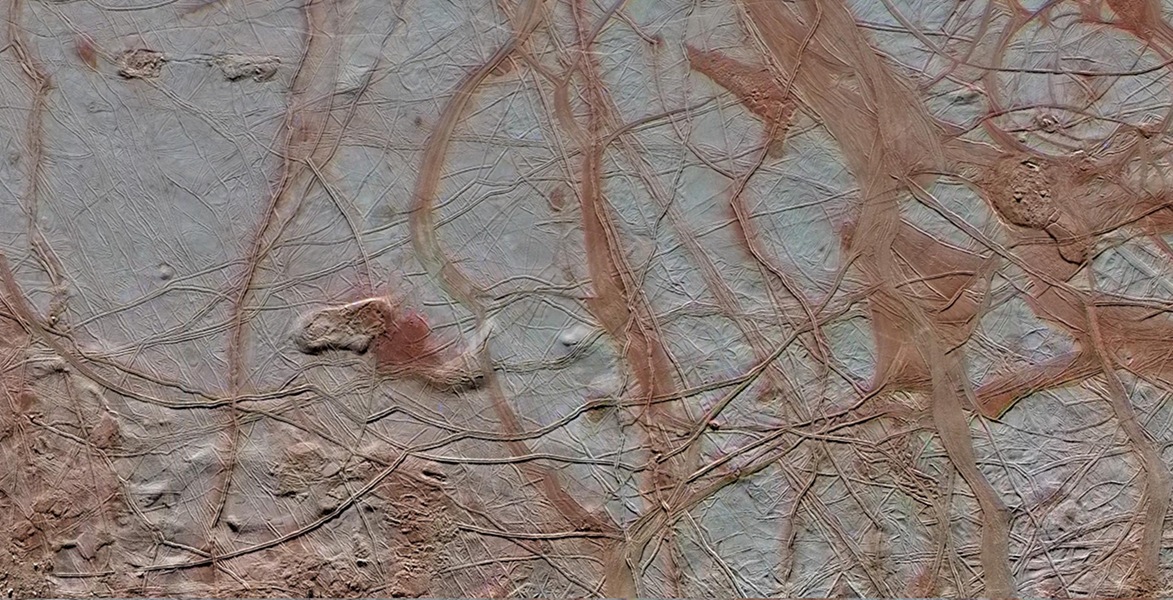

I have a new follower on Twitter
CSG, Inc
Facility Services custom designed to meet your high standards and do It consistently. Nationwide Cleaning and Building Maintenance. Dennis O'Brien, CEO
Danvers, MA
https://t.co/8sPKtP8Zjq
Following: 1178 - Followers: 1236
May 20, 2016 at 12:22AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/csginc11
Thursday, May 19, 2016
Heuristics for Planning, Plan Recognition and Parsing. (arXiv:1605.05807v1 [cs.AI])
In a recent paper, we have shown that Plan Recognition over STRIPS can be formulated and solved using Classical Planning heuristics and algorithms. In this work, we show that this formulation subsumes the standard formulation of Plan Recognition over libraries through a compilation of libraries into STRIPS theories. The libraries correspond to AND/OR graphs that may be cyclic and where children of AND nodes may be partially ordered. These libraries include Context-Free Grammars as a special case, where the Plan Recognition problem becomes a parsing with missing tokens problem. Plan Recognition over the standard libraries become
Planning problems that can be easily solved by any modern planner, while recognition over more complex libraries, including Context--Free Grammars (CFGs), illustrate limitations of current Planning heuristics and suggest improvements that may be relevant in other Planning problems too.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1rXJBOP
via IFTTT
Interactive Debugging of Knowledge Bases. (arXiv:1605.05950v1 [cs.AI])
Many AI applications rely on knowledge about a relevant real-world domain that is encoded by means of some logical knowledge base (KB). The most essential benefit of logical KBs is the opportunity to perform automatic reasoning to derive implicit knowledge or to answer complex queries about the modeled domain. The feasibility of meaningful reasoning requires KBs to meet some minimal quality criteria such as logical consistency. Without adequate tool assistance, the task of resolving violated quality criteria in KBs can be extremely tough even for domain experts, especially when the problematic KB includes a large number of logical formulas or comprises complicated logical formalisms.
Published non-interactive debugging systems often cannot localize all possible faults (incompleteness), suggest the deletion or modification of unnecessarily large parts of the KB (non-minimality), return incorrect solutions which lead to a repaired KB not satisfying the imposed quality requirements (unsoundness) or suffer from poor scalability due to the inherent complexity of the KB debugging problem. Even if a system is complete and sound and considers only minimal solutions, there are generally exponentially many solution candidates to select one from. However, any two repaired KBs obtained from these candidates differ in their semantics in terms of entailments and non-entailments. Selection of just any of these repaired KBs might result in unexpected entailments, the loss of desired entailments or unwanted changes to the KB.
