Latest YouTube Video
Saturday, February 4, 2017
Block or Redirect Anonymous Proxy IPs
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kBnz4r
via IFTTT
dotnet/roslyn
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2l5YwHk
via IFTTT
Goddesses Anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jMWhIV
via IFTTT
Anonymous Couple in Sauna
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2l9OPDM
via IFTTT
Bind, Call, Apply, Arrow, Direct, Anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kdP82Q
via IFTTT
NH Food Bank receives $1M anonymous donation
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jJzuxB
via IFTTT
Milky Way with Airglow Australis
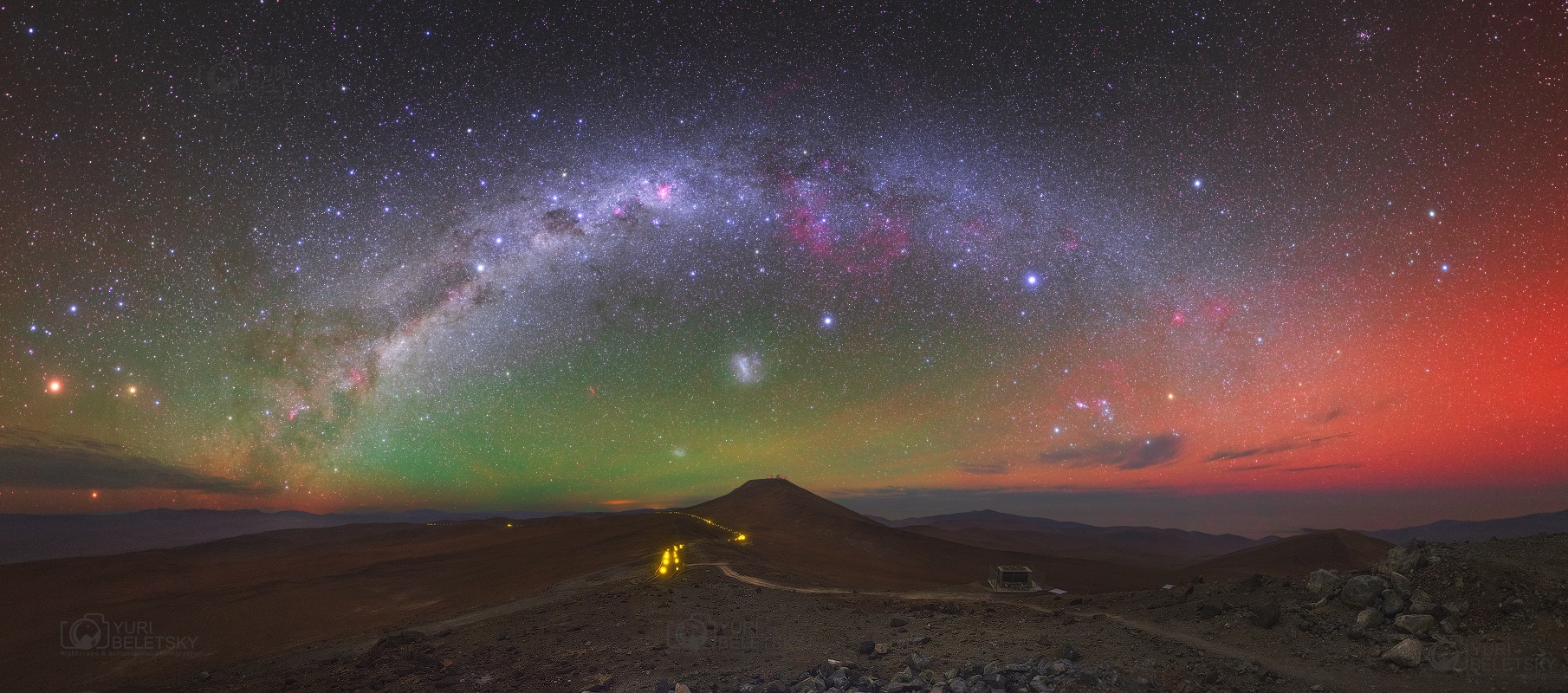

Friday, February 3, 2017
Anonymous letter writer spreads joy, love to strangers
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2l7nv9e
via IFTTT
Anonymous Gamer
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kCbgV6
via IFTTT
An Anonymous Group Just Took Down a Fifth of the Dark Web
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2l6Vrmj
via IFTTT
Food Bank gets anonymous $1M donation
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kynKxL
via IFTTT
Dobrado O Arrogante (Anonymous)
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2l5tUCD
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 2/02/2017
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/2jL99Kx
via IFTTT
Radio Stations Hacked to Play "F**k Donald Trump" on Repeat Across the Country
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2jEAWBc
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Ash Maurya
Author of #RunningLean and Creator of #LeanCanvas. My new book: #ScalingLean - https://t.co/UvYpBnJsIA
Austin, TX
https://t.co/dFcdquFcS0
Following: 11501 - Followers: 40665
February 03, 2017 at 01:07AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/ashmaurya
Two Arrested for Hacking Washington CCTV Cameras Before Trump Inauguration
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2k23G2X
via IFTTT
NGC 1316: After Galaxies Collide
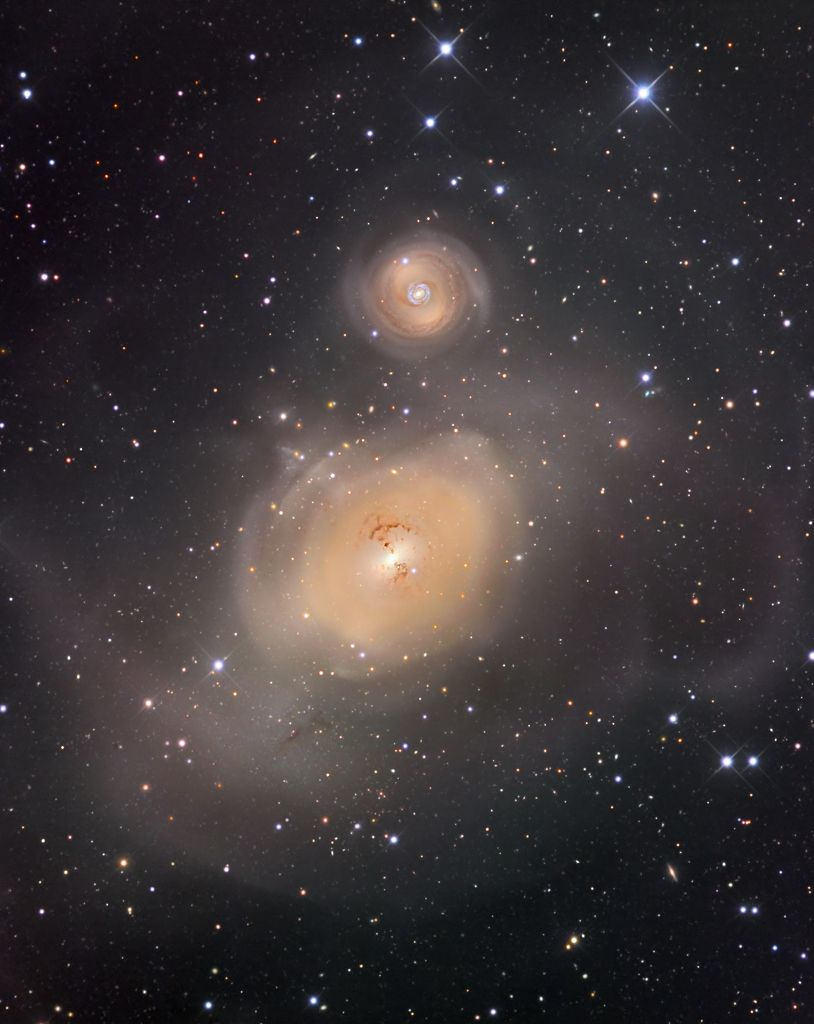

Thursday, February 2, 2017
I have a new follower on Twitter
FrankNoack
Wordpress Produkte: https://t.co/8nCOCfzFB5
Hamburg Germany
https://t.co/tsHNC0MfHd
Following: 7944 - Followers: 16479
February 02, 2017 at 11:02PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/Knarfkcaon
Procedural Content Generation via Machine Learning (PCGML). (arXiv:1702.00539v1 [cs.AI])
This survey explores Procedural Content Generation via Machine Learning (PCGML), defined as the generation of game content using machine learning models trained on existing content. As the importance of PCG for game development increases, researchers explore new avenues for generating high-quality content with or without human involvement; this paper addresses the relatively new paradigm of using machine learning (in contrast with search-based, solver-based, and constructive methods). We focus on what is most often considered functional game content such as platformer levels, game maps, interactive fiction stories, and cards in collectible card games, as opposed to cosmetic content such as sprites and sound effects. In addition to using PCG for autonomous generation, co-creativity, mixed-initiative design, and compression, PCGML is suited for repair, critique, and content analysis because of its focus on modeling existing content. We discuss various data sources and representations that affect the resulting generated content. Multiple PCGML methods are covered, including neural networks, long short-term memory (LSTM) networks, autoencoders, and deep convolutional networks; Markov models, $n$-grams, and multi-dimensional Markov chains; clustering; and matrix factorization. Finally, we discuss open problems in the application of PCGML, including learning from small datasets, lack of training data, multi-layered learning, style-transfer, parameter tuning, and PCG as a game mechanic.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2l0Cu5w
via IFTTT
Multilingual and Cross-lingual Timeline Extraction. (arXiv:1702.00700v1 [cs.CL])
In this paper we present an approach to extract ordered timelines of events, their participants, locations and times from a set of multilingual and cross-lingual data sources. Based on the assumption that event-related information can be recovered from different documents written in different languages, we extend the Cross-document Event Ordering task presented at SemEval 2015 by specifying two new tasks for, respectively, Multilingual and Cross-lingual Timeline Extraction. We then develop three deterministic algorithms for timeline extraction based on two main ideas. First, we address implicit temporal relations at document level since explicit time-anchors are too scarce to build a wide coverage timeline extraction system. Second, we leverage several multilingual resources to obtain a single, inter-operable, semantic representation of events across documents and across languages. The result is a highly competitive system that strongly outperforms the current state-of-the-art. Nonetheless, further analysis of the results reveals that linking the event mentions with their target entities and time-anchors remains a difficult challenge. The systems, resources and scorers are freely available to facilitate its use and guarantee the reproducibility of results.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kyskeD
