Latest YouTube Video
Saturday, September 24, 2016
2 Valses
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2dfPvbR
via IFTTT
Crime Stoppers of Halton
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2ctlDmr
via IFTTT
Anonymous Woman by Patty Carroll
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2d86dVD
via IFTTT
Anonymous user 480107
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cBR1T3
via IFTTT
Alcoholics Anonymous plays important role in society
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cv6hCU
via IFTTT
How can I change front-end form for anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cQkKHY
via IFTTT
Anonymous ECC-Authentication and Intrusion Detection Based on Execution Tracing for Mobile ...
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2dhNOGR
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Grant Maloy Smith
Singer-songwriter of American Roots music. Voting member of the Grammys®, The CMA, AMA & BMI recording artist. New record coming 4/17!
Rhode Island, USA
http://t.co/pUFgNG8vcZ
Following: 44977 - Followers: 104440
September 24, 2016 at 06:27AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/GrantMaloySmith
First Columbus District Convention
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2dho9On
via IFTTT
Hacker Who Helped ISIS to Build 'Hit List' Of US Military Personnel Jailed for 20 Years
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2d7cYZR
via IFTTT
Google WiFi Router — Combine Multiple Routers to Boost WiFi Signal
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2d80qmK
via IFTTT
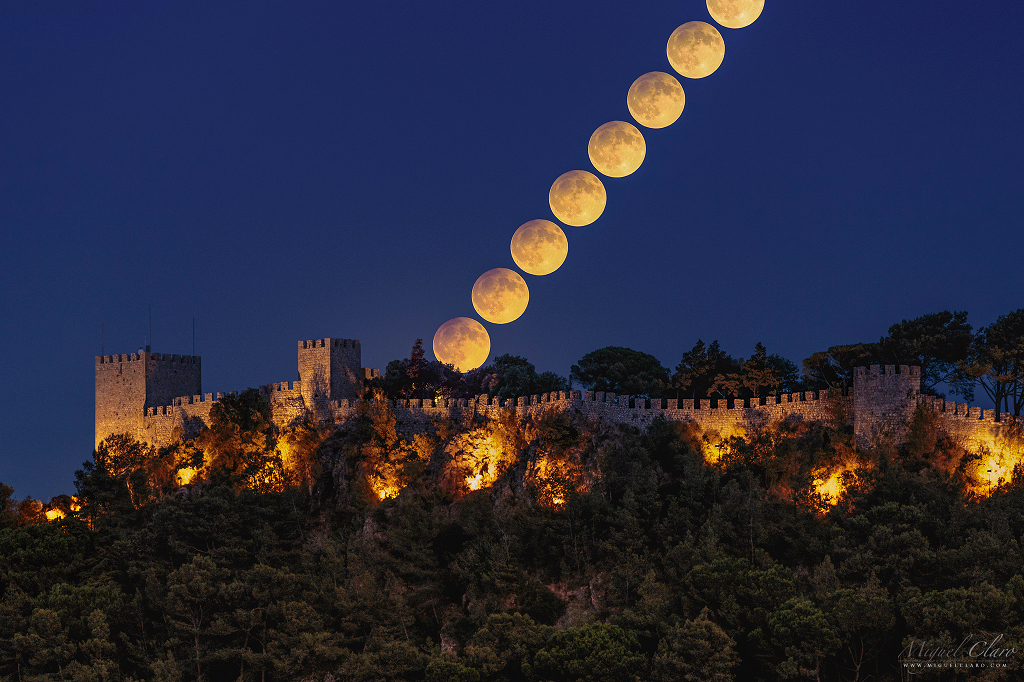
Harvest Moon Eclipse

can i publish a book as anonymous or
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cTO4QW
via IFTTT
Friday, September 23, 2016
Orioles trail Tigers for the final AL wild-card spot by 0.5 game after defeating Diamondbacks 3-2 in 12 innings (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Joseph M Erhardt
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2dqWzlb
via IFTTT
Apple Weakens iOS 10 Backup Encryption; Now Can Be Cracked 2,500 Times Faster
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2dpOj4Q
via IFTTT
anonymous 11
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2dfKZWA
via IFTTT
Anonymous 4 – 3 Decades of Anonymous 4: 1986 – 2016 (Bonus Track Version)
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cSjrLw
via IFTTT
Ravens Video: Justin Tucker raps about fried chicken, uses drumstick as mic in commercial for regional convenience store (ESPN)
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 09/22/2016
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/2d5suXP
via IFTTT
Critical DoS Flaw found in OpenSSL — How It Works
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2doVw5n
via IFTTT
[FD] DllHijackAuditor 3.5 - Stack Buffer Overflow Vulnerability
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Leaked NSA Hacking Tools Were 'Mistakenly' Left By An Agent On A Remote Server
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2d5rfGk
via IFTTT
Yahoo Confirms 500 Million Accounts Were Hacked by 'State Sponsored' Hackers
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2d4NUnX
via IFTTT
How Does Crimestoppers Keep You Anonymous?