This work proposes complete, sound and optimal methods for the interactive debugging of KBs that suggest the one (minimally invasive) error correction of the faulty KB that yields a repaired KB with exactly the intended semantics. Users, e.g. domain experts, are involved in the debugging process by answering automatically generated queries about the intended domain.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1YGYOyj
via IFTTT
Dynamic Bayesian Networks to simulate occupant behaviours in office buildings related to indoor air quality. (arXiv:1605.05966v1 [cs.AI])
This paper proposes a new general approach based on Bayesian networks to model the human behaviour. This approach represents human behaviour with probabilistic cause-effect relations based on knowledge, but also with conditional probabilities coming either from knowledge or deduced from observations. This approach has been applied to the co-simulation of the CO2 concentration in an office coupled with human behaviour.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1NB4h9a
via IFTTT
AMSOM: Adaptive Moving Self-organizing Map for Clustering and Visualization. (arXiv:1605.06047v1 [cs.AI])
Self-Organizing Map (SOM) is a neural network model which is used to obtain a topology-preserving mapping from the (usually high dimensional) input/feature space to an output/map space of fewer dimensions (usually two or three in order to facilitate visualization). Neurons in the output space are connected with each other but this structure remains fixed throughout training and learning is achieved through the updating of neuron reference vectors in feature space. Despite the fact that growing variants of SOM overcome the fixed structure limitation they increase computational cost and also do not allow the removal of a neuron after its introduction. In this paper, a variant of SOM is proposed called AMSOM (Adaptive Moving Self-Organizing Map) that on the one hand creates a more flexible structure where neuron positions are dynamically altered during training and on the other hand tackles the drawback of having a predefined grid by allowing neuron addition and/or removal during training. Experiments using multiple literature datasets show that the proposed method improves training performance of SOM, leads to a better visualization of the input dataset and provides a framework for determining the optimal number and structure of neurons.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1YGYG1F
via IFTTT
Philosophy in the Face of Artificial Intelligence. (arXiv:1605.06048v1 [cs.AI])
In this article, I discuss how the AI community views concerns about the emergence of superintelligent AI and related philosophical issues.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1NB3VPX
via IFTTT
A Hierarchical Latent Variable Encoder-Decoder Model for Generating Dialogues. (arXiv:1605.06069v1 [cs.CL])
Sequential data often possesses a hierarchical structure with complex dependencies between subsequences, such as found between the utterances in a dialogue. In an effort to model this kind of generative process, we propose a neural network-based generative architecture, with latent stochastic variables that span a variable number of time steps. We apply the proposed model to the task of dialogue response generation and compare it with recent neural network architectures. We evaluate the model performance through automatic evaluation metrics and by carrying out a human evaluation. The experiments demonstrate that our model improves upon recently proposed models and that the latent variables facilitate the generation of long outputs and maintain the context.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1YGYFuH
via IFTTT
How Many Workers to Ask? Adaptive Exploration for Collecting High Quality Labels. (arXiv:1411.0149v3 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
Crowdsourcing has been part of the IR toolbox as a cheap and fast mechanism to obtain labels for system development and evaluation. Successful deployment of crowdsourcing at scale involves adjusting many variables, a very important one being the number of workers needed per human intelligence task (HIT). We consider the crowdsourcing task of learning the answer to simple multiple-choice HITs, which are representative of many relevance experiments. In order to provide statistically significant results, one often needs to ask multiple workers to answer the same HIT. A stopping rule is an algorithm that, given a HIT, decides for any given set of worker answers if the system should stop and output an answer or iterate and ask one more worker. Knowing the historic performance of a worker in the form of a quality score can be beneficial in such a scenario. In this paper we investigate how to devise better stopping rules given such quality scores. We also suggest adaptive exploration as a promising approach for scalable and automatic creation of ground truth. We conduct a data analysis on an industrial crowdsourcing platform, and use the observations from this analysis to design new stopping rules that use the workers' quality scores in a non-trivial manner. We then perform a simulation based on a real-world workload, showing that our algorithm performs better than the more naive approaches.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1uoj1hz
via IFTTT
COCO: The Experimental Procedure. (arXiv:1603.08776v2 [cs.AI] CROSS LISTED)