via IFTTT
Two forms of minimality in ASPIC+. (arXiv:1702.00780v1 [cs.AI])
Many systems of structured argumentation explicitly require that the facts and rules that make up the argument for a conclusion be the minimal set required to derive the conclusion. ASPIC+ does not place such a requirement on arguments, instead requiring that every rule and fact that are part of an argument be used in its construction. Thus ASPIC+ arguments are minimal in the sense that removing any element of the argument would lead to a structure that is not an argument. In this brief note we discuss these two types of minimality and show how the first kind of minimality can, if desired, be recovered in ASPIC+.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kyi06o
via IFTTT
A Simplified and Improved Free-Variable Framework for Hilbert's epsilon as an Operator of Indefinite Committed Choice. (arXiv:1104.2444v9 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
Free variables occur frequently in mathematics and computer science with ad hoc and altering semantics. We present the most recent version of our free-variable framework for two-valued logics with properly improved functionality, but only two kinds of free variables left (instead of three): implicitly universally and implicitly existentially quantified ones, now simply called "free atoms" and "free variables", respectively. The quantificational expressiveness and the problem-solving facilities of our framework exceed standard first-order and even higher-order modal logics, and directly support Fermat's descente infinie. With the improved version of our framework, we can now model also Henkin quantification, neither using quantifiers (binders) nor raising (Skolemization). We propose a new semantics for Hilbert's epsilon as a choice operator with the following features: We avoid overspecification (such as right-uniqueness), but admit indefinite choice, committed choice, and classical logics. Moreover, our semantics for the epsilon supports reductive proof search optimally.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/12jZYm9
via IFTTT
Exploration and Exploitation of Victorian Science in Darwin's Reading Notebooks. (arXiv:1509.07175v5 [cs.CL] UPDATED)
Search in an environment with an uncertain distribution of resources involves a trade-off between exploitation of past discoveries and further exploration. This extends to information foraging, where a knowledge-seeker shifts between reading in depth and studying new domains. To study this decision-making process, we examine the reading choices made by one of the most celebrated scientists of the modern era: Charles Darwin. From the full-text of books listed in his chronologically-organized reading journals, we generate topic models to quantify his local (text-to-text) and global (text-to-past) reading decisions using Kullback-Liebler Divergence, a cognitively-validated, information-theoretic measure of relative surprise. Rather than a pattern of surprise-minimization, corresponding to a pure exploitation strategy, Darwin's behavior shifts from early exploitation to later exploration, seeking unusually high levels of cognitive surprise relative to previous eras. These shifts, detected by an unsupervised Bayesian model, correlate with major intellectual epochs of his career as identified both by qualitative scholarship and Darwin's own self-commentary. Our methods allow us to compare his consumption of texts with their publication order. We find Darwin's consumption more exploratory than the culture's production, suggesting that underneath gradual societal changes are the explorations of individual synthesis and discovery. Our quantitative methods advance the study of cognitive search through a framework for testing interactions between individual and collective behavior and between short- and long-term consumption choices. This novel application of topic modeling to characterize individual reading complements widespread studies of collective scientific behavior.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1FxghEk
via IFTTT
Bootstrap Model Aggregation for Distributed Statistical Learning. (arXiv:1607.01036v2 [stat.ML] UPDATED)
In distributed, or privacy-preserving learning, we are often given a set of probabilistic models estimated from different local repositories, and asked to combine them into a single model that gives efficient statistical estimation. A simple method is to linearly average the parameters of the local models, which, however, tends to be degenerate or not applicable on non-convex models, or models with different parameter dimensions. One more practical strategy is to generate bootstrap samples from the local models, and then learn a joint model based on the combined bootstrap set. Unfortunately, the bootstrap procedure introduces additional noise and can significantly deteriorate the performance. In this work, we propose two variance reduction methods to correct the bootstrap noise, including a weighted M-estimator that is both statistically efficient and practically powerful. Both theoretical and empirical analysis is provided to demonstrate our methods.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/29ljlaZ
via IFTTT