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2d1J1s5
via IFTTT
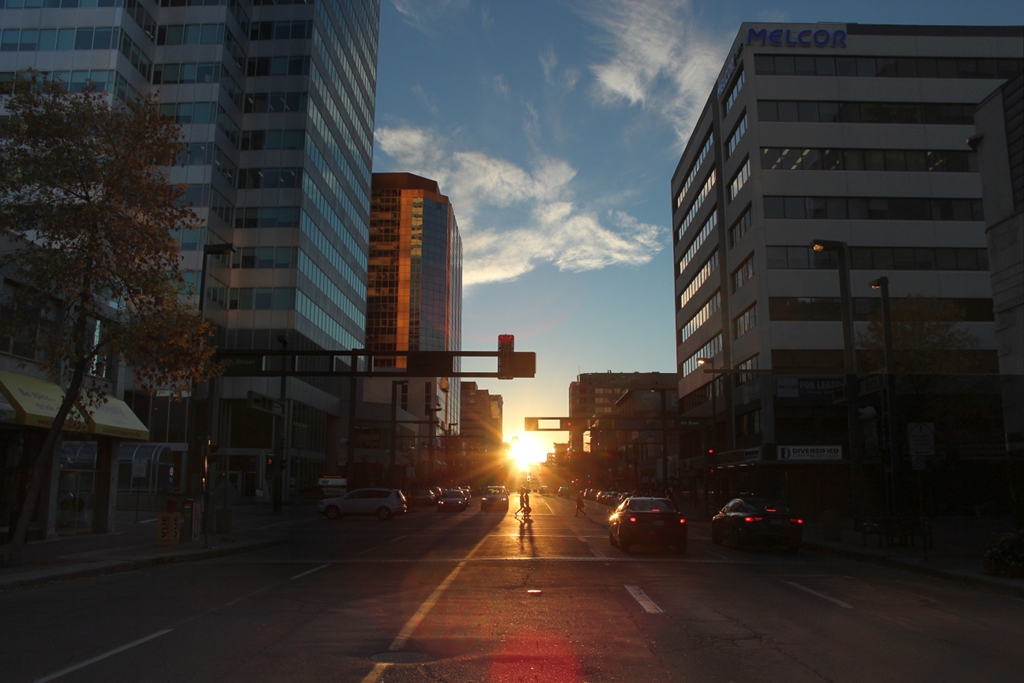
Sunset at Edmontonhenge

Thursday, September 22, 2016
Orioles fall one-half game behind Tigers for 2nd wild card; swept in 4-game series by Red Sox after 5-3 loss (ESPN)
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Max Stewart
Director of Software Engineering at @cybLdn. #startup #leanstartup #programming #nodejs #java #reactjs #angularjs
London
https://t.co/oTQSZ0mWry
Following: 18222 - Followers: 20300
September 22, 2016 at 10:44PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/superafroman
Deep-Learned Collision Avoidance Policy for Distributed Multi-Agent Navigation. (arXiv:1609.06838v1 [cs.AI])
High-speed, low-latency obstacle avoidance that is insensitive to sensor noise is essential for enabling multiple decentralized robots to function reliably in cluttered and dynamic environments. While other distributed multi-agent collision avoidance systems exist, these systems require online geometric optimization where tedious parameter tuning and perfect sensing are necessary.
We present a novel end-to-end framework to generate reactive collision avoidance policy for efficient distributed multi-agent navigation. Our method formulates an agent's navigation strategy as a deep neural network mapping from the observed noisy sensor measurements to the agent's steering commands in terms of movement velocity. We train the network on a large number of frames of collision avoidance data collected by repeatedly running a multi-agent simulator with different parameter settings. We validate the learned deep neural network policy in a set of simulated scenarios with noisy measurements and demonstrate that our method is able to generate a robust navigation strategy that is insensitive to imperfect sensing and works reliably in all situations. We also show that our method can be well generalized to scenarios that do not appear in our training data, including scenes with static obstacles and agents with different shapes. A video is available at https://youtu.be/uMcdMmcR67A.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cH20YZ
via IFTTT
The Digital Synaptic Neural Substrate: Size and Quality Matters. (arXiv:1609.06953v1 [cs.AI])
We investigate the 'Digital Synaptic Neural Substrate' (DSNS) computational creativity approach further with respect to the size and quality of images that can be used to seed the process. In previous work we demonstrated how combining photographs of people and sequences taken from chess games between weak players can be used to generate chess problems or puzzles of higher aesthetic quality, on average, compared to alternative approaches. In this work we show experimentally that using larger images as opposed to smaller ones improves the output quality even further. The same is also true for using clearer or less corrupted images. The reasons why these things influence the DSNS process is presently not well-understood and debatable but the findings are nevertheless immediately applicable for obtaining better results.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2crWwFG
via IFTTT
Semiring Programming: A Framework for Search, Inference and Learning. (arXiv:1609.06954v1 [cs.AI])
To solve hard problems, AI relies on a variety of disciplines such as logic, probabilistic reasoning, machine learning and mathematical programming. Although it is widely accepted that solving real-world problems requires an integration amongst these, contemporary representation methodologies offer little support for this.
In an attempt to alleviate this situation, we introduce a new declarative programming framework that provides abstractions of well-known problems such as SAT, Bayesian inference, generative models, and convex optimization. The semantics of programs is defined in terms of first-order structures with semiring labels, which allows us to freely combine and integrate problems from different AI disciplines.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2dnJcCm
via IFTTT
NdFluents: A Multi-dimensional Contexts Ontology. (arXiv:1609.07102v1 [cs.AI])
Annotating semantic data with metadata is becoming more and more important to provide information about the statements being asserted. While initial solutions proposed a data model to represent a specific dimension of meta-information (such as time or provenance), the need for a general annotation framework which allows representing different context dimensions is needed. In this paper, we extend the 4dFluents ontology by Welty and Fikes---on associating temporal validity to statements---to any dimension of context, and discuss possible issues that multidimensional context representations have to face and how we address them.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2d4Pqou
via IFTTT
Social Network Processes in the Isabelle and Coq Theorem Proving Communities. (arXiv:1609.07127v1 [cs.SI])
We identify the main actors in the Isabelle and Coq communities and describe how they affect and influence their peers. This work explores selected foundations of social networking analysis that we expect to be useful in the context of the ProofPeer project, which is developing a new model for interactive theorem proving based on collaboration and social interactions.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2dnJkll
via IFTTT
Focused Model-Learning and Planning for Non-Gaussian Continuous State-Action Systems. (arXiv:1607.07762v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
We introduce a framework for model learning and planning in stochastic domains with continuous state and action spaces and non-Gaussian transition models. It is efficient because (1) local models are estimated only when the planner requires them; (2) the planner focuses on the most relevant states to the current planning problem; and (3) the planner focuses on the most informative and/or high-value actions. Our theoretical analysis shows the validity and asymptotic optimality of the proposed approach. Empirically, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our algorithm on a simulated multi-modal pushing problem.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2atId3l
via IFTTT
Bi-directional Attention with Agreement for Dependency Parsing. (arXiv:1608.02076v2 [cs.CL] UPDATED)
We develop a novel bi-directional attention model for dependency parsing, which learns to agree on headword predictions from the forward and backward parsing directions. The parsing procedure for each direction is formulated as sequentially querying the memory component that stores continuous headword embeddings. The proposed parser makes use of {\it soft} headword embeddings, allowing the model to implicitly capture high-order parsing history without dramatically increasing the computational complexity. We conduct experiments on English, Chinese, and 12 other languages from the CoNLL 2006 shared task, showing that the proposed model achieves state-of-the-art unlabeled attachment scores on 6 languages.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2bfjJXL
via IFTTT
Empirically Grounded Agent-Based Models of Innovation Diffusion: A Critical Review. (arXiv:1608.08517v3 [cs.SI] UPDATED)
Innovation diffusion has been studied extensively in a variety of disciplines, including sociology, economics, marketing, ecology, and computer science. Traditional literature on innovation diffusion has been dominated by models of aggregate behavior and trends. However, the agent-based modeling (ABM) paradigm is gaining popularity as it captures agent heterogeneity and enables fine-grained modeling of interactions mediated by social and geographic networks. While most ABM work on innovation diffusion is theoretical, empirically grounded models are increasingly important, particularly in guiding policy decisions. We present a critical review of empirically grounded agent-based models of innovation diffusion, developing a categorization of this research based on types of agent models as well as applications. By connecting the modeling methodologies in the fields of information and innovation diffusion, we suggest that the maximum likelihood estimation framework widely used in the former is a promising paradigm for calibration of agent-based models for innovation diffusion. Although many advances have been made to standardize ABM methodology, we identify four major issues in model calibration and validation, and suggest potential solutions. Finally, we discuss open problems that are critical for the future development of empirically grounded agent-based models of innovation diffusion that enable reliable decision support for stakeholders.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cpEg0n
via IFTTT
Change Existing Registration from Anonymous to User
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2d1866e
via IFTTT
Ravens: LB Elvis Dumervil (foot) says he hopes to play Sunday vs. Jaguars; "it's heading in the right direction" (ESPN)
via IFTTT
iPhone 7 Jailbreak Has Already Been Achieved In Just 24 Hours!