We present a budget-free experimental setup and procedure for benchmarking numericaloptimization algorithms in a black-box scenario. This procedure can be applied with the COCO benchmarking platform. We describe initialization of and input to the algorithm and touch upon therelevance of termination and restarts.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1RJcKma
via IFTTT
Orioles: P Zach Britton says he hates the stigma that closers should only work one inning - Eddie Matz (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Hacker Steals Money from Bank and Donates $11,000 to Anti-ISIS Group
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1sCJr0b
via IFTTT
How to Decrypt TeslaCrypt Ransomware Files Using Master Key
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/20bPrXZ
via IFTTT
Ravens withdraw proposal to overhaul and completely open up NFL's replay review system - multiple reports (ESPN)
via IFTTT
dotnet/roslyn
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1W4EAAC
via IFTTT
Orioles: 3B Manny Machado earns Jayson Stark's first-quarter AL MVP; .321 BA and on pace for 47 HR, 64 2B, 213 H, 128 R (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Dave & Chuck the Freak Peep Show: Lisa's Anonymous Tip
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1TmpAsc
via IFTTT
The Information-Collecting Vehicle Routing Problem: Stochastic Optimization for Emergency Storm Response. (arXiv:1605.05711v1 [cs.SY])
Utilities face the challenge of responding to power outages due to storms and ice damage, but most power grids are not equipped with sensors to pinpoint the precise location of the faults causing the outage. Instead, utilities have to depend primarily on phone calls (trouble calls) from customers who have lost power to guide the dispatching of utility trucks. In this paper, we develop a policy that routes a utility truck to restore outages in the power grid as quickly as possible, using phone calls to create beliefs about outages, but also using utility trucks as a mechanism for collecting additional information. This means that routing decisions change not only the physical state of the truck (as it moves from one location to another) and the grid (as the truck performs repairs), but also our belief about the network, creating the first stochastic vehicle routing problem that explicitly models information collection and belief modeling. We address the problem of managing a single utility truck, which we start by formulating as a sequential stochastic optimization model which captures our belief about the state of the grid. We propose a stochastic lookahead policy, and use Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) to produce a practical policy that is asymptotically optimal. Simulation results show that the developed policy restores the power grid much faster compared to standard industry heuristics.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1W4u5gN
via IFTTT
Sherman goes Anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1TrmMNU
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Protectimus
https://t.co/UHu4fuvMsC
Following: 3000 - Followers: 2560
May 19, 2016 at 09:30AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/Protectimus
I have a new follower on Twitter
Anna Korobkina
www.protectimus.com
Following: 3116 - Followers: 987
May 19, 2016 at 09:15AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/anna_korobkina
The preview should not cache also if the user is anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/20akwuR
via IFTTT
Hey Allo! Meet Google's AI-powered Smart Messaging App
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/27Dd4Ot
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 05/18/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/27CY6bt
via IFTTT
Android Instant Apps — Run Apps Quickly Without Installation
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1qvPqSe
via IFTTT
1-RAAP: An Efficient 1-Round Anonymous Authentication Protocol for Wireless Body Area Networks
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1OB1cRz
via IFTTT
Halo from Atacama
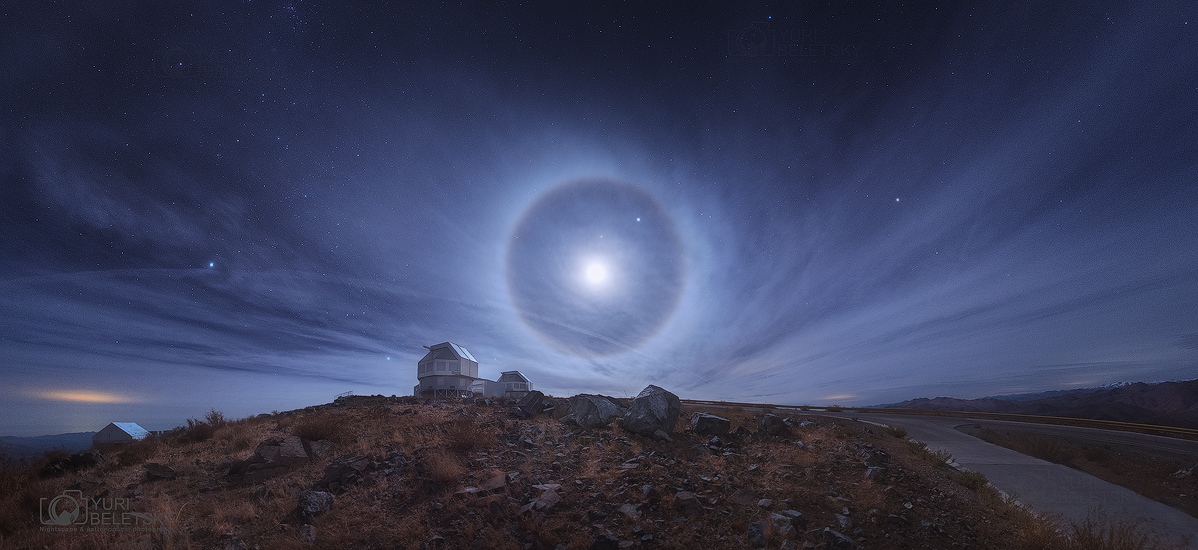

Wednesday, May 18, 2016
I have a new follower on Twitter
Tracey Vincel
Tracey Vincel PT MPhty is co-founder @kimawellness KIMA Center for Physiotherapy and Wellness : http://t.co/P31SLT4TD1
New York NY
http://t.co/YtTaPY0Vlh
Following: 8234 - Followers: 9158
May 18, 2016 at 11:59PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/traceyvincel
Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning using Spatio-Temporal Abstractions and Deep Neural Networks. (arXiv:1605.05359v1 [cs.LG])