A correlation coefficient of belief functions. (arXiv:1612.05497v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
How to manage conflict is still an open issue in Dempster-Shafer evidence theory. The correlation coefficient can be used to measure the similarity of evidence in Dempster-Shafer evidence theory. However, existing correlation coefficients of belief functions have some shortcomings. In this paper, a new correlation coefficient is proposed with many desirable properties. One of its applications is to measure the conflict degree among belief functions. Some numerical examples and comparisons demonstrate the effectiveness of the correlation coefficient.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2h1gZTV
via IFTTT
Jointly Extracting Relations with Class Ties via Effective Deep Ranking. (arXiv:1612.07602v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
Connections between relations in relation extraction, which we call class ties, are common. In distantly supervised scenario, one entity tuple may have multiple relation facts. Exploiting class ties between relations of one entity tuple will be promising for distantly supervised relation extraction. However, previous models are not effective or ignore to model this property. In this work, to effectively leverage class ties, we propose to make joint relation extraction with a unified model that integrates convolutional neural network with a general pairwise ranking framework, in which two novel ranking loss functions are introduced. Additionally, an effective method is presented to relieve the impact of NR (not relation) for model training, which significantly boosts our model performance. Experiments on a widely used dataset show that leveraging class ties will enhance extraction and demonstrate that our model is effective to learn class ties. Our model outperforms baselines significantly, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2i7dI2c
via IFTTT
Pose-Selective Max Pooling for Measuring Similarity. (arXiv:1609.07042v4 [cs.CV] CROSS LISTED)
In this paper, we deal with two challenges for measuring the similarity of the subject identities in practical video-based face recognition - the variation of the head pose in uncontrolled environments and the computational expense of processing videos. Since the frame-wise feature mean is unable to characterize the pose diversity among frames, we define and preserve the overall pose diversity and closeness in a video. Then, identity will be the only source of variation across videos since the pose varies even within a single video. Instead of simply using all the frames, we select those faces whose pose point is closest to the centroid of the K-means cluster containing that pose point. Then, we represent a video as a bag of frame-wise deep face features while the number of features has been reduced from hundreds to K. Since the video representation can well represent the identity, now we measure the subject similarity between two videos as the max correlation among all possible pairs in the two bags of features. On the official 5,000 video-pairs of the YouTube Face dataset for face verification, our algorithm achieves a comparable performance with VGG-face that averages over deep features of all frames. Other vision tasks can also benefit from the generic idea of employing geometric cues to improve the descriptiveness of deep features.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2cVF35F
via IFTTT
Overeaters Anonymous to hold local workshop
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2k1r4Oc
via IFTTT
[FD] HP Printers Wi-Fi Direct Improper Access Control
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] [FOXMOLE SA 2016-07-05] ZoneMinder - Multiple Issues
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Re: [FD] Multiple vulnerabilities found in the Dlink DWR-932B (backdoor, backdoor accounts, weak WPS, RCE ...)
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Remember The Anonymous Guy Who Wrote The 'Flight 93' Trump Essay?
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2l1U1d7
via IFTTT
40 comments
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kmu2hl
via IFTTT
Orioles: C Caleb Joseph loses salary arbitration case after setting MLB records for most AB and PA in a season with no RBI (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Ten anonymous Twitter profiles we like on #copolitics
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kxmx9d
via IFTTT
Anonymous wants to 'make humanity great again' with global protest against Trump
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kxllD0
via IFTTT
Anonymous Stranger Donates Generously To PRRA
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2k4W6av
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
BB&A
We are an award-winning agency that has achieved global recognition for our change communications, employee engagement, and learning and development work
Surrey, UK
http://t.co/gToGdEuNtc
Following: 4187 - Followers: 4541
February 02, 2017 at 10:17AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/BBandA_Chat
ISS Daily Summary Report – 2/01/2017
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/2kVPe0Q
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
CodaKid
CodaKid is an online kids coding and game design academy for kids ages 7 to 15.