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2cZISoR
via IFTTT
Ravens: LB Elvis Dumervil (foot) practiced for 2nd straight day Thu.; LT Ronnie Stanley (foot) back after missing 1 day (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Anonymous user b30463
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2dmjMoK
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 09/21/2016
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/2cUh07a
via IFTTT
Beware — Someone is dropping Malware-infected USB Sticks into People's Letterbox
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2coasf0
via IFTTT
Anonymous worker Free Vector
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cJfK7R
via IFTTT
Russian Media Watchdog May Ban Anonymous Wi-Fi Access
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cY8qD8
via IFTTT
[FD] SEC Consult SA-20160922-0 :: Potential backdoor access through multiple vulnerabilities in Kerio Control Unified Threat Management
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Anonymous function with summation of parameters
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cvrBqi
via IFTTT
Wednesday, September 21, 2016
Orioles remain 1 game behind Blue Jays for AL's top wild card following 5-1 loss to the Red Sox (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Recognizing Detailed Human Context In-the-Wild from Smartphones and Smartwatches. (arXiv:1609.06354v1 [cs.AI])
We demonstrate that a person's behavioral and environmental context can be automatically recognized by harnessing the sensors built into smartphones and smartwatches. We propose a generic system that can simultaneously recognize many contextual attributes from diverse behavioral domains. By fusing complementary information from different types of sensors our system successfully recognizes fine details of work and leisure activities, body movement, transportation, and more. Health monitoring, clinical intervention, aging care, personal assistance and many more applications will benefit from automatic, frequent and detailed context recognition.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2dc8jsU
via IFTTT
A Consumer BCI for Automated Music Evaluation Within a Popular On-Demand Music Streaming Service - Taking Listener's Brainwaves to Extremes. (arXiv:1609.06374v1 [cs.AI])
We investigated the possibility of using a machine-learning scheme in conjunction with commercial wearable EEG-devices for translating listener's subjective experience of music into scores that can be used for the automated annotation of music in popular on-demand streaming services. Based on the established -neuroscientifically sound- concepts of brainwave frequency bands, activation asymmetry index and cross-frequency-coupling (CFC), we introduce a Brain Computer Interface (BCI) system that automatically assigns a rating score to the listened song. Our research operated in two distinct stages: i) a generic feature engineering stage, in which features from signal-analytics were ranked and selected based on their ability to associate music induced perturbations in brainwaves with listener's appraisal of music. ii) a personalization stage, during which the efficiency of ex- treme learning machines (ELMs) is exploited so as to translate the derived pat- terns into a listener's score. Encouraging experimental results, from a pragmatic use of the system, are presented.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cSFz4J
via IFTTT
A Theory of Interactive Debugging of Knowledge Bases in Monotonic Logics. (arXiv:1609.06375v1 [cs.AI])
A broad variety of knowledge-based applications such as recommender, expert, planning or configuration systems usually operate on the basis of knowledge represented by means of some logical language. Such a logical knowledge base (KB) enables intelligent behavior of such systems by allowing them to automatically reason, answer queries of interest or solve complex real-world problems. Nowadays, where information acquisition comes at low costs and often happens automatically, the applied KBs are continuously growing in terms of size, information content and complexity. These developments foster the emergence of errors in these KBs and thus pose a significant challenge on all people and tools involved in KB evolution, maintenance and application.
If some minimal quality criteria such as logical consistency are not met by some KB, it becomes useless for knowledge-based applications. To guarantee the compliance of KBs with given requirements, (non-interactive) KB debuggers have been proposed. These however often cannot localize all potential faults, suggest too large or incorrect modifications of the faulty KB or suffer from poor scalability due to the inherent complexity of the KB debugging problem.