This paper introduces an automated skill acquisition framework in reinforcement learning which involves identifying a hierarchical description of the given task in terms of abstract states and extended actions between abstract states. Identifying such structures present in the task provides ways to simplify and speed up reinforcement learning learning algorithms. These structures also help to generalize such algorithms over multiple tasks without relearning policies from scratch. We use ideas from dynamical systems to find metastable regions in the state space and associate them with abstract states. The spectral clustering algorithm PCCA+ is used to identify suitable abstractions aligned to the underlying structure. Skills are defined in terms of the transitions between such abstract states. The connectivity information from PCCA+ is used to generate these skills or options. The skills are independent of the learning task and can be efficiently reused across a variety of tasks defined over a common state space. Another major advantage of the approach is that it does not need a prior model of the MDP and can work well even when the MDPs are constructed from sampled trajectories. Finally, we present our attempts to extend the automated skills acquisition framework to complex tasks such as learning to play video games where we use deep learning techniques for representation learning to aid our spatio-temporal abstraction framework.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1U0cfoJ
via IFTTT
Dynamic Frame skip Deep Q Network. (arXiv:1605.05365v1 [cs.LG])
Deep Reinforcement Learning methods have achieved state of the art performance in learning control policies for the games in the Atari 2600 domain. One of the important parameters in the Arcade Learning Environment (ALE) is the frame skip rate. It decides the granularity at which agents can control game play. A frame skip value of $k$ allows the agent to repeat a selected action $k$ number of times. The current state of the art architectures like Deep Q-Network (DQN) and Dueling Network Architectures (DuDQN) consist of a framework with a static frame skip rate, where the action output from the network is repeated for a fixed number of frames regardless of the current state. In this paper, we propose a new architecture, Dynamic Frame skip Deep Q-Network (DFDQN) which makes the frame skip rate a dynamic learnable parameter. This allows us to choose the number of times an action is to be repeated based on the current state. We show empirically that such a setting improves the performance on relatively harder games like Seaquest.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1OLkmJW
via IFTTT
Relations such as Hypernymy: Identifying and Exploiting Hearst Patterns in Distributional Vectors for Lexical Entailment. (arXiv:1605.05433v1 [cs.CL])
We consider the task of predicting lexical entailment using distributional vectors. We focus experiments on one previous classifier which was shown to only learn to detect prototypicality of a word pair. Analysis shows that the model single-mindedly learns to detect Hearst Patterns, which are well known to be predictive of lexical relations. We present a new model which exploits this Hearst Detector functionality, matching or outperforming prior work on multiple data sets.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1U0ca4A
via IFTTT
The Bees Algorithm for the Vehicle Routing Problem. (arXiv:1605.05448v1 [cs.NE])
In this thesis we present a new algorithm for the Vehicle Routing Problem called the Enhanced Bees Algorithm. It is adapted from a fairly recent algorithm, the Bees Algorithm, which was developed for continuous optimisation problems. We show that the results obtained by the Enhanced Bees Algorithm are competitive with the best meta-heuristics available for the Vehicle Routing Problem (within 0.5% of the optimal solution for common benchmark problems). We show that the algorithm has good runtime performance, producing results within 2% of the optimal solution within 60 seconds, making it suitable for use within real world dispatch scenarios.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1OLkfhl
via IFTTT
Towards information based spatiotemporal patterns as a foundation for agent representation in dynamical systems. (arXiv:1605.05676v1 [cs.AI])
We present some arguments why existing methods for representing agents fall short in applications crucial to artificial life. Using a thought experiment involving a fictitious dynamical systems model of the biosphere we argue that the metabolism, motility, and the concept of counterfactual variation should be compatible with any agent representation in dynamical systems. We then propose an information-theoretic notion of \emph{integrated spatiotemporal patterns} which we believe can serve as the basic building block of an agent definition. We argue that these patterns are capable of solving the problems mentioned before. We also test this in some preliminary experiments.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1R9C8Ro
via IFTTT
Fair task allocation in transportation. (arXiv:1505.07434v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
Task allocation problems have traditionally focused on cost optimization. However, more and more attention is being given to cases in which cost should not always be the sole or major consideration. In this paper we study a fair task allocation problem in transportation where an optimal allocation not only has low cost but more importantly, it distributes tasks as even as possible among heterogeneous participants who have different capacities and costs to execute tasks. To tackle this fair minimum cost allocation problem we analyze and solve it in two parts using two novel polynomial-time algorithms. We show that despite the new fairness criterion, the proposed algorithms can solve the fair minimum cost allocation problem optimally in polynomial time. In addition, we conduct an extensive set of experiments to investigate the trade-off between cost minimization and fairness. Our experimental results demonstrate the benefit of factoring fairness into task allocation. Among the majority of test instances, fairness comes with a very small price in terms of cost.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1exr6u1