Scottsdale AZ
http://t.co/QxUCw6eZSW
Following: 4949 - Followers: 6063
February 02, 2017 at 09:57AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/CodaKid
THN Deal: Join Certified Ethical Hacker Boot Camp Online Course (99% Off)
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2jGNsLV
via IFTTT
Hackers Offering Money to Company Insiders in Return for Confidential Data
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2jYSrsc
via IFTTT
I have a new follower on Twitter
Jay Graves
Jay Graves. Dad. Database nerd. Dude who quotes Fletch. Overly enthusiastic about most things data, business and productivity. And there are two b's in Babar...
Nashville, TN
https://t.co/dH5Ekt1x9u
Following: 934 - Followers: 1355
February 02, 2017 at 06:07AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/allballbearings
I have a new follower on Twitter
AllSight
AllSight is the first Customer Intelligence Management system that manages and synthesizes ALL data to provide the 'big picture' for your customer.
Toronto, ON
http://t.co/hZm9rPLRZf
Following: 1718 - Followers: 2255
February 02, 2017 at 06:07AM via Twitter http://twitter.com/AllSight
Critical WordPress REST API Bug: Prevent Your Blog From Being Hacked!
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2kk4wJB
via IFTTT
New anonymous reporting system helps keep Edgerton students safe
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kVnQwI
via IFTTT
Wednesday, February 1, 2017
I have a new follower on Twitter
KellyMartinBroderick
#feminist I ♥ Wonder Woman, red lipstick, Irish Whiskey, and Ellen Ripley - my cat. https://t.co/VNFfalHmSL
Baltimore, MD
https://t.co/fN9pq7OURf
Following: 1539 - Followers: 751
February 01, 2017 at 10:06PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/artsykelly
Towards "AlphaChem": Chemical Synthesis Planning with Tree Search and Deep Neural Network Policies. (arXiv:1702.00020v1 [cs.AI])
Retrosynthesis is a technique to plan the chemical synthesis of organic molecules, for example drugs, agro- and fine chemicals. In retrosynthesis, a search tree is built by analysing molecules recursively and dissecting them into simpler molecular building blocks until one obtains a set of known building blocks. The search space is intractably large, and it is difficult to determine the value of retrosynthetic positions. Here, we propose to model retrosynthesis as a Markov Decision Process. In combination with a Deep Neural Network policy learned from essentially the complete published knowledge of chemistry, Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) can be used to evaluate positions. In exploratory studies, we demonstrate that MCTS with neural network policies outperforms the traditionally used best-first search with hand-coded heuristics.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kTo5va
via IFTTT
Blue Sky Ideas in Artificial Intelligence Education from the EAAI 2017 New and Future AI Educator Program. (arXiv:1702.00137v1 [cs.AI])
The 7th Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence (EAAI'17, co-chaired by Sven Koenig and Eric Eaton) launched the EAAI New and Future AI Educator Program to support the training of early-career university faculty, secondary school faculty, and future educators (PhD candidates or postdocs who intend a career in academia). As part of the program, awardees were asked to address one of the following "blue sky" questions:
* How could/should Artificial Intelligence (AI) courses incorporate ethics into the curriculum?
* How could we teach AI topics at an early undergraduate or a secondary school level?
* AI has the potential for broad impact to numerous disciplines. How could we make AI education more interdisciplinary, specifically to benefit non-engineering fields?
This paper is a collection of their responses, intended to help motivate discussion around these issues in AI education.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kj4gKM
via IFTTT
Robust Order Scheduling in the Fashion Industry: A Multi-Objective Optimization Approach. (arXiv:1702.00159v1 [cs.NE])
In the fashion industry, order scheduling focuses on the assignment of production orders to appropriate production lines. In reality, before a new order can be put into production, a series of activities known as pre-production events need to be completed. In addition, in real production process, owing to various uncertainties, the daily production quantity of each order is not always as expected. In this research, by considering the pre-production events and the uncertainties in the daily production quantity, robust order scheduling problems in the fashion industry are investigated with the aid of a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm (MOEA) called nondominated sorting adaptive differential evolution (NSJADE). The experimental results illustrate that it is of paramount importance to consider pre-production events in order scheduling problems in the fashion industry. We also unveil that the existence of the uncertainties in the daily production quantity heavily affects the order scheduling.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kTsyOD
via IFTTT