As a remedy to these issues, based on a well-founded theoretical basis this work proposes complete, sound and optimal methods for the interactive debugging of KBs that suggest the one (minimally invasive) error correction of the faulty KB that yields a repaired KB with exactly the intended semantics. Users, e.g. domain experts, are involved in the debugging process by answering automatically generated queries whether some given statements must or must not hold in the domain that should be modeled by the problematic KB at hand.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2dkMR3P
via IFTTT
Recognizing Implicit Discourse Relations via Repeated Reading: Neural Networks with Multi-Level Attention. (arXiv:1609.06380v1 [cs.CL])
Recognizing implicit discourse relations is a challenging but important task in the field of Natural Language Processing. For such a complex text processing task, different from previous studies, we argue that it is necessary to repeatedly read the arguments and dynamically exploit the efficient features useful for recognizing discourse relations. To mimic the repeated reading strategy, we propose the neural networks with multi-level attention (NNMA), combining the attention mechanism and external memories to gradually fix the attention on some specific words helpful to judging the discourse relations. Experiments on the PDTB dataset show that our proposed method achieves the state-of-art results. The visualization of the attention weights also illustrates the progress that our model observes the arguments on each level and progressively locates the important words.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cE7WSN
via IFTTT
A Logic of Knowing Why. (arXiv:1609.06405v1 [cs.AI])
When we say "I know why he was late", we know not only the fact that he was late, but also an explanation of this fact. We propose a logical framework of "knowing why" inspired by the existing formal studies on why-questions, scientific explanation, and justification logic. We introduce the Ky_i operator into the language of epistemic logic to express "agent i knows why phi" and propose a Kripke-style semantics of such expressions in terms of knowing an explanation of phi. We obtain two sound and complete axiomatizations w.r.t. two different model classes.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cSFI7V
via IFTTT
Document Image Coding and Clustering for Script Discrimination. (arXiv:1609.06492v1 [cs.CV])
The paper introduces a new method for discrimination of documents given in different scripts. The document is mapped into a uniformly coded text of numerical values. It is derived from the position of the letters in the text line, based on their typographical characteristics. Each code is considered as a gray level. Accordingly, the coded text determines a 1-D image, on which texture analysis by run-length statistics and local binary pattern is performed. It defines feature vectors representing the script content of the document. A modified clustering approach employed on document feature vector groups documents written in the same script. Experimentation performed on two custom oriented databases of historical documents in old Cyrillic, angular and round Glagolitic as well as Antiqua and Fraktur scripts demonstrates the superiority of the proposed method with respect to well-known methods in the state-of-the-art.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2dc7O1W
via IFTTT
Vote3Deep: Fast Object Detection in 3D Point Clouds Using Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks. (arXiv:1609.06666v1 [cs.RO])
This paper proposes a computationally efficient approach to detecting objects natively in 3D point clouds using convolutional neural networks (CNNs). In particular, this is achieved by leveraging a feature-centric voting scheme to implement novel convolutional layers which explicitly exploit the sparsity encountered in the input. To this end we examine the trade-off between accuracy and speed for different architectures and additionally propose to use an L1 penalty on the filter activations to further encourage sparsity in the intermediate representations. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to propose sparse convolutional layers and L1 regularisation for efficient large-scale processing of 3D data. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach on the KITTI object detection benchmark and show that Vote3Deep models with as few as three layers outperform the previous state of the art in both laser and laser-vision based approaches across the board by margins of up to 40% while remaining highly competitive in terms of processing time.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cneJiB
via IFTTT
How Relevant Are Chess Composition Conventions?. (arXiv:1309.3039v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
Composition conventions are guidelines used by human composers in composing chess problems. They are particularly significant in composition tournaments. Examples include, not having any check in the first move of the solution and not dressing up the board with unnecessary pieces. Conventions are often associated or even directly conflated with the overall aesthetics or beauty of a composition. Using an existing experimentally-validated computational aesthetics model for three-move mate problems, we analyzed sets of computer-generated compositions adhering to at least 2, 3 and 4 comparable conventions to test if simply conforming to more conventions had a positive effect on their aesthetics, as is generally believed by human composers. We found slight but statistically significant evidence that it does, but only to a point. We also analyzed human judge scores of 145 three-move mate problems composed by humans to see if they had any positive correlation with the computational aesthetic scores of those problems. We found that they did not. These seemingly conflicting findings suggest two main things. First, the right amount of adherence to composition conventions in a composition has a positive effect on its perceived aesthetics. Second, human judges either do not look at the same conventions related to aesthetics in the model used or emphasize others that have less to do with beauty as perceived by the majority of players, even though they may mistakenly consider their judgements beautiful in the traditional, non-esoteric sense. Human judges may also be relying significantly on personal tastes as we found no correlation between their individual scores either.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/14Q1i0S
via IFTTT
Length bias in Encoder Decoder Models and a Case for Global Conditioning. (arXiv:1606.03402v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
Encoder-decoder networks are popular for modeling sequences probabilistically in many applications. These models use the power of the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) architecture to capture the full dependence among variables, unlike earlier models like CRFs that typically assumed conditional independence among non-adjacent variables. However in practice encoder-decoder models exhibit a bias towards short sequences that surprisingly gets worse with increasing beam size.
In this paper we show that such phenomenon is due to a discrepancy between the full sequence margin and the per-element margin enforced by the locally conditioned training objective of a encoder-decoder model. The discrepancy more adversely impacts long sequences, explaining the bias towards predicting short sequences.
For the case where the predicted sequences come from a closed set, we show that a globally conditioned model alleviates the above problems of encoder-decoder models. From a practical point of view, our proposed model also eliminates the need for a beam-search during inference, which reduces to an efficient dot-product based search in a vector-space.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Ym4FLz
via IFTTT
anonymous-sums
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2dc8KTR
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Lenovo Fan
Following: 1879 - Followers: 850
September 21, 2016 at 07:54PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/LenovoFan1
Narcotics Anonymous in Galapagos
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2dc33oW
via IFTTT
MLB: Red Sox's magic number down to 8 as they host Orioles, who hold 1 AL wild-card spot; watch live in the ESPN App (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Orioles: Adam Jones says \"it's sad\" when asked about poor attendance (19,422 average) in first two games vs. Red Sox (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Allow anonymous submission to be updated using a secure token
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cuJxS8
via IFTTT
[FD] CVE-2016-5725 - JCraft/JSch Java Secure Channel <= 0.1.53 recursive sftp-get path traversal (client-side, windows)
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] XSS Wordpress W3 Total Cache <= 0.9.4.1
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Orioles Video: Rookie Trey Mancini hits HR in 2nd career AB Tuesday night and his mom goes crazy with excitement (ESPN)
via IFTTT
News: Icarus: 10 most downloaded papers in 2016
Discover the 10 most popular downloaded papers in 2016* from Icarus’ homepage.
from Icarus http://ift.tt/2cZN7EQ
via IFTTT
Warning — You Can't Install Linux On Microsoft Signature Edition PCs from Lenovo
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2clZR48
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 09/20/2016
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/2couoDs
via IFTTT
This Wi-Fi Router can read your Emotions; Maybe of your Girl's too!