via IFTTT
Ravens: NFL believes Baltimore was aware of non-contact rules for rookie camp, but still moved forward - Adam Schefter (ESPN)
via IFTTT
This App Lets You Find Anyone's Social Profile Just By Taking Their Photo
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/250jZzg
via IFTTT
Ravens propose to make replay \"fundamental part of officiating\" not just limited to certain situations - Kevin Seifert (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Hacker puts up 167 Million LinkedIn Passwords for Sale
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1TnWI6c
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 05/17/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/1srkcND
via IFTTT
Core Tor Developer who accuses FBI of Harassment moves to Germany
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1TjBdA4
via IFTTT
Navigator component showing Siteareas not accessible to Anonymous users
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/204P41g
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
The Digital Dragons
Digital & Internet #Marketing agency in #Wales , plus the very best social media tips and advice. Don't just tweet, ROAR!!! ✉ info@the-digital-dragons.co.uk
Caerphilly, Wales
http://t.co/JxcR6exNK6
Following: 17324 - Followers: 22796
May 18, 2016 at 02:45AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/_DigitalDragons
I have a new follower on Twitter
StreetLight Data
StreetLight Data transforms messy, disparate data about how people use their city into actionable analytics for planning, real estate and more.
San Francisco, CA
http://t.co/zuU8ZbgJim
Following: 3170 - Followers: 3882
May 18, 2016 at 02:16AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/StreetLightData
I have a new follower on Twitter
Eadith
Bored?
UK
Following: 101 - Followers: 11
May 18, 2016 at 01:15AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/i917pivl25
The Orion Nebula in Visible and Infrared

Tuesday, May 17, 2016
Self-Reflective Risk-Aware Artificial Cognitive Modeling for Robot Response to Human Behaviors. (arXiv:1605.04934v1 [cs.RO])
In order for cooperative robots ("co-robots") to respond to human behaviors accurately and efficiently in human-robot collaboration, interpretation of human actions, awareness of new situations, and appropriate decision making are all crucial abilities for co-robots. For this purpose, the human behaviors should be interpreted by co-robots in the same manner as human peers. To address this issue, a novel interpretability indicator is introduced so that robot actions are appropriate to the current human behaviors. In addition, the complete consideration of all potential situations of a robot's environment is nearly impossible in real-world applications, making it difficult for the co-robot to act appropriately and safely in new scenarios. This is true even when the pretrained model is highly accurate in a known situation. For effective and safe teaming with humans, we introduce a new generalizability indicator that allows a co-robot to self-reflect and reason about when an observation falls outside the co-robot's learned model. Based on topic modeling and two novel indicators, we propose a new Self-reflective Risk-aware Artificial Cognitive (SRAC) model. The co-robots are able to consider action risks and identify new situations so that better decisions can be made. Experiments both using real-world datasets and on physical robots suggest that our SRAC model significantly outperforms the traditional methodology and enables better decision making in response to human activities.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/27xmlYm
via IFTTT
Digital Stylometry: Linking Profiles Across Social Networks. (arXiv:1605.05166v1 [cs.SI])
There is an ever growing number of users with accounts on multiple social media and networking sites. Consequently, there is increasing interest in matching user accounts and profiles across different social networks in order to create aggregate profiles of users. In this paper, we present models for Digital Stylometry, which is a method for matching users through stylometry inspired techniques. We experimented with linguistic, temporal, and combined temporal-linguistic models for matching user accounts, using standard and novel techniques. Using publicly available data, our best model, a combined temporal-linguistic one, was able to correctly match the accounts of 31% of 5,612 distinct users across Twitter and Facebook.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/27xlWVR
via IFTTT
Enhanced Twitter Sentiment Classification Using Contextual Information. (arXiv:1605.05195v1 [cs.SI])