A Hybrid Evolutionary Algorithm Based on Solution Merging for the Longest Arc-Preserving Common Subsequence Problem. (arXiv:1702.00318v1 [cs.AI])
The longest arc-preserving common subsequence problem is an NP-hard combinatorial optimization problem from the field of computational biology. This problem finds applications, in particular, in the comparison of arc-annotated Ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequences. In this work we propose a simple, hybrid evolutionary algorithm to tackle this problem. The most important feature of this algorithm concerns a crossover operator based on solution merging. In solution merging, two or more solutions to the problem are merged, and an exact technique is used to find the best solution within this union. It is experimentally shown that the proposed algorithm outperforms a heuristic from the literature.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kj0H7x
via IFTTT
Edward: A library for probabilistic modeling, inference, and criticism. (arXiv:1610.09787v3 [stat.CO] UPDATED)
Probabilistic modeling is a powerful approach for analyzing empirical information. We describe Edward, a library for probabilistic modeling. Edward's design reflects an iterative process pioneered by George Box: build a model of a phenomenon, make inferences about the model given data, and criticize the model's fit to the data. Edward supports a broad class of probabilistic models, efficient algorithms for inference, and many techniques for model criticism. The library builds on top of TensorFlow to support distributed training and hardware such as GPUs. Edward enables the development of complex probabilistic models and their algorithms at a massive scale.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2fb93u5
via IFTTT
Online Sequence-to-Sequence Active Learning for Open-Domain Dialogue Generation. (arXiv:1612.03929v4 [cs.CL] UPDATED)
We propose an online, end-to-end, neural generative conversational model for open-domain dialog. It is trained using a unique combination of offline two-phase supervised learning and online human-in-the-loop active learning. While most existing research proposes offline supervision or hand-crafted reward functions for online reinforcement, we devise a novel interactive learning mechanism based on a diversity-promoting heuristic for response generation and one-character user-feedback at each step. Experiments show that our model inherently promotes the generation of meaningful, relevant and interesting responses, and can be used to train agents with customized personas, moods and conversational styles.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2hCSEDX
via IFTTT
Anonymous calls for travel ban on U.S. citizens, boycott of Trump…
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kT4MCi
via IFTTT
Anonymous donor spends $13250 to pay lunch debts for 148 students
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jZulQx
via IFTTT
Goddesses Anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kTyx2v
via IFTTT
Buddy Montana for Ballers Anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kTuaEN
via IFTTT
Immediately Executing Anonymous Functions
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kWpfCe
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 1/31/2017
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/2kUYL3U
via IFTTT
Completing checkout as anonymous user stores payment method
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jCsRYR
via IFTTT
[FD] secuvera-SA-2017-02: Reflected XSS and Open Redirect in MailStore Server
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] secuvera-SA-2017-02: Reflected XSS and Open Redirect in MailStore Server
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability in Bitrix Site Manager
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
[FD] Viscosity for Windows 1.6.7 Privilege Escalation
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Popular PlayStation and Xbox Gaming Forums Hacked; 2.5 Million Users' Data Leaked
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2kfBVoK
via IFTTT
Police Arrested Suspected Hacker Who Hacked the 'Hacking Team'
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2kqbzCr
via IFTTT
Where to See the American Eclipse
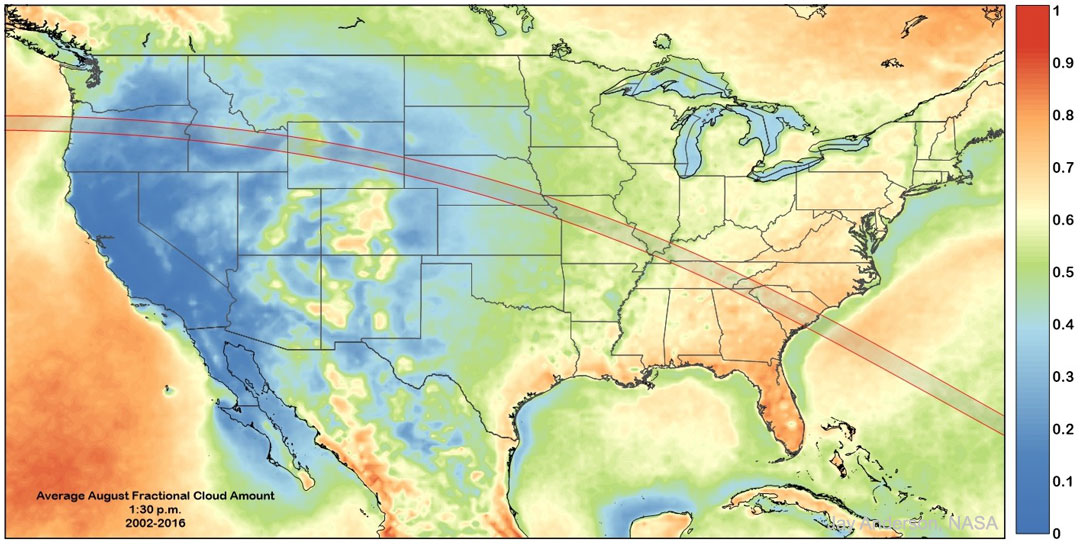
Tuesday, January 31, 2017
A Muvver (Anonymous)
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2kSO0z2
via IFTTT
C3A: A Cognitive Collaborative Control Architecture For an Intelligent Wheelchair. (arXiv:1701.08761v1 [cs.RO])
Retention of residual skills for persons who partially lose their cognitive or physical ability is of utmost importance. Research is focused on developing systems that provide need-based assistance for retention of such residual skills. This paper describes a novel cognitive collaborative control architecture C3A, designed to address the challenges of developing need- based assistance for wheelchair navigation. Organization of C3A is detailed and results from simulation of the proposed architecture is presented. For simulation of our proposed architecture, we have used ROS (Robot Operating System) as a control framework and a 3D robotic simulator called USARSim (Unified System for Automation and Robot Simulation).