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2conQ7w
via IFTTT
Valse in C major
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2clR7e8
via IFTTT
Notification emails for subscribed content types for anonymous users
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cTTkhA
via IFTTT
Photos On Dark Web Reveal Geo-locations Of 229 Drug Dealers — Here's How
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2cJhCke
via IFTTT
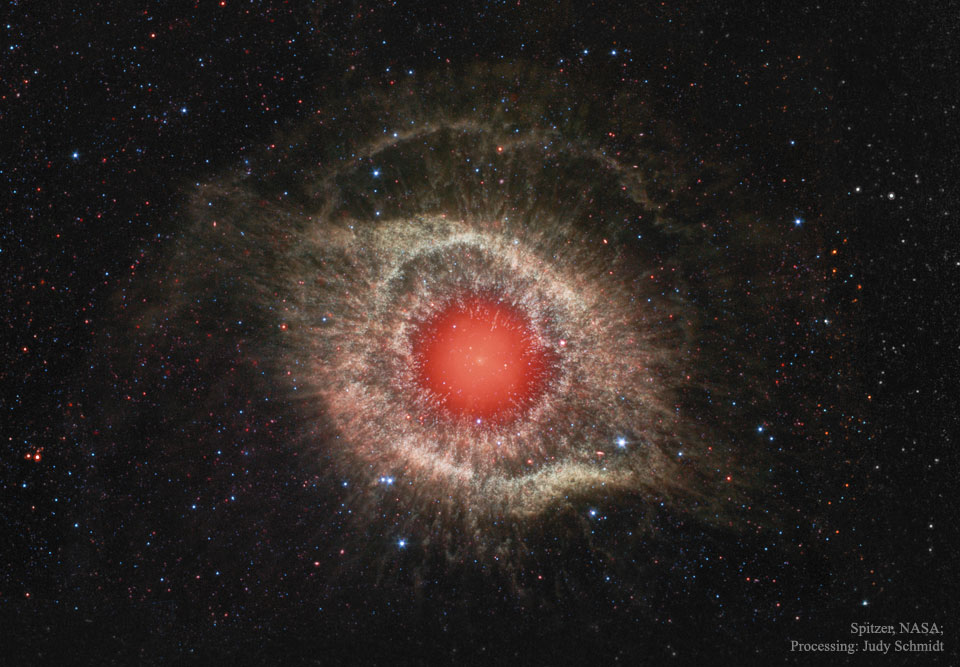
The Helix Nebula in Infrared

GPM scans hurricane Hermine
from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio: Most Recent Items http://ift.tt/2d3lYll
via IFTTT
WFIRST: The Road to L2
from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio: Most Recent Items http://ift.tt/2cQft2j
via IFTTT
WFIRST: The Road to L2. The view from above
from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio: Most Recent Items http://ift.tt/2d3lHiF
via IFTTT
WFIRST: The Road to L2. Oblique view
from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio: Most Recent Items http://ift.tt/2cQeRJN
via IFTTT
Tuesday, September 20, 2016
Orioles fall to Red Sox 5-2, trail Boston by 5 games in AL East; lead Tigers by 1.5 games for final AL wild-card spot (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Mazurek and Anglaise
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cBJCki
via IFTTT
Incremental Sampling-based Motion Planners Using Policy Iteration Methods. (arXiv:1609.05960v1 [cs.RO])
Recent progress in randomized motion planners has led to the development of a new class of sampling-based algorithms that provide asymptotic optimality guarantees, notably the RRT* and the PRM* algorithms. Careful analysis reveals that the so-called "rewiring" step in these algorithms can be interpreted as a local policy iteration (PI) step (i.e., a local policy evaluation step followed by a local policy improvement step) so that asymptotically, as the number of samples tend to infinity, both algorithms converge to the optimal path almost surely (with probability 1). Policy iteration, along with value iteration (VI) are common methods for solving dynamic programming (DP) problems. Based on this observation, recently, the RRT$^{\#}$ algorithm has been proposed, which performs, during each iteration, Bellman updates (aka "backups") on those vertices of the graph that have the potential of being part of the optimal path (i.e., the "promising" vertices). The RRT$^{\#}$ algorithm thus utilizes dynamic programming ideas and implements them incrementally on randomly generated graphs to obtain high quality solutions. In this work, and based on this key insight, we explore a different class of dynamic programming algorithms for solving shortest-path problems on random graphs generated by iterative sampling methods. These class of algorithms utilize policy iteration instead of value iteration, and thus are better suited for massive parallelization. Contrary to the RRT* algorithm, the policy improvement during the rewiring step is not performed only locally but rather on a set of vertices that are classified as "promising" during the current iteration. This tends to speed-up the whole process. The resulting algorithm, aptly named Policy Iteration-RRT$^{\#}$ (PI-RRT$^{\#}$) is the first of a new class of DP-inspired algorithms for randomized motion planning that utilize PI methods.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2d0xICt
via IFTTT
Macro-optimization of email recommendation response rates harnessing individual activity levels and group affinity trends. (arXiv:1609.05989v1 [cs.AI])
Recommendation emails are among the best ways to re-engage with customers after they have left a website. While on-site recommendation systems focus on finding the most relevant items for a user at the moment (right item), email recommendations add two critical additional dimensions: who to send recommendations to (right person) and when to send them (right time). It is critical that a recommendation email system not send too many emails to too many users in too short of a time-window, as users may unsubscribe from future emails or become desensitized and ignore future emails if they receive too many. Also, email service providers may mark such emails as spam if too many of their users are contacted in a short time-window. Optimizing email recommendation systems such that they can yield a maximum response rate for a minimum number of email sends is thus critical for the long-term performance of such a system. In this paper, we present a novel recommendation email system that not only generates recommendations, but which also leverages a combination of individual user activity data, as well as the behavior of the group to which they belong, in order to determine each user's likelihood to respond to any given set of recommendations within a given time period. In doing this, we have effectively created a meta-recommendation system which recommends sets of recommendations in order to optimize the aggregate response rate of the entire system. The proposed technique has been applied successfully within CareerBuilder's job recommendation email system to generate a 50\% increase in total conversions while also decreasing sent emails by 72%
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2dhSZcO
via IFTTT
Modelling Stock-market Investors as Reinforcement Learning Agents [Correction]. (arXiv:1609.06086v1 [cs.CE])
Decision making in uncertain and risky environments is a prominent area of research. Standard economic theories fail to fully explain human behaviour, while a potentially promising alternative may lie in the direction of Reinforcement Learning (RL) theory. We analyse data for 46 players extracted from a financial market online game and test whether Reinforcement Learning (Q-Learning) could capture these players behaviour using a risk measure based on financial modeling. Moreover we test an earlier hypothesis that players are "na\"ive" (short-sighted). Our results indicate that a simple Reinforcement Learning model which considers only the selling component of the task captures the decision-making process for a subset of players but this is not sufficient to draw any conclusion on the population. We also find that there is not a significant improvement of fitting of the players when using a full RL model against a myopic version, where only immediate reward is valued by the players. This indicates that players, if using a Reinforcement Learning approach, do so na\"ively
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2d0y3VP
via IFTTT
An Efficient Method of Partitioning High Volumes of Multidimensional Data for Parallel Clustering Algorithms. (arXiv:1609.06221v1 [cs.AI])
An optimal data partitioning in parallel & distributed implementation of clustering algorithms is a necessary computation as it ensures independent task completion, fair distribution, less number of affected points and better & faster merging. Though partitioning using Kd Tree is being conventionally used in academia, it suffers from performance drenches and bias (non equal distribution) as dimensionality of data increases and hence is not suitable for practical use in industry where dimensionality can be of order of 100s to 1000s. To address these issues we propose two new partitioning techniques using existing mathematical models & study their feasibility, performance (bias and partitioning speed) & possible variants in choosing initial seeds. First method uses an n dimensional hashed grid based approach which is based on mapping the points in space to a set of cubes which hashes the points. Second method uses a tree of voronoi planes where each plane corresponds to a partition. We found that grid based approach was computationally impractical, while using a tree of voronoi planes (using scalable K-Means++ initial seeds) drastically outperformed the Kd-tree tree method as dimensionality increased.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2dhQR4W