The rise in popularity and ubiquity of Twitter has made sentiment analysis of tweets an important and well-covered area of research. However, the 140 character limit imposed on tweets makes it hard to use standard linguistic methods for sentiment classification. On the other hand, what tweets lack in structure they make up with sheer volume and rich metadata. This metadata includes geolocation, temporal and author information. We hypothesize that sentiment is dependent on all these contextual factors. Different locations, times and authors have different emotional valences. In this paper, we explored this hypothesis by utilizing distant supervision to collect millions of labelled tweets from different locations, times and authors. We used this data to analyse the variation of tweet sentiments across different authors, times and locations. Once we explored and understood the relationship between these variables and sentiment, we used a Bayesian approach to combine these variables with more standard linguistic features such as n-grams to create a Twitter sentiment classifier. This combined classifier outperforms the purely linguistic classifier, showing that integrating the rich contextual information available on Twitter into sentiment classification is a promising direction of research.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/27xlK96
via IFTTT
Heart Rate Variability and Respiration Signal as Diagnostic Tools for Late Onset Sepsis in Neonatal Intensive Care Units. (arXiv:1605.05247v1 [q-bio.QM])
Apnea-bradycardia is one of the major clinical early indicators of late-onset sepsis occurring in approximately 7% to 10% of all neonates and in more than 25% of very low birth weight infants in NICU. The objective of this paper was to determine if HRV, respiration and their relationships help to diagnose infection in premature infants via non-invasive ways in NICU. Therefore, we implement Mono-Channel (MC) and Bi-Channel (BC) Analysis in two groups: sepsis (S) vs. non-sepsis (NS). Firstly, we studied RR series not only by linear methods: time domain and frequency domain, but also by non-linear methods: chaos theory and information theory. The results show that alpha Slow, alpha Fast and Sample Entropy are significant parameters to distinguish S from NS. Secondly, the question about the functional coupling of HRV and nasal respiration is addressed. Local linear correlation coefficient r2t,f has been explored, while non-linear regression coefficient h2 was calculated in two directions. It is obvious that r2t,f within the third frequency band (0.2<f<0.4 Hz) and h2 in two directions were complementary approaches to diagnose sepsis. Thirdly, feasibility study is carried out on the candidate parameters selected from MC and BC respectively. We discovered that the proposed test based on optimal fusion of 6 features shows good performance with the largest AUC and a reduced probability of false alarm (PFA).
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1TYe3l3
via IFTTT
Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Graphs. (arXiv:1605.05273v1 [cs.LG])
Numerous important problems can be framed as learning from graph data. We propose a framework for learning convolutional neural networks for arbitrary graphs. These graphs may be undirected, directed, and with both discrete and continuous node and edge attributes. Analogous to image-based convolutional networks that operate on locally connected regions of the input, we present a general approach to extracting locallyconnected regions from graphs. Using established benchmark data sets, we demonstrate that the learned feature representations are competitive with state of the art graph kernels and that their computation is highly efficient.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1TmtgxF
via IFTTT
Fuzzy Sets Across the Natural Language Generation Pipeline. (arXiv:1605.05303v1 [cs.AI])
We explore the implications of using fuzzy techniques (mainly those commonly used in the linguistic description/summarization of data discipline) from a natural language generation perspective. For this, we provide an extensive discussion of some general convergence points and an exploration of the relationship between the different tasks involved in the standard NLG system pipeline architecture and the most common fuzzy approaches used in linguistic summarization/description of data, such as fuzzy quantified statements, evaluation criteria or aggregation operators. Each individual discussion is illustrated with a related use case. Recent work made in the context of cross-fertilization of both research fields is also referenced. This paper encompasses general ideas that emerged as part of the PhD thesis "Application of fuzzy sets in data-to-text systems". It does not present a specific application or a formal approach, but rather discusses current high-level issues and potential usages of fuzzy sets (focused on linguistic summarization of data) in natural language generation.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1TiMel5
via IFTTT
Combat Models for RTS Games. (arXiv:1605.05305v1 [cs.AI])
Game tree search algorithms, such as Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), require access to a forward model (or "simulator") of the game at hand. However, in some games such forward model is not readily available. This paper presents three forward models for two-player attrition games, which we call "combat models", and show how they can be used to simulate combat in RTS games. We also show how these combat models can be learned from replay data. We use StarCraft as our application domain. We report experiments comparing our combat models predicting a combat output and their impact when used for tactical decisions during a real game.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/27xmafT
via IFTTT
Geometry of Interest (GOI): Spatio-Temporal Destination Extraction and Partitioning in GPS Trajectory Data. (arXiv:1603.04110v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