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kSzK9s
via IFTTT
Algorithm selection of off-policy reinforcement learning algorithm. (arXiv:1701.08810v1 [stat.ML])
Dialogue systems rely on a careful reinforcement learning design: the learning algorithm and its state space representation. In lack of more rigorous knowledge, the designer resorts to its practical experience to choose the best option. In order to automate and to improve the performance of the aforementioned process, this article formalises the problem of online off-policy reinforcement learning algorithm selection. A meta-algorithm is given for input a portfolio constituted of several off-policy reinforcement learning algorithms. It then determines at the beginning of each new trajectory, which algorithm in the portfolio is in control of the behaviour during the full next trajectory, in order to maximise the return. The article presents a novel meta-algorithm, called Epochal Stochastic Bandit Algorithm Selection (ESBAS). Its principle is to freeze the policy updates at each epoch, and to leave a rebooted stochastic bandit in charge of the algorithm selection. Under some assumptions, a thorough theoretical analysis demonstrates its near-optimality considering the structural sampling budget limitations. Then, ESBAS is put to the test in a set of experiments with various portfolios, on a negotiation dialogue game. The results show the practical benefits of the algorithm selection for dialogue systems, in most cases even outperforming the best algorithm in the portfolio, even when the aforementioned assumptions are transgressed.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kpeITa
via IFTTT
Expert Level control of Ramp Metering based on Multi-task Deep Reinforcement Learning. (arXiv:1701.08832v1 [cs.AI])
This article shows how the recent breakthroughs in Reinforcement Learning (RL) that have enabled robots to learn to play arcade video games, walk or assemble colored bricks, can be used to perform other tasks that are currently at the core of engineering cyberphysical systems. We present the first use of RL for the control of systems modeled by discretized non-linear Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) and devise a novel algorithm to use non-parametric control techniques for large multi-agent systems. We show how neural network based RL enables the control of discretized PDEs whose parameters are unknown, random, and time-varying. We introduce an algorithm of Mutual Weight Regularization (MWR) which alleviates the curse of dimensionality of multi-agent control schemes by sharing experience between agents while giving each agent the opportunity to specialize its action policy so as to tailor it to the local parameters of the part of the system it is located in.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kOsgW3
via IFTTT
Interaction Information for Causal Inference: The Case of Directed Triangle. (arXiv:1701.08868v1 [cs.AI])
Interaction information is one of the multivariate generalizations of mutual information, which expresses the amount information shared among a set of variables, beyond the information, which is shared in any proper subset of those variables. Unlike (conditional) mutual information, which is always non-negative, interaction information can be negative. We utilize this property to find the direction of causal influences among variables in a triangle topology under some mild assumptions.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kpeJqc
via IFTTT
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robotic Manipulation-The state of the art. (arXiv:1701.08878v1 [cs.RO])
The focus of this work is to enumerate the various approaches and algorithms that center around application of reinforcement learning in robotic ma- ]]nipulation tasks. Earlier methods utilized specialized policy representations and human demonstrations to constrict the policy. Such methods worked well with continuous state and policy space of robots but failed to come up with generalized policies. Subsequently, high dimensional non-linear function approximators like neural networks have been used to learn policies from scratch. Several novel and recent approaches have also embedded control policy with efficient perceptual representation using deep learning. This has led to the emergence of a new branch of dynamic robot control system called deep r inforcement learning(DRL). This work embodies a survey of the most recent algorithms, architectures and their implementations in simulations and real world robotic platforms. The gamut of DRL architectures are partitioned into two different branches namely, discrete action space algorithms(DAS) and continuous action space algorithms(CAS). Further, the CAS algorithms are divided into stochastic continuous action space(SCAS) and deterministic continuous action space(DCAS) algorithms. Along with elucidating an organ- isation of the DRL algorithms this work also manifests some of the state of the art applications of these approaches in robotic manipulation tasks.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kppSHu
via IFTTT
CommAI: Evaluating the first steps towards a useful general AI. (arXiv:1701.08954v1 [cs.LG])
With machine learning successfully applied to new daunting problems almost every day, general AI starts looking like an attainable goal. However, most current research focuses instead on important but narrow applications, such as image classification or machine translation. We believe this to be largely due to the lack of objective ways to measure progress towards broad machine intelligence. In order to fill this gap, we propose here a set of concrete desiderata for general AI, together with a platform to test machines on how well they satisfy such desiderata, while keeping all further complexities to a minimum.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kSrOoN
via IFTTT
On the Semantics and Complexity of Probabilistic Logic Programs. (arXiv:1701.09000v1 [cs.AI])
We examine the meaning and the complexity of probabilistic logic programs that consist of a set of rules and a set of independent probabilistic facts (that is, programs based on Sato's distribution semantics). We focus on two semantics, respectively based on stable and on well-founded models. We show that the semantics based on stable models (referred to as the "credal semantics") produces sets of probability models that dominate infinitely monotone Choquet capacities, we describe several useful consequences of this result. We then examine the complexity of inference with probabilistic logic programs. We distinguish between the complexity of inference when a probabilistic program and a query are given (the inferential complexity), and the complexity of inference when the probabilistic program is fixed and the query is given (the query complexity, akin to data complexity as used in database theory). We obtain results on the inferential and query complexity for acyclic, stratified, and cyclic propositional and relational programs, complexity reaches various levels of the counting hierarchy and even exponential levels.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kOo3kX
via IFTTT
Comparing Dataset Characteristics that Favor the Apriori, Eclat or FP-Growth Frequent Itemset Mining Algorithms. (arXiv:1701.09042v1 [cs.DB])
Frequent itemset mining is a popular data mining technique. Apriori, Eclat, and FP-Growth are among the most common algorithms for frequent itemset mining. Considerable research has been performed to compare the relative performance between these three algorithms, by evaluating the scalability of each algorithm as the dataset size increases. While scalability as data size increases is important, previous papers have not examined the performance impact of similarly sized datasets that contain different itemset characteristics. This paper explores the effects that two dataset characteristics can have on the performance of these three frequent itemset algorithms. To perform this empirical analysis, a dataset generator is created to measure the effects of frequent item density and the maximum transaction size on performance. The generated datasets contain the same number of rows. This provides some insight into dataset characteristics that are conducive to each algorithm. The results of this paper's research demonstrate Eclat and FP-Growth both handle increases in maximum transaction size and frequent itemset density considerably better than the Apriori algorithm.