via IFTTT
An Ensemble Blocking Scheme for Entity Resolution of Large and Sparse Datasets. (arXiv:1609.06265v1 [cs.AI])
Entity Resolution, also called record linkage or deduplication, refers to the process of identifying and merging duplicate versions of the same entity into a unified representation. The standard practice is to use a Rule based or Machine Learning based model that compares entity pairs and assigns a score to represent the pairs' Match/Non-Match status. However, performing an exhaustive pair-wise comparison on all pairs of records leads to quadratic matcher complexity and hence a Blocking step is performed before the Matching to group similar entities into smaller blocks that the matcher can then examine exhaustively. Several blocking schemes have been developed to efficiently and effectively block the input dataset into manageable groups. At CareerBuilder (CB), we perform deduplication on massive datasets of people profiles collected from disparate sources with varying informational content. We observed that, employing a single blocking technique did not cover the base for all possible scenarios due to the multi-faceted nature of our data sources. In this paper, we describe our ensemble approach to blocking that combines two different blocking techniques to leverage their respective strengths.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2d0wNSH
via IFTTT
Semantic Similarity Strategies for Job Title Classification. (arXiv:1609.06268v1 [cs.AI])
Automatic and accurate classification of items enables numerous downstream applications in many domains. These applications can range from faceted browsing of items to product recommendations and big data analytics. In the online recruitment domain, we refer to classifying job ads to pre-defined or custom occupation categories as job title classification. A large-scale job title classification system can power various downstream applications such as semantic search, job recommendations and labor market analytics. In this paper, we discuss experiments conducted to improve our in-house job title classification system. The classification component of the system is composed of a two-stage coarse and fine level classifier cascade that classifies input text such as job title and/or job ads to one of the thousands of job titles in our taxonomy. To improve classification accuracy and effectiveness, we experiment with various semantic representation strategies such as average W2V vectors and document similarity measures such as Word Movers Distance (WMD). Our initial results show an overall improvement in accuracy of Carotene[1].
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2dhQMyi
via IFTTT
The Digital Synaptic Neural Substrate: A New Approach to Computational Creativity. (arXiv:1507.07058v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
We introduce a new artificial intelligence (AI) approach called, the 'Digital Synaptic Neural Substrate' (DSNS). It uses selected attributes from objects in various domains (e.g. chess problems, classical music, renowned artworks) and recombines them in such a way as to generate new attributes that can then, in principle, be used to create novel objects of creative value to humans relating to any one of the source domains. This allows some of the burden of creative content generation to be passed from humans to machines. The approach was tested in the domain of chess problem composition. We used it to automatically compose numerous sets of chess problems based on attributes extracted and recombined from chess problems and tournament games by humans, renowned paintings, computer-evolved abstract art, photographs of people, and classical music tracks. The quality of these generated chess problems was then assessed automatically using an existing and experimentally-validated computational chess aesthetics model. They were also assessed by human experts in the domain. The results suggest that attributes collected and recombined from chess and other domains using the DSNS approach can indeed be used to automatically generate chess problems of reasonably high aesthetic quality. In particular, a low quality chess source (i.e. tournament game sequences between weak players) used in combination with actual photographs of people was able to produce three-move chess problems of comparable quality or better to those generated using a high quality chess source (i.e. published compositions by human experts), and more efficiently as well. Why information from a foreign domain can be integrated and functional in this way remains an open question for now. The DSNS approach is, in principle, scalable and applicable to any domain in which objects have attributes that can be represented using real numbers.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1Io5BTF
via IFTTT
ViZDoom: A Doom-based AI Research Platform for Visual Reinforcement Learning. (arXiv:1605.02097v2 [cs.LG] UPDATED)
The recent advances in deep neural networks have led to effective vision-based reinforcement learning methods that have been employed to obtain human-level controllers in Atari 2600 games from pixel data. Atari 2600 games, however, do not resemble real-world tasks since they involve non-realistic 2D environments and the third-person perspective. Here, we propose a novel test-bed platform for reinforcement learning research from raw visual information which employs the first-person perspective in a semi-realistic 3D world. The software, called ViZDoom, is based on the classical first-person shooter video game, Doom. It allows developing bots that play the game using the screen buffer. ViZDoom is lightweight, fast, and highly customizable via a convenient mechanism of user scenarios. In the experimental part, we test the environment by trying to learn bots for two scenarios: a basic move-and-shoot task and a more complex maze-navigation problem. Using convolutional deep neural networks with Q-learning and experience replay, for both scenarios, we were able to train competent bots, which exhibit human-like behaviors. The results confirm the utility of ViZDoom as an AI research platform and imply that visual reinforcement learning in 3D realistic first-person perspective environments is feasible.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1s8S0Q6
via IFTTT
Option Discovery in Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning using Spatio-Temporal Clustering. (arXiv:1605.05359v2 [cs.LG] UPDATED)