Nowadays large amounts of GPS trajectory data is being continuously collected by GPS-enabled devices such as vehicles navigation systems and mobile phones. GPS trajectory data is useful for applications such as traffic management, location forecasting, and itinerary planning. Such applications often need to extract the time-stamped Sequence of Visited Locations (SVLs) of the mobile objects. The nearest neighbor query (NNQ) is the most applied method for labeling the visited locations based on the IDs of the POIs in the process of SVL generation. NNQ in some scenarios is not accurate enough. To improve the quality of the extracted SVLs, instead of using NNQ, we label the visited locations as the IDs of the POIs which geometrically intersect with the GPS observations. Intersection operator requires the accurate geometry of the points of interest which we refer to them as the Geometries of Interest (GOIs). In some application domains (e.g. movement trajectories of animals), adequate information about the POIs and their GOIs may not be available a priori, or they may not be publicly accessible and, therefore, they need to be derived from GPS trajectory data. In this paper we propose a novel method for estimating the POIs and their GOIs, which consists of three phases: (i) extracting the geometries of the stay regions; (ii) constructing the geometry of destination regions based on the extracted stay regions; and (iii) constructing the GOIs based on the geometries of the destination regions. Using the geometric similarity to known GOIs as the major evaluation criterion, the experiments we performed using long-term GPS trajectory data show that our method outperforms the existing approaches.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1pklvw0
via IFTTT
Moving Beyond the Turing Test with the Allen AI Science Challenge. (arXiv:1604.04315v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
Given recent successes in AI (e.g., AlphaGo's victory against Lee Sedol in the game of GO), it's become increasingly important to assess: how close are AI systems to human-level intelligence? This paper describes the Allen AI Science Challenge---an approach towards that goal which led to a unique Kaggle Competition, its results, the lessons learned, and our next steps.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1r7Yz4K
via IFTTT
1 Million Computers Hacked for making big Money from Adsense
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/27wuH2r
via IFTTT
RSS feed says authored by Anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1YzBkLn
via IFTTT
Hacker finds flaws that could let anyone steal $25 Billion from a Bank
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/27wdiHl
via IFTTT
Ukrainian Hacker Admits Stealing Corporate Press Releases for $30 Million Profit
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/1smKWPf
via IFTTT
[FD] [ICS] Meteocontrol WEB’log Multiple Vulnerabilities
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] OWTF 2.0a "Tikka Masala" released!
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
CVC Guidelines On Anonymous/Ps...
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1XiRjii
via IFTTT
Re: [FD] Code Execution Vulnerabilities In 7zip
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] Code Execution Vulnerabilities In 7zip
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Re: [FD] Skype Phishing Attack
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Re: [FD] runAV mod_security Remote Command Execution
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] APPLE-SA-2016-05-16-6 iTunes 12.4
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] APPLE-SA-2016-05-16-5 Safari 9.1.1
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] APPLE-SA-2016-05-16-4 OS X El Capitan 10.11.5 and Security Update 2016-003
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] APPLE-SA-2016-05-16-3 watchOS 2.2.1
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] APPLE-SA-2016-05-16-2 iOS 9.3.2
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] APPLE-SA-2016-05-16-1 tvOS 9.2.1
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] [ERPSCAN-16-009] SAP xMII - directory traversal vulnerability
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] [ERPSCAN-16-008] SAP NetWeaver AS JAVA - XSS vulnerability in ProxyServer servlet
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Marco Rubio criticizes anonymous sources, tweets workout plans
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/24X25x8
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 05/16/16
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/22eT4xP
via IFTTT
Why the Name Icarus? - The Latest Anonymous Operation
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1slZtdR
via IFTTT
Anonymous Beach Hotel
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/1rRbF6G
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Miles Austin
I help sales leaders and managers understand and acquire the rapidly evolving tech and tools that are creating new opportunities in sales.
North Bend, WA
http://t.co/l6GGQbDh9u
Following: 6948 - Followers: 30693
May 17, 2016 at 03:55AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/milesaustin
I have a new follower on Twitter
Cycle Computing
Leader in #CloudComputing orchestration software for #BigCompute & #BigData.