This paper explores the effects that two dataset characteristics can have on the performance of these three frequent itemset algorithms. To perform this empirical analysis, a dataset generator is created to measure the effects of frequent item density and the maximum transaction size on performance. The generated datasets contain the same number of rows. This provides some insight into dataset characteristics that are conducive to each algorithm. The results of this paper's research demonstrate Eclat and FP-Growth both handle increases in maximum transaction size and frequent itemset density considerably better than the Apriori algorithm.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2jsVixp
via IFTTT
Efficient Rank Aggregation via Lehmer Codes. (arXiv:1701.09083v1 [cs.LG])
We propose a novel rank aggregation method based on converting permutations into their corresponding Lehmer codes or other subdiagonal images. Lehmer codes, also known as inversion vectors, are vector representations of permutations in which each coordinate can take values not restricted by the values of other coordinates. This transformation allows for decoupling of the coordinates and for performing aggregation via simple scalar median or mode computations. We present simulation results illustrating the performance of this completely parallelizable approach and analytically prove that both the mode and median aggregation procedure recover the correct centroid aggregate with small sample complexity when the permutations are drawn according to the well-known Mallows models. The proposed Lehmer code approach may also be used on partial rankings, with similar performance guarantees.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kplubs
via IFTTT
Robust Multilingual Named Entity Recognition with Shallow Semi-Supervised Features. (arXiv:1701.09123v1 [cs.CL])
We present a multilingual Named Entity Recognition approach based on a robust and general set of features across languages and datasets. Our system combines shallow local information with clustering semi-supervised features induced on large amounts of unlabeled text. Understanding via empirical experimentation how to effectively combine various types of clustering features allows us to seamlessly export our system to other datasets and languages. The result is a simple but highly competitive system which obtains state of the art results across five languages and twelve datasets. The results are reported on standard shared task evaluation data such as CoNLL for English, Spanish and Dutch. Furthermore, and despite the lack of linguistically motivated features, we also report best results for languages such as Basque and German. In addition, we demonstrate that our method also obtains very competitive results even when the amount of supervised data is cut by half, alleviating the dependency on manually annotated data. Finally, the results show that our emphasis on clustering features is crucial to develop robust out-of-domain models. The system and models are freely available to facilitate its use and guarantee the reproducibility of results.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kpuRb1
via IFTTT
Efficient Learning in Large-Scale Combinatorial Semi-Bandits. (arXiv:1406.7443v4 [cs.LG] UPDATED)
A stochastic combinatorial semi-bandit is an online learning problem where at each step a learning agent chooses a subset of ground items subject to combinatorial constraints, and then observes stochastic weights of these items and receives their sum as a payoff. In this paper, we consider efficient learning in large-scale combinatorial semi-bandits with linear generalization, and as a solution, propose two learning algorithms called Combinatorial Linear Thompson Sampling (CombLinTS) and Combinatorial Linear UCB (CombLinUCB). Both algorithms are computationally efficient as long as the offline version of the combinatorial problem can be solved efficiently. We establish that CombLinTS and CombLinUCB are also provably statistically efficient under reasonable assumptions, by developing regret bounds that are independent of the problem scale (number of items) and sublinear in time. We also evaluate CombLinTS on a variety of problems with thousands of items. Our experiment results demonstrate that CombLinTS is scalable, robust to the choice of algorithm parameters, and significantly outperforms the best of our baselines.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1x7UzyF
via IFTTT
Combinatorial Aspects of the Distribution of Rough Objects. (arXiv:1605.01778v2 [cs.AI] UPDATED)
The inverse problem of general rough sets, considered by the present author in some of her earlier papers, in one of its manifestations is essentially the question of when an agent's view about crisp and non crisp objects over a set of objects has a rough evolution. In this research the nature of the problem is examined from number-theoretic and combinatorial perspectives under very few assumptions about the nature of data and some necessary conditions are proved.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/1XgbehY
via IFTTT
Evaluating Induced CCG Parsers on Grounded Semantic Parsing. (arXiv:1609.09405v2 [cs.CL] UPDATED)
We compare the effectiveness of four different syntactic CCG parsers for a semantic slot-filling task to explore how much syntactic supervision is required for downstream semantic analysis. This extrinsic, task-based evaluation provides a unique window to explore the strengths and weaknesses of semantics captured by unsupervised grammar induction systems. We release a new Freebase semantic parsing dataset called SPADES (Semantic PArsing of DEclarative Sentences) containing 93K cloze-style questions paired with answers. We evaluate all our models on this dataset. Our code and data are available at http://ift.tt/2kOi2oC.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2dDK0QD
via IFTTT
Design Mining Microbial Fuel Cell Cascades. (arXiv:1610.05716v2 [cs.NE] UPDATED)
Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) perform wastewater treatment and electricity production through the conversion of organic matter using microorganisms. For practical applications, it has been suggested that greater efficiency can be achieved by arranging multiple MFC units into physical stacks in a cascade with feedstock flowing sequentially between units. In this paper, we investigate the use of computational intelligence to physically explore and optimise (potentially) heterogeneous MFC designs in a cascade, i.e. without simulation. Conductive structures are 3-D printed and inserted into the anodic chamber of each MFC unit, augmenting a carbon fibre veil anode and affecting the hydrodynamics, including the feedstock volume and hydraulic retention time, as well as providing unique habitats for microbial colonisation. We show that it is possible to use design mining to identify new conductive inserts that increase both the cascade power output and power density.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2dm3pZm