This paper introduces an automated skill acquisition framework in reinforcement learning which involves identifying a hierarchical description of the given task in terms of abstract states and extended actions between abstract states. Identifying such structures present in the task provides ways to simplify and speed up reinforcement learning algorithms. These structures also help to generalize such algorithms over multiple tasks without relearning policies from scratch. We use ideas from dynamical systems to find metastable regions in the state space and associate them with abstract states. The spectral clustering algorithm PCCA+ is used to identify suitable abstractions aligned to the underlying structure. Skills are defined in terms of the sequence of actions that lead to transitions between such abstract states. The connectivity information from PCCA+ is used to generate these skills or options. These skills are independent of the learning task and can be efficiently reused across a variety of tasks defined over the same model. This approach works well even without the exact model of the environment by using sample trajectories to construct an approximate estimate. We also present our approach to scaling the skill acquisition framework to complex tasks with large state spaces for which we perform state aggregation using the representation learned from an action conditional video prediction network and use the skill acquisition framework on the aggregated state space.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1U0cfoJ
via IFTTT
Alternating Optimisation and Quadrature for Robust Reinforcement Learning. (arXiv:1605.07496v2 [cs.LG] UPDATED)
Bayesian optimisation has been successfully applied to a variety of reinforcement learning problems. However, the traditional approach for learning optimal policies in simulators does not utilise the opportunity to improve learning by adjusting certain environment variables - state features that are randomly determined by the environment in a physical setting but are controllable in a simulator. This paper considers the problem of finding an optimal policy while taking into account the impact of environment variables. We present alternating optimisation and quadrature (ALOQ), which uses Bayesian optimisation and Bayesian quadrature to address such settings. ALOQ is robust to the presence of significant rare events, which may not be observable under random sampling, but have a considerable impact on determining the optimal policy. We provide experimental results demonstrating our approach learning more efficiently than existing methods.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/25kHmXD
via IFTTT
Exploiting Vagueness for Multi-Agent Consensus. (arXiv:1607.05540v2 [cs.MA] UPDATED)
A framework for consensus modelling is introduced using Kleene's three valued logic as a means to express vagueness in agents' beliefs. Explicitly borderline cases are inherent to propositions involving vague concepts where sentences of a propositional language may be absolutely true, absolutely false or borderline. By exploiting these intermediate truth values, we can allow agents to adopt a more vague interpretation of underlying concepts in order to weaken their beliefs and reduce the levels of inconsistency, so as to achieve consensus. We consider a consensus combination operation which results in agents adopting the borderline truth value as a shared viewpoint if they are in direct conflict. Simulation experiments are presented which show that applying this operator to agents chosen at random (subject to a consistency threshold) from a population, with initially diverse opinions, results in convergence to a smaller set of more precise shared beliefs. Furthermore, if the choice of agents for combination is dependent on the payoff of their beliefs, this acting as a proxy for performance or usefulness, then the system converges to beliefs which, on average, have higher payoff.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/29TN8Yz
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Asset TV U.S.
Online TV channel for financial advisors and institutional investors, with an audience of 190,000 investment professionals.
United States
https://t.co/nTPBbmCIGl
Following: 5605 - Followers: 5096
September 20, 2016 at 07:54PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/AssetTVUS
Ravens Image: Players greet drivers at the Fort McHenry toll booth, bring pizza to firefighters after defeating Browns (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Not work for anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2d9h6fj
via IFTTT
[FD] Blind SQL Injection in Exponent CMS <= v2.3.9
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Anonymous webform results tied to specific user
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2crJztL
via IFTTT
[FD] Critical Vulnerabilities in Sparkassen Bank Server discovered by German Security Researchers
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
ISS Daily Summary Report – 09/19/2016
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/2cAhbU7
via IFTTT
Hackers take Remote Control of Tesla's Brakes and Door locks from 12 Miles Away
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2cEs6y1
via IFTTT
Cisco finds new Zero-Day Exploit linked to NSA Hackers
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2czKt4V
via IFTTT
50000 Kilometers over the Sun
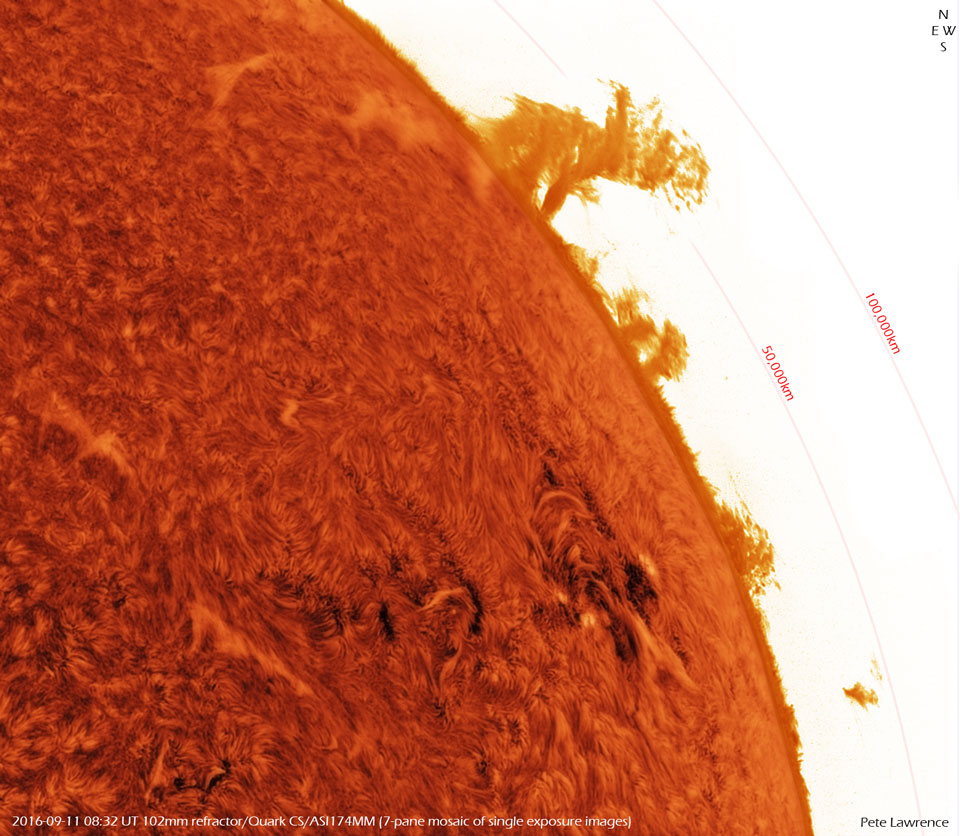
Monday, September 19, 2016
Anonymous Group
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cUTYPM
via IFTTT
Orioles fall to Red Sox 5-2, trail AL East leaders by 4 games with 12 left to play this season; hold 0.5-game lead in WC (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Burgers Anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2cOQmLo
via IFTTT
Prioritised Default Logic as Argumentation with Partial Order Default Priorities. (arXiv:1609.05224v1 [cs.AI])
We express Brewka's prioritised default logic (PDL) as argumentation using ASPIC+. By representing PDL as argumentation and designing an argument preference relation that takes the argument structure into account, we prove that the conclusions of the justified arguments correspond to the PDL extensions. We will first assume that the default priority is total, and then generalise to the case where it is a partial order. This provides a characterisation of non-monotonic inference in PDL as an exchange of argument and counter-argument, providing a basis for distributed non-monotonic reasoning in the form of dialogue.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cMimkz
via IFTTT
Continuous occurrence theory. (arXiv:1609.05228v1 [cs.AI])
Usually gradual and continuous changes in entities will lead to appear events. But usually it is supposed that an event is occurred at once. In this research an integrated framework called continuous occurrence theory (COT) is presented to investigate respective path leading to occurrence of the events in the real world. For this purpose initially fundamental concepts are defined. Afterwards, the appropriate tools such as occurrence variables computations, occurrence dependency function and occurrence model are introduced and explained in a systematic manner. Indeed, COT provides the possibility to: (a) monitor occurrence of events during time; (b) study background of the events; (c) recognize the relevant issues of each event; and (d) understand how these issues affect on the considered event. The developed framework (COT) provides the necessary context to analyze accurately continual changes of the issues and the relevant events in the various branches of science and business. Finally, typical applications of COT and an applied modeling example of it have been explained and a mathematical programming example is modeled in the occurrence based environment.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cZK7JE