NYC, SF, BOS
http://t.co/lv5kX0pXta
Following: 452 - Followers: 1348
May 17, 2016 at 02:56AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/cyclecomputing
I have a new follower on Twitter
TIMEXTENDER
It’s all about Automation! You need the right data, at the right time, to make the right decisions. TX DWA provide the data you need at your fingertips!
http://t.co/1OZlLyNXYK
Following: 8542 - Followers: 15311
May 17, 2016 at 02:11AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/TimeXtender
Clouds of the Carina Nebula
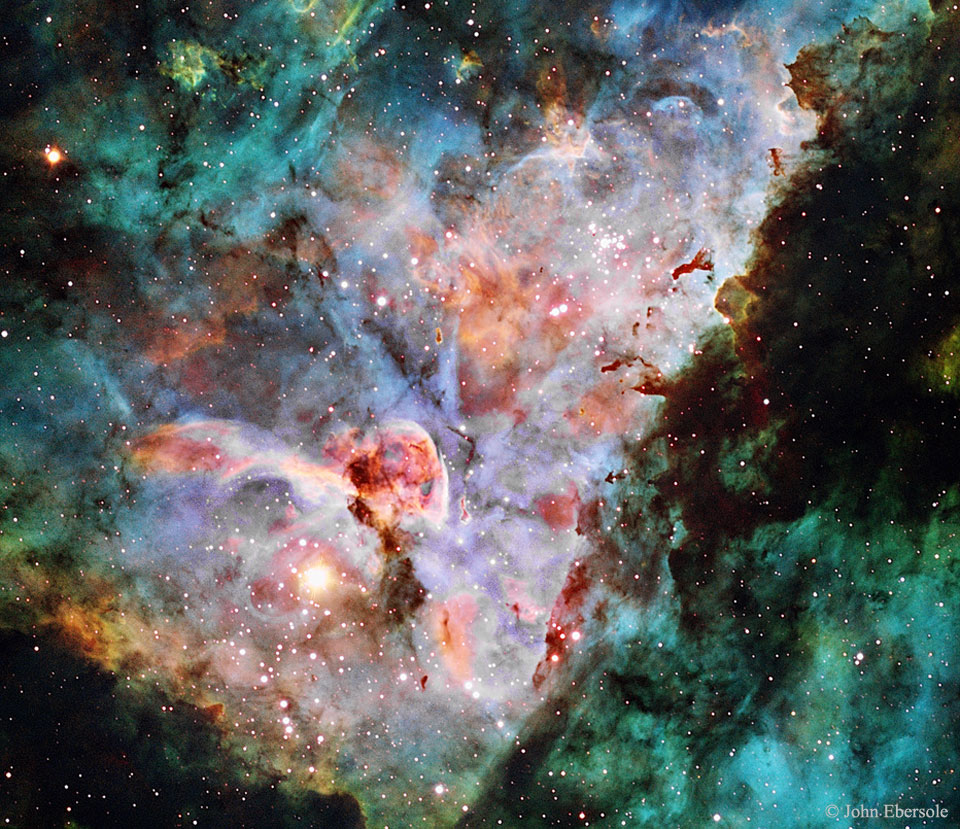

Monday, May 16, 2016
I have a new follower on Twitter
Sean O'Meara
High Performance Lifestyle Coach, tech geek, musician, dog lover, vegan, fitness maniac
SJ/SF Bay Area, CA
https://t.co/c4RNTlUQD6
Following: 12678 - Followers: 13189
May 16, 2016 at 11:50PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/_sean_omeara
Monotone Retargeting for Unsupervised Rank Aggregation with Object Features. (arXiv:1605.04465v1 [stat.ML])
Learning the true ordering between objects by aggregating a set of expert opinion rank order lists is an important and ubiquitous problem in many applications ranging from social choice theory to natural language processing and search aggregation. We study the problem of unsupervised rank aggregation where no ground truth ordering information in available, neither about the true preference ordering between any set of objects nor about the quality of individual rank lists. Aggregating the often inconsistent and poor quality rank lists in such an unsupervised manner is a highly challenging problem, and standard consensus-based methods are often ill-defined, and difficult to solve. In this manuscript we propose a novel framework to bypass these issues by using object attributes to augment the standard rank aggregation framework. We design algorithms that learn joint models on both rank lists and object features to obtain an aggregated rank ordering that is more accurate and robust, and also helps weed out rank lists of dubious validity. We validate our techniques on synthetic datasets where our algorithm is able to estimate the true rank ordering even when the rank lists are corrupted. Experiments on three real datasets, MQ2008, MQ2008 and OHSUMED, show that using object features can result in significant improvement in performance over existing rank aggregation methods that do not use object information. Furthermore, when at least some of the rank lists are of high quality, our methods are able to effectively exploit their high expertise to output an aggregated rank ordering of great accuracy.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1TTLimG
via IFTTT