via IFTTT
An Integrated Optimization + Learning Approach to Optimal Dynamic Pricing for the Retailer with Multi-type Customers in Smart Grids. (arXiv:1612.05971v2 [cs.SY] UPDATED)
In this paper, we consider a realistic and meaningful scenario in the context of smart grids where an electricity retailer serves three different types of customers, i.e., customers with an optimal home energy management system embedded in their smart meters (C-HEMS), customers with only smart meters (C-SM), and customers without smart meters (C-NONE). The main objective of this paper is to support the retailer to make optimal day-ahead dynamic pricing decisions in such a mixed customer pool. To this end, we propose a two-level decision-making framework where the retailer acting as upper-level agent firstly announces its electricity prices of next 24 hours and customers acting as lower-level agents subsequently schedule their energy usages accordingly. For the lower level problem, we model the price responsiveness of different customers according to their unique characteristics. For the upper level problem, we optimize the dynamic prices for the retailer to maximize its profit subject to realistic market constraints. The above two-level model is tackled by genetic algorithms (GAs) based distributed optimization methods while its feasibility and effectiveness are confirmed via simulation results.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2hOrJot
via IFTTT
Plotting an Anonymous Function
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jTb6Ir
via IFTTT
Anonymous Group Reveals Phone Numbers For White House Staffers
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jSn4iO
via IFTTT
Rumor Central: Orioles could still be looking to add defensive OF like Angel Pagan, Michael Bourn - BaltimoreBaseball.com (ESPN)
via IFTTT
Anonymous call to action against Trump regime
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jRR7aH
via IFTTT
Program Supervisor (Parents Anonymous) -436
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jRgSdD
via IFTTT
Piedmont Opera receives $100000 anonymous donation
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jQyJkH
via IFTTT
ISS Daily Summary Report – 1/30/2017
from ISS On-Orbit Status Report http://ift.tt/2kNMtyy
via IFTTT
Lítačka can be anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jQkwEj
via IFTTT
Trappin Anonymous
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jqoTYr
via IFTTT
Galena ARC receives anonymous $270 donation
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jPxItm
via IFTTT
Facebook Unveils 'Delegated Recovery' to Replace Traditional Password Recovery Methods
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2kKFH9m
via IFTTT
Re: [FD] [0-day] RCE and admin credential disclosure in NETGEAR WNR2000
Source: Gmail -> IFTTT-> Blogger
Violin Sonata in B-flat major, Schrank II/34/47 (Anonymous)
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jP7B5J
via IFTTT
Check If Your Netgear Router is also Vulnerable to this Password Bypass Flaw
from The Hacker News http://ift.tt/2jOSCso
via IFTTT
Dobrado Landulpho Lintz
from Google Alert - anonymous http://ift.tt/2jpcbsL
via IFTTT
The Cats Eye Nebula from Hubble
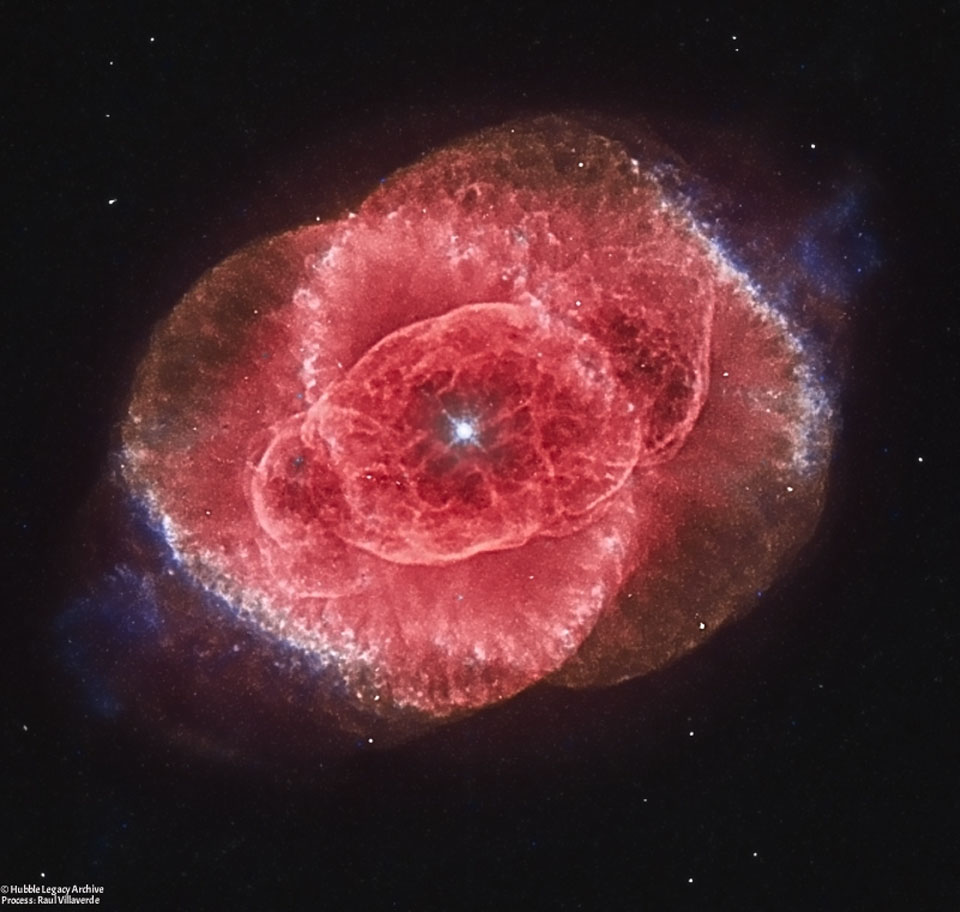

Monday, January 30, 2017
I have a new follower on Twitter
IronPlanet Auctions
IronPlanet is the leading online marketplace for used heavy equipment and an innovative participant in the multi-billion dollar heavy equipment auction market.
North America,Europe,Australia
http://t.co/uphDv8mXPU
Following: 4168 - Followers: 26775
January 30, 2017 at 11:01PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/IronPlanet
I have a new follower on Twitter
Adrian Pineda López
Following: 86 - Followers: 0
January 30, 2017 at 09:36PM via Twitter http://twitter.com/AdrianPinedaLp1
Comparative Study Of Data Mining Query Languages. (arXiv:1701.08190v1 [cs.AI])
Since formulation of Inductive Database (IDB) problem, several Data Mining (DM) languages have been proposed, confirming that KDD process could be supported via inductive queries (IQ) answering. This paper reviews the existing DM languages. We are presenting important primitives of the DM language and classifying our languages according to primitives' satisfaction. In addition, we presented languages' syntaxes and tried to apply each one to a database sample to test a set of KDD operations. This study allows us to highlight languages capabilities and limits, which is very useful for future work and perspectives.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2jNcw78
via IFTTT
Incremental Maintenance Of Association Rules Under Support Threshold Change. (arXiv:1701.08191v1 [cs.AI])
Maintenance of association rules is an interesting problem. Several incremental maintenance algorithms were proposed since the work of (Cheung et al, 1996). The majority of these algorithms maintain rule bases assuming that support threshold doesn't change. In this paper, we present incremental maintenance algorithm under support threshold change. This solution allows user to maintain its rule base under any support threshold.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2jPkSsv
via IFTTT
Image-Grounded Conversations: Multimodal Context for Natural Question and Response Generation. (arXiv:1701.08251v1 [cs.CL])
The popularity of image sharing on social media reflects the important role visual context plays in everyday conversation. In this paper, we present a novel task, Image-Grounded Conversations (IGC), in which natural-sounding conversations are generated about shared photographic images. We investigate this task using training data derived from image-grounded conversations on social media and introduce a new dataset of crowd-sourced conversations for benchmarking progress. Experiments using deep neural network models trained on social media data show that the combination of visual and textual context can enhance the quality of generated conversational turns. In human evaluation, a gap between human performance and that of both neural and retrieval architectures suggests that IGC presents an interesting challenge for vision and language research.
from cs.AI updates on arXiv.org http://ift.tt/2kaGK2v
via IFTTT