via IFTTT
The ACRV Picking Benchmark (APB): A Robotic Shelf Picking Benchmark to Foster Reproducible Research. (arXiv:1609.05258v1 [cs.RO])
Robotic challenges like the Amazon Picking Challenge (APC) or the DARPA Challenges are an established and important way to drive scientific progress as they make research comparable on a well-defined benchmark with equal test conditions for all participants. However, such challenge events occur only occasionally, are limited to a small number of contestants, and the test conditions are very difficult to replicate after the main event. We present a new physical benchmark challenge for robotic picking. The ACRV Picking Benchmark is designed to be reproducible by using a set of 42 common objects, a widely available shelf, and exact guidelines for object arrangement using stencils. A well-defined evaluation protocol enables the comparability of complete robotic systems -- including perception and manipulation -- instead of sub-systems only. Our paper describes this new benchmark challenge and presents results acquired by a baseline system based on a Baxter robot.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cMhpc5
via IFTTT
NPCs Vote! Changing Voter Reactions Over Time Using the Extreme AI Personality Engine. (arXiv:1609.05315v1 [cs.AI])
Can non-player characters have human-realistic personalities, changing over time depending on input from those around them? And can they have different reactions and thoughts about different people? Using Extreme AI, a psychology-based personality engine using the Five Factor model of personality, I answer these questions by creating personalities for 100 voters and allowing them to react to two politicians to see if the NPC voters' choice of candidate develops in a realistic-seeming way, based on initial and changing personality facets and on their differing feelings toward the politicians (in this case, across liking, trusting, and feeling affiliated with the candidates). After 16 test runs, the voters did indeed change their attitudes and feelings toward the candidates in different and yet generally realistic ways, and even changed their attitudes about other issues based on what a candidate extolled.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cZKFzd
via IFTTT
Solving the Wastewater Treatment Plant Problem with SMT. (arXiv:1609.05367v1 [cs.AI])
In this paper we introduce the Wastewater Treatment Plant Problem, a real-world scheduling problem, and compare the performance of several tools on it. We show that, for a naive modeling, state-of-the-art SMT solvers outperform other tools ranging from mathematical programming to constraint programming. We use both real and randomly generated benchmarks.
From this and similar results, we claim for the convenience of developing compiler front-ends being able to translate from constraint programming languages to the SMT-LIB standard language.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cMixfN
via IFTTT
Applications of Data Mining (DM) in Science and Engineering: State of the art and perspectives. (arXiv:1609.05401v1 [cs.AI])
The continuous increase in the availability of data of any kind, coupled with the development of networks of high-speed communications, the popularization of cloud computing and the growth of data centers and the emergence of high-performance computing does essential the task to develop techniques that allow more efficient data processing and analyzing of large volumes datasets and extraction of valuable information. In the following pages we will discuss about development of this field in recent decades, and its potential and applicability present in the various branches of scientific research. Also, we try to review briefly the different families of algorithms that are included in data mining research area, its scalability with increasing dimensionality of the input data and how they can be addressed and what behavior different methods in a scenario in which the information is distributed or decentralized processed so as to increment performance optimization in heterogeneous environments.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cZKDaz
via IFTTT
SeqGAN: Sequence Generative Adversarial Nets with Policy Gradient. (arXiv:1609.05473v1 [cs.LG])
As a new way of training generative models, Generative Adversarial Nets (GAN) that uses a discriminative model to guide the training of the generative model has enjoyed considerable success in generating real-valued data. However, it has limitations when the goal is for generating sequences of discrete tokens. A major reason lies in that the discrete outputs from the generative model make it difficult to pass the gradient update from the discriminative model to the generative model. Also, the discriminative model can only assess a complete sequence, while for a partially generated sequence, it is non-trivial to balance its current score and the future one once the entire sequence has been generated. In this paper, we propose a sequence generation framework, called SeqGAN, to solve the problems. Modeling the data generator as a stochastic policy in reinforcement learning (RL), SeqGAN bypasses the generator differentiation problem by directly performing gradient policy update. The RL reward signal comes from the GAN discriminator judged on a complete sequence, and is passed back to the intermediate state-action steps using Monte Carlo search. Extensive experiments on synthetic data and real-world tasks demonstrate significant improvements over strong baselines.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cUGC6a
via IFTTT
Towards Deep Symbolic Reinforcement Learning. (arXiv:1609.05518v1 [cs.AI])
Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) brings the power of deep neural networks to bear on the generic task of trial-and-error learning, and its effectiveness has been convincingly demonstrated on tasks such as Atari video games and the game of Go. However, contemporary DRL systems inherit a number of shortcomings from the current generation of deep learning techniques. For example, they require very large datasets to work effectively, entailing that they are slow to learn even when such datasets are available. Moreover, they lack the ability to reason on an abstract level, which makes it difficult to implement high-level cognitive functions such as transfer learning, analogical reasoning, and hypothesis-based reasoning. Finally, their operation is largely opaque to humans, rendering them unsuitable for domains in which verifiability is important. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end reinforcement learning architecture comprising a neural back end and a symbolic front end with the potential to overcome each of these shortcomings. As proof-of-concept, we present a preliminary implementation of the architecture and apply it to several variants of a simple video game. We show that the resulting system -- though just a prototype -- learns effectively, and, by acquiring a set of symbolic rules that are easily comprehensible to humans, dramatically outperforms a conventional, fully neural DRL system on a stochastic variant of the game.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cUI5sU
via IFTTT